Sample Talk
advertisement

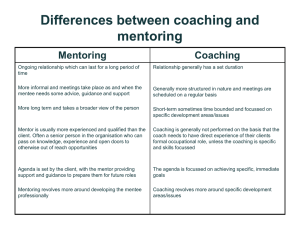
Aligning Individual and Team Performance The EDGE: Foundations for Successful Leadership Our Framework Continuous Improvement Process People Aligning Individual and Team Performance Purpose Adapted from Toyota Culture. The Heart and Soul of the Toyota Way. J. Liker, M Hosues, Mc Graw Hill 2008 Module Overview Purpose: • Enhance the ability to set and communicate performance expectations and job goals that are aligned with the organization’s goals • Develop teaching and coaching skills that optimize your staff’s performance • Create a high performance team • Develop awareness of available resources PM pg. 1 Objectives: • Explain the UMHS performance management process • Receive and provide timely performance feedback with greater comfort • Set your team up for success PM pg. 1 Agenda I. Welcome and Overview VI. Video: “The Practical Coach” II. UMHS Performance Development System VII. Giving and Receiving Feedback VIII. Performance Review III. Job Expectations IX. IV. Writing SMART Goals X. V. Performance Coaching High Performance Teams Wrap-up PM pg. 1 Busting Up Performance Management – What is it? Performance Management is an inclusive process to influence (lead) the attainment of performance goals. It is a process to manage the overall performance goals of the individual, department, and the institution. •It begins at the time of hire or transfer •It is a dynamic and on-going process •It bears a shared responsibility PM pg. 2 UMHS Performance Development System Hire/Transfer Performance Management Identify Performance Expectation Developing Coaching Evaluation See manual for details PM pg. 3 Performance Management Cycle V. I. Periodically Rate Progress Set Performance Expectations IV. II. Reward & Recognize Performance Observe & Measure Performance III. Coach & Develop PM pg. 4 The Role of the Supervisor in Performance Management A supervisor : • Sets performance expectations • Provides coaching and development • Gives feedback • Facilitates development opportunities • Observes and evaluates performance PM pg. 5 Assessing Your Work Climate Employee attitudes are paramount in managing and improving the workplace. Activity: Complete “Assessing Your Work Climate” - first, for yourself - second, for your staff PM pg. 6 Performance management begins with setting expectations Set your employee up for success Obtain Your Necessary Resources a) b) c) d) e) f) Up-to-date job description Current schedules and processes Employee Performance File Accreditation program requirements Procedures manuals, lists, posters Performance Management Evaluation Form PM pg. 7 Set SMART goals • Specific • Measurable • Attainable • Relevant To Your Mission • Time-Limited PM pg. 8 SMART Goal ACTIVITY I: Dissect the following goal: “6 month goal: Develop a powerpoint presentation after attending the seminar Powerpoint Made Easy.” PM pg. 8 SMART Goal ACTIVITY II: Work in table groups Write a SMART goal for one of the following: - “Answer phone.” - “Demonstrate good customer service skills” - “Be a team player.” - “Show more self-initiative” PM pg. 9-10 Activity: Writing Performance Goals Purpose: To practice writing your own Performance Goals Agenda: • Write a performance goal using the job description provided in the previous module • Identify three key areas of responsibility (KAR) • For one of the KARs, identify one goal • Share with a partner and evaluate based on SMART criteria Limit: 20 min PM pg. 11 Performance Planning Meeting Preparing for the Session 1. Review performance goals set by you or your staff member 2. Check alignment with your unit’s goals 3. Reflect on the individual’s development needs PM pg. 12 Planning Meeting Agenda Together, • Review the goals • Clarify outcome expectations • Discuss development plan • Agree to meet for one-three review sessions throughout the year PM pg. 12 After you’ve set goals… How do you know how they’re doing? Throughout the year… 1. Go to the Gemba or Go See 2. Talk to others 3. 4. Hold mid-year review sessions • Make changes, as needed Maintain an ongoing discussion PM pg. 12 Coaching and Feedback Activity: “Best Practices” Performance Coaching Purpose: To identify elements of past positive coaching experiences Agenda: 1. Select a time when you had an excellent supervisor and staff relationship that helped you be successful. 