SIOP Chapter 9 - Moroni-ITEP
advertisement

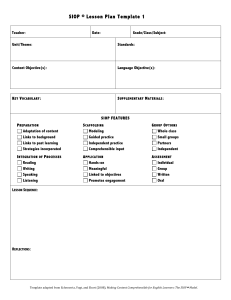
Welcome Complete Credit Registration Form ED 326 SIOP Summer 2013 Opening Prayer 2 Credit Hours Rasmussen Lesson Preparation Review and Assessment Building Background THE SIOP MODEL Lesson Delivery Practice and Application Comprehensible Input Strategies Interaction Lesson Preparation Review and Assessment Building Background THE SIOP MODEL Practice and Application Comprehensible Input Strategies Interaction Lesson Preparation Review and Assessment Building Background THE SIOP MODEL Lesson Delivery Practice and Application Comprehensible Input Strategies Review and Assessment Building Background THE SIOP MODEL Lesson Delivery Practice and Application Comprehensible Input Strategies Interaction Lesson Preparation Review and Assessment Lesson Delivery Building Background THE SIOP MODEL Comprehensible Input Strategies Interaction Lesson Preparation Review and Assessment Building Background THE SIOP MODEL Lesson Delivery Practice and Application Interaction Comprehensible Input Indicators of Review/Assessment Content Objectives I will identify several techniques for reviewing key vocabulary and concepts. I will identify several techniques for assessing students. Language Objectives I will write a lesson plan which includes ALL 8 SIOP components. I will teach and reflect on the above lesson Review Lesson Objectives Key Vocabulary Key Content Concepts Assess Lesson Objectives Regular Feedback on Student Output Assess Student Comprehension of Objectives Scheduling time for review and assessment is often difficult. However, effective teachers realize that throughout a lesson and particularly at the end, it is important to determine how well students have learned. Background During class, students are receiving 40-50 minutes of input through a new language. Unless the teacher takes the time to highlight and review key information, and explicitly indicate what students should focus on and learn, they may not know what is important. Students need to know, of all they have tried to process during the lesson, which pieces are most important, which pieces they need to focus on and remember. In the end, you must have enough information to evaluate the extent to which students have mastered your lesson’s objectives, both while you teach, and at the end before you move on. This teach, assess, review, and reteach process is cyclical and recursive. Teach Assess Reteach Review Effective Teaching Cycle for English Learners Develop Lesson Teach Lesson Reteach Make Adjustments to Improve Student Comprehension Assess Student Comprehension and Student Work Review Key Concepts and Vocabulary Review of Key Vocabulary Teach and review terminology and concepts: Through analogy—relating new words and terms to known words and terms with the same structure of pattern. By drawing attention to tense, parts of speech, and sentence structure. Repeat and reinforce key words and language patterns. Learn to define words and terms in the same sentence you use them. Review of Key Vocabulary (cont.) Remember, word lists with definitions are the least effective way to learn new vocabulary. Have students keep a personal Word Study Book, which can be organized many different ways: by topic, parts of speech, letter patterns, graphic organizers, etc. Remember the difference between Tier 1, 2, and 3 words. Be sure students know the language of schooling. Use cooperative learning structures to summarize and review. Quick Write: With your partner, discuss and list as many ways as you can think of to review key vocabulary. Class Share Review of Key Concepts Review and summarize by using “Outcome Sentences.” Put outcome sentences (or sentence starters) on the board and students take turns selecting one and completing an outcome sentence orally or in writing. 1. “I wonder…” 2. “I discovered…” 3. “I still want to know…” 4. “I learned…” 5. “I still don’t understand…” Think, Pair, Share 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. “I wonder…” “I discovered…” “I still want to know…” “I learned…” “I still don’t understand…” Class Share Providing Feedback on Student Output Teachers can model correct English usage when restating a student’s response: “Yes, you are correct, the scientists were confused by what they thought was a baby’s skull lying next to the mummy.” or ‘You are right! Embalming is the process of preserving bodies.” Repeat – Correct – Expand – Recontextualize Assessment of Lesson Objectives Informal Assessment involves on-the-spot, ongoing opportunities for determining the extent to which students are learning content. Teacher observation Anecdotal reports Quick-writes Brainstorming Guided practice Cooperative learning activities Assessment of Lesson Objectives Authentic Assessment is characterized by its application to real life, where students are engaged in meaningful tasks that take place in real-life contexts. Written pieces Audiotapes Interviews Videotapes Observations Creative work and art Discussion Performance Assessment of Lesson Objectives Group responses… Thumbs up/thumbs down – for questions designed to elicit agree/disagree, true/false, yes/no responses Number wheels – students can indicate their response to multiple-choice items Response boards – small chalk boards or small dry erase boards on which students can write a response Content Objectives I will identify several techniques for reviewing key vocabulary and concepts. I will identify several techniques for assessing students. Language Objectives I will write a lesson plan which includes ALL SIOP components. I will teach and reflect on the above lesson Final Assignment Complete a lesson plan which contains ALL 8 SIOP components. Teach the lesson Write a short reflection as to how the lesson went.