Conceptual Modeling with ER Diagrams
advertisement

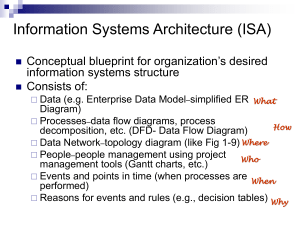
Conceptual Modeling with ER Diagrams Peter Chen introduced ER Diagrams E-R Modeling E-R Modeling is a design methodology for modeling the – Entities – Relationships using a diagram with specified shapes for entities, relationships, roles of entities in these relationships, and cardinality. E-R Diagram Conventions Symbol Meaning Entity Type Weak Entity Type Relationship Identifying Relationship Attribute ER-Diagram Conventions - CONTINUED Symbol Meaning Key Attribute Multivalued Attribute Composite Attribute Entities, Relationships and Attributes • A entity is a object or event which needs to be tracked. Attributes characterize entity sets and relationships. Relationships relate two entity sets Employee Name SSNum Employee Name Project Assigned Date Payroll Application A contractor does custom work (projects). He keeps track of employee time for each project. Besides materials, the customer is charged by invoice for employee time on his job. To keep track of employee time, the employee submits a time sheet with entries of project number, hours, description. These are entered into the system along with the employee ID. The hourly rate for the employee is used for each entry to generate a labor charge. The labor charges are totaled for each project and used as a basis for the customer invoice. Understanding the Requirements Conference Management End Users Analysts • Management – know high level business rules • End users – have used paper system or previous software system and have expectations • Analysts – have understanding of what can / cannot be done and must requirements into system ER Diagrams for Payroll Step 1. Identify the Entity Sets with Attributes • Customers : Name, Address,Phone,CustID • Projects : Name,Description,ProjID,Total,CustID • Employees : Name,SSNo,PayRate,EmpID • LaborCharges : EmpID,ProjID,Description,Hours,Amount ER Diagrams for Payroll Step 1. Identify Relationships between Entity Sets with any Attributes • Customers Has Project … Project is Weak Entity Set • Employee Works_On Project • Employee Has_Labor_Charge For Project … Labor_Charge is Weak Entity Set E-R Modeling – Entity Sets, Attributes, Relationships Racquet Club Example • A Racquet Club has members with one year or two year contracts. • Members pay contract amount up front, quarterly, or monthly. • Members may reserve a court for the next day. – E-R Modeling Entity Sets, Attributes, Relationships Racquet Club Example Continued • Entity Sets – Members : Name, Start, Contract_Amount, Contract_Period, Initial_Balance, Member_ID – Payments : PayerID, Amount, Paid_Date, Payment_ID – Reservations : Member_ID, CourtNumber, Hour • Relations : – Member - Makes – Payment – Member - Makes - Reservation Data Modeling – Racquet Club Example Keys, Cardinality Constraints and Participation Constraints • A key of a relation is a minimal set of attributes and roles which uniquely determine each entity. • A cardinality constraint m..n constrains the number of times a single entity can participate in a role of a relationship : m <= times <= n. • A participation constraint ensures that an entity will particpate at least this many times. ER-Diagram Cardinality Conventions Symbol Meaning Calculated Attribute Cardinality Constraints and Participation Constraints 0 .. * 0 .. 1 1 .. * 1 .. 1 Cardinality and Participation in the E-R model. 1 .. 2 means that at least 1 d must participate in the A relation with C and that not more that 2 d’s can participate. If A is represented by a table, then there is at least one row and not more than 2 rows with a single c value. Many-to-one, one-to-one, and many-to-many correspondences Cardinality & Participation Constraints Library Circulation Motel/Hotel Video Store Employment Company Cardinality & Participation Constraints Library Circulation Book is_checked_out to Patron Motel/Hotel Customer rents a room Video Store Customer rents a video Employment Company Applicant is hired for a job Example of an E-R diagram with an ISA hierarchy. Using IsA for data partitioning. New York Customer Pennsylvania Customer Participation Constraints A participation constraint is a lower bound on the number of times an entity can particpate in a relation. Examples: An employee belongs to ONE department. This is a participation and a cardinality constraint 1 .. 1. Employee 0 .. * 0 .. 1 1 .. * 1 .. 1 Department Participation constraints. Relationship Types – Two Entity Set Relations An employee is assigned to at least one project (participation) Employee Assigned To Project Num-Hours A customer will pay for at least one project Customer Project Will Pay For Fixed-Cost Relationship Types – One & Three Entity Set Relations One Set : ReportsTo( SupID, SubID ) subordinate Reports_To Employee supervisor Three Sets : Sale( ProdID, CustID,SuppID;Date) Customer Date Sold Supplier Product Price ER Diagrams for Payroll Phone Name Customer CustID Address Has Name Description Total CustID Projects ProjID ER Diagrams for Payroll PayRate Name Employee EmpID SSNo Has Year EmpID TimeSheet Month TSID Has Has TSID TSID ... Labor Charges PayCheck ... NetPay Amount The IS-A Relationship Employee Name SSNo Is-A Salaried Employee Salary disjoint Hourly Employee PayRate Construct an ER Diagram • Lawn Furniture Manufacturer • Stores Information for Catalog of products and parts • Stores Information for Manufacturing, including quantity on hand • Identify product entities (picnic table and lawn chair) with attributes • Identify relationships IsA and PartOf The Part-Of Relationship OutDoorProducts IsA Lawn_Chair Picnic_Table Price ProdNo Price Part_Of Top Seats Base Price ProdNo Quantity ProdNo From E-R Diagrams to Relational Database Schema • Converting entities into relations (tables) – Each entity becomes a relation – Each attribute of the entity becomes an attribute of that relation (column) – If attributes K1 ... Kn form a key of the entity, then K1 ... Kn form a candidate key of the relation. From ER Diagrams to Relational Database Schema • Translating Entities Employee Name SSNo Type Termination HireDate Create Table Employee ( Name char(20), Type char(1), HireDate date, Termination date, SSNo char(9), Primary Key (SSNo) ) From E-R Diagrams to Relational Database Schema • Representing relationships in the database schema – R is a relationship between entity set A and weak entity set B • A becomes a relation with primary key K and B+K becomes a relation with K being a foreign key – e.g. employees and dependents – R is a relationship between entity sets A,B and C • A,B and C become relations with KA , KB , and Kc as keys. R becomes a relation with foreign keys KA , KB , and Kc From ER Diagrams to Relational Database Schema • Translating Relationships Customer SaleDate Sold Supplier SaleID Product Price Create Table Sold ( SaleDate Date, Price Currency, SaleID autonumber, Customer Integer, Supplier Integer, Product Integer, Primary Key (SaleID), Foreign Key ( Customer ) References Customers( CustID), Foreign Key ( Supplier ) References Suppliers( SuppID ), Foreign Key ( Product ) References Products ProdID ) ) Translate into Schema Employee Name SSNo Is-A Salaried Employee Salary disjoint Hourly Employee PayRate Translate Into Schema OutDoorProducts IsA Lawn_Chair Picnic_Table Price ProdNo Price Part_Of Top Seats Base Price ProdNo Quantity ProdNo