2. Describe the key characteristics of that working relationship 3. Share key characteristics with your table group. Limit: 15 min PM pg. 13 Video: The Practical Coach Purpose: To identify the key elements of effective coaching feedback. Agenda: View video -Discuss key points Limit: Video: 20 min Discussion: 10 min PM pg. 14-15 Coaching and Feedback: Recognize Good Performance When you see it, say it. PM pg. 15 Prepare Before engaging in any feedback, ask yourself: • What are your observations? • Why are the observations important? • Do I have all the information I need? Is there another side to the story? PM - pg. 16 Five-Part Feedback Model 1. Describe current behaviors 2. Identify situations 3. Describe impact and consequences 4. Seek further input - optional 5A. Listen and recognize/praise PM - pg. 16 Practice • Divide into pairs • Write a feedback for: – Employee handled a difficult patient – Employee stayed late – Employee re-scheduled a patient who was late – …your own PM pg. 17-18 Ways to Reward and Recognize Your Employees • Put a letter in their file • Write a Thank You note • Give praise in a staff meeting • Give “Making a Difference” awards • Celebrate team success • Certificates • Educational Opportunities • $5 gift cards PM pg. 19 Corrective Feedback: Don’t Let Poor Work go Unnoticed Make it Private And Make it Positive Activity: Giving Corrective Feedback Purpose: To identify the critical components of corrective feedback Agenda: - Select one volunteer. The volunteer will throw wads of paper into a bucket. The bucket will be behind them. - Provide feedback until the volunteer has successfully thrown one paper wad into the bucket. - Debrief Limit: 5 minutes PM - pg. 20 Common Mistakes in Feedback Senders: Receivers: • Vagueness • Expecting the worst • Shutting down • Counter attacking • Anticipation • Passiveness PM - pg. 21 Tools for Effective Corrective Feedback “I” Statements • Neutral Phrasing • Questioning • Five Part Feedback Model • Feedforward • The “Right” Environment • PM - pg. 21 A Good Beginning: “I” Statements Substituting “I” for “You” at the beginning of a sentence can alter the sound and perceived intent of your message. Instead of being accusatory, you own your own feelings, needs and wants. Nobody can argue with that. Read the Examples… -“You need to be on time.” “I need you to be on time.” -“You really made a bad decision.” “I don’t agree with that decision.” Activity: Create an “I” statement for “You’re making way too big a deal of this.” PM - pg. 22 Neutral Phrasing Useful technique for lowering the emotional context of verbal communication. Use it to: • Clarify a statement • Disagree • Enhance assertiveness • Lower emotion and maintain neutrality PM - pg. 23 How To Reframe Neutrally • Use open-ended questions. – But not leading questions • Avoid absolutes. • Help people save face. • Focus on the underlying feelings and issues. • Learn to say “I’m sorry.” • Summarize the facts, not interpretations PM - pg. 23 Activity: Neutral Phrasing Purpose: To practice framing issues neutrally Agenda: 1. As a class, neutralize the phrases a-d 2. Individually, read the scenario and decide how to best respond. 3. Find a partner and discuss your response. How could your response be improved? Limit: 5 minutes PM - pg. 24-25 Corrective Feedback Planner 1. Describe current behaviors 2. Identify situations 3. Describe impact and consequences 4. Seek further input 5B. Identify alternative behaviors PM - pg. 26 Seek Further Input Reminders • Actively listen and check for understanding • Check your defensiveness • Do not rebut or explain • The input is simply another piece of information • Thank the person PM pg. 26 Sample Coaching Challenges I. Performance Examples: • Poor Service Interactions • Anti-team actions • Poor work techniques • Unsafe work behavior PM pg. 27 Sample Coaching Challenges II. Work Habit Examples: • Leaving work undone • Wasting time • Poor personal hygiene • Not following directions • Showing up late to work PM pg. 27 Feedback Practice In pairs, • Write a corrective feedback • Keep it positive • Use an example from your own experience PM pg. 28 Coaching on a Dead–end Road The Practical Coach: Two Minute Challenge 1. State what you’ve observed 2. Wait for a response 3. Remind them of the goal 4. Ask for a specific solution 5. Agree together 6. Follow-up Don’t skip a step! PM pg. 29 Activity: Two-Minute Challenge Practice Purpose: Practice a corrective feedback Agenda: Limit: - In groups of three, write a coaching feedback for one of the scenarios in the manual - One person will be the manager, one person the employee and one the coach - Employee will use a side-track to challenge the manager; be prepared as a Coach to help out (7 min/round) - Rotate roles. - Share one learning with the larger group. 