PowerPoint
advertisement

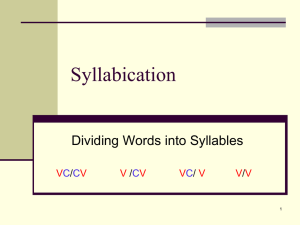
Spelling Development Elizabeth Norwood RE 5730 Stages of Spelling Spelling is developmental, but not all students go through the stages at the same rate. Emergent Letter Name Within Word Syllable Juncture Derivational Constancy Emergent Stage- 3-5 Years Old Lacks concept of word Scribbles letters and numbers Lacks letter-sound correspondence Pretends to read and write Focus of Instruction- Emergent Level read aloud often encourage finger pointing use environmental print create big books and picture dictionaries use dictations and experience charts chant and choral read familiar stories and dictations sort words by common patterns develop word bags or banks Letter Name Stage- 5-7 Year Olds Represents beginning and ending sounds Has functional concept of word Reads word by word in beginning reading materials Focus of Instruction- Letter Name Stage Early Letter Name practice identifying familiar spelling patterns and sounds use word bags or banks sort words by beginning sounds and short vowels study blends and diagraphs Late Letter Name Continue to examine consonant blends and digraphs Sort pictures and words by short vowel sounds and CVC patterns Begin simple sound sorts comparing short and long vowel sounds Collect known words for word banks (up to 200) Within Word Stage- 7-9 Years Old Spells most single-syllable short vowel words correctly Spells most beginning consonant digraphs and 2-letter consonant blends Attempts to use silent-E markers and r-controlled vowels Reads silently and more fluently Writes more fluently Focus of Instruction- Within Word Stage Sort words by long and short vowel sounds and by common long vowel patterns Compare words with r-controlled vowels Explore less common vowels and diphthongs (OI, OU, AU, OW) Review blends and digraphs and examine triple blends and complex consonant units (THR, STR, DGE, TCH, CK) Have students develop personal word lists Syllable Juncture Stage- 8-11 Years Old Spells most single syllable words correctly Makes errors at syllable juncture and in unaccented syllables Adds inflectional endings (-ed, -es, -ing) Differentiates between homophones Reads with good fluency and expression Reads faster silently than orally Focus on Instruction- Syllable Juncture Stage Examine consonant doubling and inflected endings Join spelling and vocabulary studies; link meaning and spelling Explore grammar through word study Sort and study affixes Study stress or accent in two-syllable words Derivational Constancy Stage- 11-14 Years Old Have mastered high-frequency words Make errors on low-frequency words derived from Greek and Latin Can understand Greek and Latin roots and derivational affixes Read with good fluency and expression Read faster silently than orally Focus of Instruction- Derivational Constancy Stage Focus on words that students bring to word study from reading and writing Examine common and then less common roots, prefixes and suffixes Examine vowel alterations in derivationally related pairs (native, national; combine, combination) Explore etymology, especially in the content areas Examine content-related foreign borrowings have students keep personal word lists provide minilessons to individuals and groups to review and refine spelling knowledge and strategies