Canada`s Economy PPT
advertisement

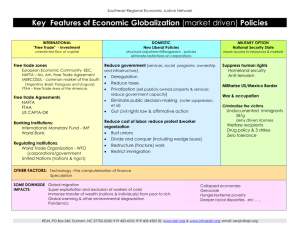
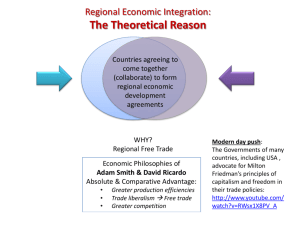
Canada’s Economy SS6E1, SS6E5, SS6E8 The student will analyze different economic systems a. Compare how traditional, command, and market economies answer the economic questions of 1 – what to produce, 2 – how to produce, and 3 – for whom to produce b. Explain how most countries have a mixed economy located on a continuum between pure market and pure command SS6E2 The student will give examples of how voluntary trade benefits buyers and sellers in Latin America and the Caribbean and Canada c. Explain the functions of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) What do you like on a Sundae? What toppings do you like on an ice cream sundae? – Plain Vanilla? – Or absolutely everything (and I mean everything)? OR… What do you like on a Sundae? Chances are, you were somewhere between plain and everything. – When discussing economies, most countries are somewhere in between too. When a country is not completely a command economy and not completely a market economy, but somewhere in between, it is called a Mixed Economy. Most countries lie somewhere in between -However, they may be closer to one side than the other Review Types of Economies 1. 2. 3. Which type of economy lets businesses do whatever they want? Which economy has the government making all the decisions? Which economy do most countries have? 3 Economic Questions… What to Produce? – Businesses decide and government approves/denies it How to produce it? – Businesses decide & government regulates procedures For whom to produce? – Businesses decide based on supply & demand (price) Which economic system does Canada have?… Canada’s Economic System Canada has a Mixed economic system – It’s actually pretty close to a Market economy; however, there is some government regulation among industries – It does have Free Enterprise (competition between businesses) Canada is economically strong! Mixed Economy Canada is a mixed economy, but it is closer to market than command Canada’s Foreign Exchange Rate The price of 1 country’s currency compared to another… – 1 US dollar = 1.02 Canadian dollars – 1 US dollar = .74 EU euros – 1 Canadian dollar = .73 EU euros What does this mean? – The US economy is a little stronger than Canada’s; however, the economy of the European Union is stronger than both! Canada’s Natural Resources What’s available? – Minerals like: iron ore, nickel, zinc, copper, gold, lead, molybdenum, potash, diamonds, and silver, – fish, timber, wildlife, coal, petroleum, natural gas, hydroelectric power Canada’s Land Use What percentage of the land is arable (capable of being farmed)? – 5% (only in Southern Canada; Northern Canada’s terrain is permafrost!) – This is actually a large amount, considering Canada is the world’s 2nd largest country What are the major agricultural products? – Wheat, barley, oilseed, tobacco, fruits, vegetables, dairy products, forest products, fish Canada’s Industries What’s being produced in the factories? – Transportation equipment, chemicals, processed and unprocessed minerals, food products, wood and paper products, fish products, petroleum, natural gas Which country is Canada’s biggest trading partner? Exports: US 77.7%, UK 2.7%, Japan 2.3% Imports: US 52.4%, China 9.8%, Mexico 4.1% Canada’s Literacy Rate What percentage of people over the age of 15 can read and write? – 99% How long are students required to stay in school? – 17 years Canada’s Unemployment Rate What percentage of people do not have jobs? – 8% What percentage of people live in poverty? – 9.4% Canada’s GDP $1.336 trillion (2009) – 15th in the world GDP Per Capita--What is the value of goods and services produced per person? – $38,100 (2009) 4 Factors That Effect Canada’s GDP Human Capital: Canada is investing in education & training (check out literacy rate!) Capital Goods: Canada is investing in new technology & building new factories Abundant Natural Resources Entrepreneurship North American Free Trade Agreement Signed by the US, Canada, & Mexico in the mid1990s Eliminated trade barriers between the 3 countries Free Trade between the 3 countries How has it affected Canada’s economy? – It eliminated trade barriers with US & Mexico, and allows them to trade more freely at a better cost Canada’s Economic Problems Unemployment & poverty Over-depletion of natural resources Acid rain from factories near Great Lakes region is destroying timber resources Improving public services (which forces the country to raise taxes) NAFTA Activity Take out a piece of notebook paper. Complete the following – – What three countries are affected by NAFTA? – Use the letters NAFTA to start five phrases that describe five key functions of NAFTA – N _______________________________ – A _______________________________ – F _______________________________ – T _______________________________ – A _______________________________ – List one advantage and one disadvantage of NAFTA. Credits Original presentation by A. Bennett. Retrieved from www.Slideshare.net December 1, 2011 Modifications by B. Morgan CIA World Factbook Georgia Experience Sixth Grade Blacklines, Carole Marsh/Gallopade International, Peachtree City, GA