30 min PM pg. 29-30 The Annual Performance Review and Planning Creating a Successful Performance Review and Planning Session The year-end review should NOT be a surprise! Creating a Successful Performance Review and Planning Session 1. Review your performance files 2. Review the UMHS evaluation form 3. Review the employee’s goals 4. Use the UMHS rating scale N = Not met A = Approaching S = Solid Performance E = Exemplary Caution: Rater Error Performance File PM pg. 31 Preparing for the Evaluation Session 1. Ask the employee to prepare by creating a selfappraisal • • • • 2. Review performance goals set at the beginning of the year Review any meeting notes from throughout the year Self-rate performance toward goals. Identify performance goals for the upcoming year Prepare yourself • • PM pg. 32 • Review your employee’s goals, your notes and records from throughout the year Evaluate the performance against the performance expectations Compare with the employee’s self-appraisal Steps to an Effective Performance Evaluation • • • • • • Write out your opening lines Plan the body of your summary evaluation Appreciate Solicit feedback Summarize Outline next steps PM pg. 33 Tips For a Productive Evaluation Meeting 1. Approach with an open mind. 2. Arrange the logistics carefully: private setting, seating location, etc. 3. Prepare for the discussion. 4. Be respectful. 5. Focus on solutions. 6. Include staff members in creating action plans. PM pg. 34 During the Performance Evaluation Session 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Put the employee at ease Ask open-ended questions Review their key areas of responsibility (KARs) and accomplishment of goals Review the employee’s self-evaluation Demonstrate your commitment to training and development Share your evaluation of the individual’s performance Compare and contrast the two evaluations Adjust the final evaluation as needed PM pg. 35 Demonstration Demo 1 • How would you improve this review session? Demo 2 • What did the supervisor do well? It’s worth the effort when… 1. Staff members understand what is expected of them 2. Staff members understand how their work links to the overall organizations mission, vision and goals 3. Performance development discussions through the year have helped build mutual trust and understanding in the supervisor-staff relationship 4. Performance review does not contain any surprises for the staff member 5. Supervisors have been able to recognize and reward good performance with the end result of continuous performance improvement PM pg. 37 Final caution: if you find you’re repeating yourself… Stop. Ask yourself: Am I assuming the source of the problem is the employee? - Is training or re-training the appropriate action? - Is the employee unaware of workplace rules? - Is poor job design a contributing factor? - Is it inability rather than unwillingness? - Is there a need for additional individualized instruction? If you answer no to each of these questions, then a disciplinary process may be required. PM pg. 38 Creating a High Performance Team With High Performance Employees Brain Teaser PM pg. 39 Brain Teasers’ Answers 1. Step On It 2. Sign Post 3. Corner Store 4. Three degrees below Zero 5. An eye for an eye 6. Split Decision 7. Broken Promise 8. Up Hill 9. Bumpy Road 10. Cross Check 11. Parachute 12. Short Stop Team Leadership • Give me one word to define leadership… Influence • People follow you because they want to, not because they think they have to Find Your Passion To lead and inspire your staff, you need passion What is your passion? PM - pg. 40 Activity: Find Your Voice Purpose: To recognize who/what has influenced you and your leadership style Task: • Name five people who influenced you and why • Share one with your table group • Debrief Time: 25 minutes PM - pg. 41 Use Your Passion to Transform Your Team Transformational Leadership • Transformational leaders don’t just generate followers… their followers then become leaders. • They generate enthusiasm for a common purpose • They lead with their actions…and also with their words PM - pg. 42 Transformational Leaders • Steve Jobs – Apple Computers • John F. Kennedy – Peace Corps • Martin Luther King, Jr. • Ari Weinzweig and Paul Saginaw of Zingerman’s Community of Businesses PM - pg. 42 Become Transformational Be purpose-driven, not process-driven Ask yourself: Am I spending my time on the right things? PM - pg. 42 What are your priorities? Urgent Not Urgent QII Strategy Work Crises Develop People Deadlines Problem solving Strengthen Systems Build Relationships