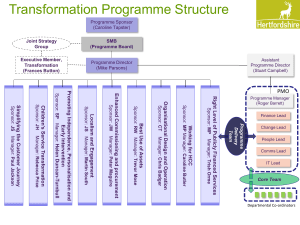
FH Legal CTA Presentation
advertisement
Clinical Trial Agreements 1 FLORIDA HOSPITAL LEGAL DEPARTMENT Outline: The best way to work with FH Legal 2 What is a Clinical Trial Agreement (CTA)? Why is it important to have a CTA? Sections contained in a typical CTA Challenges in negotiating a CTA Other types of Agreements Confidential Disclosure Agreement (CDA), Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) Material Transfer Agreement (MTA) Data Use Agreement (DUA) Who negotiates contracts for my department? When do I contact FH Legal? How do I work most effectively with FH Legal? What is a Clinical Trial Agreement? 3 A legally binding agreement that manages the relationship between the Sponsor [typically Industry] which may be providing: Study Drug or Device Financial Support Proprietary Information And the Institution [Florida Hospital] which may be providing: Data and/or Results Publication, Input into Publication Input into further Intellectual Property Other Types of Agreements 4 Confidential Disclosure Agreements/ Non-Disclosure Agreements (CDA/NDA) Agreements to ensure confidentiality of proprietary data that the Sponsor gives to Investigator in order to make a determination as to whether or not s/he will participate in the trial/research. FH requires that FH be a party to all CDAs that will in any way include FH. Depending on the circumstances, the CDA will either be between a sponsor and FH, or sponsor, FH and principal investigator. Why is it important to have a CTA? 5 Allocation of Risk Responsibility Money Obligations Protection of Rights (research, legal, intellectual property) Research Integrity Sections contained in a typical Clinical Trial Agreement 6 Preamble Acknowledgements & Responsibilities Term & Termination Payment/Reimbursement of Costs HIPAA, Patient Privacy Publication Intellectual Property Confidentiality/ Proprietary Information Indemnification Insurance Subject Injury Miscellaneous Governing Law Notices Assignment Exhibits Negotiation 7 Sponsor supplies a template. FH Legal reviews and comments on the document. Go back and forth with sponsor until all points are covered. Get to “Yes”. Challenges in negotiating a CTA 8 Top 5 Hurdles Compliance with Florida Hospital policy Ability to terminate Indemnification Insurance If sponsor will not indemnify If sponsor requires mutual indemnification If sponsor does not carry minimum levels of insurance If sponsor cannot prove liquid assets to cover liabilities Publication If sponsor requires “approval” of publication If sponsor a requires a de facto publication restriction Uncle Sam wants You….. 9 To Be Compliant. Contract language must be consistent with Federal and state laws, rules, regulations and Florida Hospital policies, requirements, and procedures. Indemnification 10 FH is a non-profit institution, Devoted to research and education. *FH will not incur liability on behalf of FH that is not warranted by the normal course of our business.* There are four specific points that FH requires it be indemnified for in standard indemnification provisions: Any provision of services by Sponsor in connection with the study FH’s participation in the study Sponsor’s manufacturing defect of the study drug or device Sponsor’s negligent use of data Insurance 11 The Sponsor is responsible for the primary burden of risk, therefore they are required to have minimum levels of insurance, that are set by Risk Management at AHS, before FH is able to participate in a study: $1 Million per Occurrence $3 Million in the Annual Aggregate Less than the minimum levels *REQUIRES RISK ASSESSMENT* Publication 12 Scholarly publication is the fundamental right and responsibility of researchers and FH. Sponsors may review manuscripts prior to publication, but may not require terms that allow for “approval” by the Sponsor. Typical provisions: 30 days for the removal of confidential information Additional 60 days for the filing of patent applications. Additional Challenges 13 If sponsor requires overreaching intellectual property clauses. If sponsor requires data/results to remain confidential or the length of confidentiality is unreasonable. If sponsor will not agree to pay subject injury reimbursements. If sponsor will not pay FH’s indirect cost rate of 25%. Reading the CTA 14 A principal investigator’s responsibility in connection with a CTA. While FH Legal reviews and negotiates agreements for the research groups, it is very important that the principal investigator review the agreement to ensure the s/he is aware of the responsibilities required of him/her in connection with a study and is in agreement with the terms being agreed upon. The principal investigator is bound by the terms of the agreement just as much as the hospital. Who negotiates contracts for my department? 15 FH Legal negotiates all contracts for all FH research groups. FH Legal provides support to the ORA and the research groups to understand the legal requirements and obligations of each study. FH Legal works with the Sponsor in revising the agreements, using as a basis previous contracts, templates and master agreements with each sponsor. When do I contact FH Legal? 16 As soon as the sponsor contacts you about any agreement, contact ORA. All requests for contract reviews must come from ORA. Submit requests to ORA via IRBnet with the appropriate documents. How to “Pump Up” our Negotiating Standpoint. 17 United front. Clear layout of goals. Know who we are dealing with. Understand the challenges. How do I work most effectively with FH Legal? 18 Alert ORA ASAP Submit requests to ORA via IRBnet Communication is key Provide contact information for the sponsor Continue to provide new information you receive How do I work most effectively with FH Legal? 19 Help us help you Agreement Protocol Budget Thanks for Listening… 20