Powerpoint - Dr Peter Jepson
Civil Court System
by Lisa Incledon
Terminology…
Civil cases involve individuals or organisations, rather than the state and an individual.
Parties are called:
Claimant
Defendant
If there is an appeal:
Appellant
Respondent
Civil Procedure Rules
1998
Rule 1: the ‘ overriding objective ’ is –
enabling the court to deal with cases justly.
What does this involve?
Overriding Objective of CPR
Ensuring parties are on an equal footing
Dealing with cases proportionately to:
Amount of money involved
Importance of the case
Complexity
Ensuring cases are dealt with fairly and efficiently
The Courts
The two courts which hear civil cases at first instance are:
County Court
High Court
What does first instance mean?
Starting a case…
When can a claimant start a case in the High Court (rather than County Court)?
How do you start a case?
What can a defendant do once a claim has been brought against them?
Allocation
The Civil Procedure Rules include the three-track system:
Small Claims track
Fast track
Multi-track
County Court
Single entity operating in 216 separate locations.
County Court can try small claims, fast track and multi-track cases.
Small Claims Track
What is the maximum value of a claim on the small claims track?
Quicker, cheaper and simpler than the other tracks.
Parties are encouraged to represent themselves to keep costs to a minimum.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the small claims track?
Fast Track
Which claims are dealt with in the fast track?
Features of the fast track include:
Timetable/case management by judge
Claims to be disposed of in one day
Hearing should be within 30 weeks of judge’s directions
Usually limited to one expert
Has the introduction of the fast track improved the civil court procedure?
Multi-track
Which claims are dealt with on the multi-track?
Heard by Circuit Judge who will also be expected to manage the case and set timetables.
Can ask parties to try alternative dispute resolution (ADR) and stay proceedings whilst they do so.
Which court(s) could these cases be heard in?
High Court
The High Court has three
Divisions which:
Act as a court of first instance
Have a Divisional Court which hears appeals
What are the three Divisions?
What areas do they focus on?
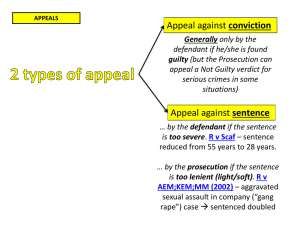
Appeals
What are the appeal routes from the:
County Court?
High Court?
Complete the flow chart with each of the main appeal routes.
Appeals
Some cases in the County Court have specific appeal routes:
Family cases in the County Court
→ Divisional Court of the Family
Division
Bankruptcy and land law cases
→ Divisional Court of the Chancery
Division



![Wrapping Machine [VP] OPP film wrapping for flat](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005550216_1-6280112292e4337f148ac93f5e8746a4-300x300.png)