File
advertisement

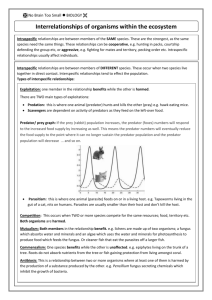
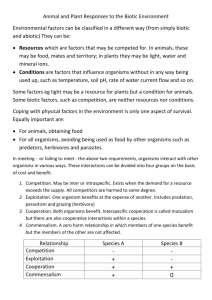
In this next series of lessons we will be exploring interactions between organisms such as predator/prey, parasites, competitors, pollinators and disease. A predator is an animal that catches live prey for food. The prey is an animal that is captured, killed and consumed by another animal e.g. lion (predator) & zebra (prey), bear & fish, fox & rabbit. Let’s watch Hunter & Hunted! (on clickview) What are predators? Worksheet (p41-42 Achieve) Competition is when organisms compete for resources that they need to survive. Giant Amazon Lily Video Tree & plant life in the jungle video For plants (producers, autotrophs) competition typically means competing for sunlight, water, and nutrients from the soil, which are all necessary for photosynthesis. These forest trees are growing taller and taller in order to compete with each other for sunlight How do plants compete for food worksheet (p35-36 Achieve) These forest trees are spreading their roots in order to maximise their ability to take in water and nutrients from the soil, as well as keep other trees out of their territory. Animal Territory Battles for Survival Video For animals (consumers, heterotrophs) competition usually occurs over territory, food, and mates. These male deer are competing to see who will be the alpha male and mate with the female deer These hyenas are competing with this lion over an animal carcass How do animals in ecosystems compete for food worksheet (p40 Achieve) Competition in ecosystems worksheet (p15-16 Achieve). Organisms in a close RELATIONSHIP where at least one organism benefits. Without one another bees and many types of flowers would not be able to exist Symbiosis general overview vid COMMENSALISM (+ 0) One partner benefits whilst the other remains unharmed Remoras hitch a ride on sharks and feed on scraps from the sharks meal. This helps the remora but has no effect on the shark Epiphytes e.g. ferns, orchids, and mosses grow on larger trees allowing them to access more sunlight and rainwater One partner (the parasite) benefits, and the other (the host) is harmed. Parasites live on or in their host Some examples are heart worm in dogs, hookworms in people, and mould (white fuzzy stuff) on aquarium fishes. Parasitism (Monsters Inside Me) vids Parasitoid wasp Create a parasite task Mutualism (++) A partnership between 2 different kinds of organisms where both of them benefit Mutualism song Clownfish & Anemone video Plover & croc video Mutualism wanted ad task Interactions summary Construct a table to summarise the similarities and differences between parasitism, mutualism, and commensalism. + − Quizlet: ecological interactions (key terms) Quizlet: examples of ecological interactions Relationships worksheet p13-14 Acheive Relationships worksheet p43-44 Achieve