Projects Prevention QIV QIII Interruptions Trivia Some voice mail Irrelevant mail Some e-mail (Information Some meetings Pollution) QI Important Not Important PM - pg. 42 Place Quadrant II Items on Your Daily To Do List • Strategy Work – Set Goals • Develop People – Identify your strengths and flaws – Help your staff members assess themselves: give feedback, • Strengthen Systems – Utilize Lean • Build Relationships – Play a role in helping the whole team feel happy to be here • Prevention – Address the “common” problems; the patterns Stages of Team Stages of Group Development Form Storm Norm Perform Adjourn Pg. 43 Forming • Stage One –Personal relations are characterized by dependence –Anxiety (search for structure) –Desire for acceptance and safety Pg. 43 Forming • Orienting to other team members –Respecting individuals –Understanding our differences –Workplace Preferences Pg. 43 Storming Stage Two • Characterized by competition and conflict • Conflicts over leadership, structure, power and authority • Team members need to adjust feelings, ideas, beliefs to suit the task organization Pg. 43 Norming Stage Three • Characterized by cohesion • There is acknowledgement of all members’ contributions and increased trust Pg. 43 Performing Stage Four • True interdependence between members and productive problemsolving with the task • Support for experimentation and a goal of productivity Pg. 44 Adjourning Stage Five This stage occurs when team members leave, a new team member comes on or a task/project is completed • Members disengage from other members • Team members feel apprehension Pg. 44 High Performance Staff Meetings Planning a Meeting Before you schedule a meeting, ask yourself: 1. Why is this group meeting? 2. What is the desired outcome of this meeting? 3. Who and how many people need to be involved? 4. Is there a time restriction? 5. Are there obstacles or baggage present that will make it difficult to achieve the desired outcome? 6. Is there another way to accomplish the desired outcome? PM pg. 45 Meeting Management Tools • “PAL” – Purpose-Agenda-Limit: a road map for each meeting • “Parking Lot” – A place to record topics that need to be set aside for a more appropriate time • Visual recording – Use of a flip chart or other visual focus point • Meeting Norms – Mutual guidelines for group behavior- “We agree that….” • Ice Breakers – Activities to warm up, break tension, energize or even diagnose readiness PM pg. 45 Participation Formats • Open discussion • Brainstorming • Presentations and reports • Individual writing • Computer-assisted meetings • Smaller groupings • Round robins • Debriefing • Multi-tasking • Straw man PM pg. 46 Facilitating Staff Discussions Purpose: To identify effective ways to utilize facilitation techniques Agenda: • Review the facilitation techniques • Think about your own experience with these tools in other meetings, good and bad experiences • How can you apply these techniques to your team effectively? Discuss with your table group • Time: 15 minutes PM - pg. 47 Team Culture Norms Culture Norms Have you ever broken an “unwritten rule” at work? • How do new employees learn your unit’s operational norms? • How do they learn the “unwritten rules?” • What level of participation in office activities do you expect? • Do you have forbidden words? Trust What is Trust? Confidence in the absence of suspicion, confirmed by the track record and our ability to self-correct. The state of readiness for unguarded interaction with someone or something. PM pg. 49 Activity: Building Trust Purpose: Identify the key elements of trust Agenda: Limit: - Choose a partner - Choose a leader and a follower - Follower will have eyes closed while leader talks him/her through a designated course - Switch roles - Discuss 15 minutes walk 5 minutes discussion Pg. 48 Three Constructs of Trust • Capacity for trusting – Your total life experiences • Perception of Competence – How you see your ability and that of others • Perception of Intentions – Mutually-serving? Or self-serving? PM - pg. 49 As a leader, you must… • personally model trust • earn buy-in from all members of the organization. PM pg. 49 Demonstrate Trust • Keep the energy flowing toward a coherent set of values. Do this by: – listening, – caring, and – offering a set of operating principles that is recognized as universal PM pg. 49 Trust is far stronger, and more reliable than fear as a means of leading, managing, and motivating people. PM pg. 49 Homework / Action Plan • Complete Action Plan for today’s Module – Aligning Individual and Team Performance Thank You!