MF Presentation Basic
advertisement

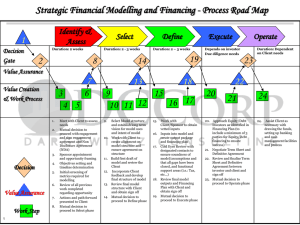
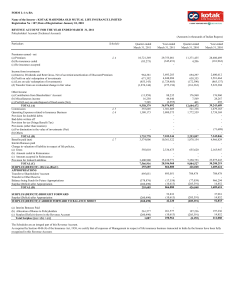
Why Invest ? To protect your purchasing power To generate sustained income post retirement. To meet key financial needs like housing, higher education and marriage of children To generate alternate income for the family in case of any unforeseen event. Where can you invest? • Equities • Bank Deposits, Debt, Bonds, Company Deposits • Gold, Real Estate • PPF, RBI Bonds, Postal Savings • Insurance Companies – Insurance Policies Product characteristics Matrix Products Return Risk Liquidity Tax Savings Convenience Bank Deposit Moderate Low High Yes High Equity Instruments High High Depends on the instrument No Moderate Debentures Moderate Moderate Low No Low Fixed Deposits by Companies Moderate Moderate Low No Moderate Bonds Moderate Moderate Moderate Yes Moderate Product characteristics Matrix Product Return Risk Liquidity Tax Savings Convenience RBI Relief Bonds Moderate Low Low Yes Moderate PPF Moderate Low Low Yes Moderate National Saving Certificate Moderate Low Low Yes Moderate Life Insurance Moderate Low Low Yes Moderate Monthly Income Scheme Moderate Low Low Yes Moderate Income v/s Real Income Real Return = Returns – Tax - Inflation Focus on Real Income is important for wealth creation What is Mutual Fund ? Mutual funds are investment companies that pool money from investors at large and offer to sell and buy back its shares on a continuous basis and use the capital thus raised to invest in securities of different companies. Mutual Fund History • 1964-UTI • 1987- Public Sector banks, Insurance Companies – SBI, Canbank, PNB LIC, GIC • 1993- Private Sector – Kothari Pioneer ( later merged with Franklin Templeton),Morgan Stanley Mutual Fund- Structure SPONSOR CUSTODIAN TRUST REGISTRAR AMC FUND OPERATIONS COMPLIANCE MANAGERS MARKETING INVESTOR DISTRIBUTOR RELATIONS Mutual Fund Process SEBI Investors Returns Mutual Fund SECURITIES Mutual fund Types •By Liquidity or Structure : Open Ended Funds Closed Ended Funds Interval Funds Mutual fund Types • By Nature of Investments: Equity Funds Debt Funds Money Market Funds Hybrid Funds By Investments Objective: Growth Funds – For medium to long term capital appreciation. Income Funds - For generating regular income and preserving capital with lesser emphasis on capital appreciation. Value Funds – for investing in undervalued equities Types of Equity Funds Diversified Funds Invests across sectors and stocks Diversifies stock or sector specific risks E.g- Kotak 30, Kotak Lifestyle Speciality Funds Funds that have an investment theme Are diversified but riskier than normal diversified funds E.g- Kotak MNC, Kotak Global India, Kotak Lifestyle Aggressive Funds Target maximum capital appreciation Are diversified but riskier than normal diversified funds May trade or invest in mid & small stocks E.g- Kotak Mid-cap, Kotak Opportunities Types of Equity funds Tax Saving Funds Index Funds Investments are eligible for tax deduction Invests exactly as per the benchmark index Lock-in period of 3 Years Risk and return are in line with the index E.g- Kotak Tax Saver Sector Funds Value Funds Invest only in one industry Invests in currently under valued stocks Offer no sector diversification hence risky Have low risk compared to growth funds E.g- Kotak Tech E.g- Kotak Contra Types of Debt Funds Money Market / Liquid Funds Gilt Funds Invest in short term debt securities. Invests in govt. securities with medium to long term maturities. Ideal for short term investments. Have a very low credit risk. Lowest in the order of risk level. Debt / Income Funds Invests in debt securities issued by various players including govt. and private companies. Invest across various maturities. May be diversified, focused or have fixed maturities. Floating Rate Funds Invest in securities with variable int. rates Ideal in a rising rate scenario. Types of Hybrid Funds Growth & Income Funds Invests in Equity and Debt markets – Balance funds & MIP’s Less risky than growth funds but more risky than Income funds E.g- Kotak Balance, Kotak Income Plus Asset Allocation Funds Invests in debt and equity based on an asset allocation policy May follow variable asset allocation and move in and out of asset