Atrial Fibrillation
advertisement

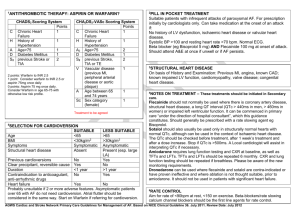
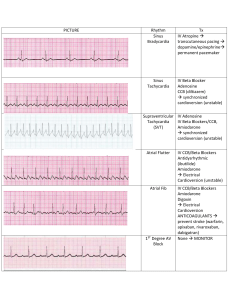
Atrial Fibrillation Statistics 1.5% of people over 65 have AF 5x increased risk of stroke 25% all strokes in elderly are caused by AF So……Time for some NICE guidelines! Diagnosis ECG on all pts where AF suspected because of irregular pulse, regardless of whether or not they have symptoms. BMJ study in 2007 – ECG not a good screening test for AF, would miss 20% cases. A good Hx and pulse check is more effective. Paroxysmal AF not detected on routine ECG: 24h ambulatory if ?asymptomatic episodes or <24h apart Event recorder if >24h apart Management Acutely unwell – Admit Further Ix for causative factors, including ?echo Rate V Rhythm control Thromboprophylaxis Referral Driving Who needs an Echo? Young pts If considering rhythm control (electricity or drugs) Possible structural heart disease (murmur, failure) – choice of antiarrhythmic agent. As part of risk assessment for stroke in pts where need evidence of LV dysfunction or valvular heart disease. Rate V Rhythm control first? Rate Over 65 Coronary artery disease Unsuitable cardioversion Unsuitable for antiarrhythmics Rhythm Under 65 Lone AF CCF Secondary to treated trigger Paroxysmal AF Rhythm control – electricity and drugs Acute AF < 48h duration – speak to Medics about Electrical or Pharmacological (amiodarone, flecainide) cardioversion. Heparinize at presentation. No anticoag necessary if maintain SR after. AF >48h – Warfarin 3 weeks before (INR 2.5) or TOE. If high R of AF recurrence then pre-treat with 4 weeks+ of amiodarone or sotalol Warfarin for 4 weeks after procedure, or long term if High R of stroke or Recurrence, eg: AF >12m, enlarged LA, prev recurrence. Assess for need of long term antiarrhythmics…. Post Cardioversion Consider antiarrythmic in anyone converted to SR who did not have a corrected precipitant eg: chest infection. (Beta blocker first line). Follow up at 1m and 6m to check still in SR. If SR at 6m then discharge back to GP. If relapse, then re-evaluate need for rate V rhythm control. Rate Control Beta Blocker or Rate Limiting Calcium Antagonist (diltiazem, verapamil) Need better control normal activities (<110) Need better control during exercise (<220-age) RLCA with Digoxin BBlocker OR RLCA with Digoxin Further rate control needed Refer or Other drugs eg: amiodarone Paroxysmal AF Thromboprophylaxis as appropriate ?Suitable for “Pill in Pocket” : One off dose of oral antiarrythmic to abort attack eg:flecainide Criteria: 1. No LV dysfunction/ valvular or IHD 2. Infreq symptomatic episodes of AF 3. SBP>100mmHg, Resting HR >70bpm 4. Understand how and when to take medication If unsuitable start standard BBlocker. Try sotalol, amiodarone or flecainide if Rx fails, then refer. Thromboprophylaxis Paroxysmal, Permanent or Persistent AF Assess Stroke/ Thromboembolism Risk High Prev isch CVA/ TIA/ TE event >75 with HT, DM, Vasc dis Echo evidence of LV dysf, failure, or valve disease Warfarin (INR 2.5) (Aspirin if contraindic) Moderate >65 with no High RFs <75 with HT, DM, Vasc disease Aspirin or Warfarin Low <65 with no mod or high RFs Aspirin 75-300mg/d Referral for Specialist Intervention Eg: Pacemaker, AV junction catheter ablation, atrial defibrillators Failed pharmacological Rx Lone AF ECG evidence of underlying pharmacological disorder eg: WPW AF and Driving Gp 1 Must cease if incapacitated by AF. Permitted if cause ID’d and controlled for 4 weeks. No need to notify DVLA unless distracting/disabling Sx Gp 2 Disqualifies if has caused or is likely to cause incapacity. May be permitted when: Controlled for 3/12 LV ejection fraction ≥0.4 No other disqualifying condition. Any Questions