classes E.g- Kotak Dynamic FOF, Kotak Flexi FOF Risk-return matrix There is no such thing as a free lunch Risk shares a direct relationship with returns Benefits of Mutual Funds DIVERSIFICATION Available even in small amounts PROFESSIONAL MANAGEMENT Best Brains in the Country Manage your Money DIFFERENT SCHEMES Providing Solutions For All Needs TRANSPARENCY Daily NAV, Monthly Portfolio CONVENIENCE Easy to buy,hold & sell WELL REGULATED Governed By SEBI Regulations Benefits of Mutual Funds Dividend from equity funds are entirely tax free Dividend from debt funds - tax free for investors Capital gain tax for equity funds : • If kept > 1 year then zero tax Capital gain tax for Debt Funds : • Benefit of lesser tax by two options : 1. 10 % without indexation 2. 20 % with indexation Benefit of set off for capital gains or loss upto 8 years Equity - Concepts Price/Earning Ratio price of the share divided by earnings per share. indicates what the investors are willing to pay for the company’s earning potential. Young or fast growing companies have high P/E ratio. Established companies in mature industries have lower P/E ratio. Dividend Yield ratio of dividend paid per share to current market price. low P/E stocks usually have high dividend yields. Equity - Concepts Cyclical stocks Earnings are related to the state of the economy Have relatively low P/E and high dividend pay outs Growth Stocks Earnings are expected to grow at a higher than expected market rate Tend to reinvest earning and have a high P/E ratios Value Stocks Stocks that are currently undervalued i.e. have a relatively low P/E Give returns in the long term when market realises their potential Debt - Concepts Par Value is the principal amount the investors will be paid upon maturity of the bond and is also known as the face value. Coupon is the annual rate of interest paid on the par value of the bond to the investor. Maturity refers to the term of the bond I.e. the date on which the issuer has to repay the principal amount to the bond. Current Yield Relates interest on a bond to its current market price by dividing annual coupon interest rate by the coupon market price. Yield to Maturity is the annual rate of return an investor would realize if he bought a bond at a particular price, received all the coupon payments, reinvested the coupons at the same YTM rate and received principal at maturity. Debt - Concepts Interest rates and debt prices share an inverse relationship Interest Rates Interest Rates Bond prices Bond prices When interest rates go up the value of existing debt papers go down as another paper with a higher rate is available in the market. So the existing paper would have to be sold at a discount and vice-versa. Investment Process or Financial Planning Process Investor Profiling Portfolio Construction Asset Allocation Portfolio Tracking & Rebalancing Execution & Servicing Product Selection Model Asset Allocation Equity Funds Fixed Income funds/ Banks FD's Age- 35-55 YRS Age- 25-35 YRS 100 Cash/ Liquid Funds/ Savings A/c Age- 55 YRS + 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Aggressive Portfolio The above asset allocation is for illustration purpose only Moderate Portfolio Conservative Portfolio Investors High Returns Aggressive Investor Savvy Investor (Kotak 30) ( Kotak Opportunities, Kotak Midcap) High Risk Low Risk Conservative Investor Irrational Investor (Kotak MIP, Kotak Debt Funds ) Low Returns TAX RECKONER FOR MUTUAL FUND Equity Scheme STCG LTGC Resident 15% Individual / HUF Partnership Firm Domestic Company NRI 15% 15% 15% Other Schemes Divident Distribution Tax TDS Dividend Income As per tax indexation or 20% slab Nil Tax Free Nil 28.33% 14.16% 30% 10% without indexation or 20% with indexation Nil Tax Free Nil 28.33% 22.66% 30% 10% without indexation or 20% with indexation Nil Tax Free Nil 28.33% 22.66% As per tax indexation or 20% LTCG - 20% after Tax Free 16.99% slab indexation 10% without STCG - 30% & Nil 28.33% 14.16% TDS STCG LTGC Equity Liquid Schemes Others 10% without Nil Nil with indexation Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil with indexation • Securities Transaction Tax : 0.25% on redemption value. • Wealth Tax : Mutual Fund Units are exempt from wealth tax. Think Investments. Think JM Securities