8-1 Royal Power Grows
advertisement

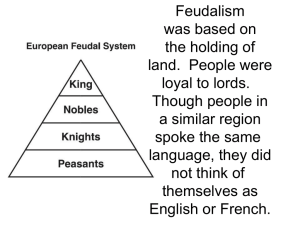
Royal Power Grows Section 8-1 pp. 244-249 Preview Questions • How did monarchs gain power over nobles and the Church? • What traditions of government developed under John and later English monarchs? • How did strong monarchs succeed in unifying France? Monarchs, Nobles, and the Church • Nobles and the Church each had their own land, taxes, and courts. • Monarchs attempted to gain power by: – Centralizing the government – Gaining support from the middle class Strong Monarchs in England • The Norman Conquest (1066) – William of Normandy defeated Harold at the Battle of Hastings to become King of England – Resulted in a blending of Anglo-Saxon and Norman cultures. Strong Monarchs in England • Growth of Royal Power – William made nobles swear loyalty to him above all other lords. – The Domesday Book was a census used for tax purposes – The royal treasury, called an exchequer, grew Strong Monarchs in England • A Unified Legal System – Henry II established common law • Based on customs and royal court rulings • Applied to all of England • Undermined power of nobles and Church • Used juries Strong Monarchs in England • Conflict with the Church – Archbishop Thomas Becket didn’t support Henry II’s attempt to try clergy in royal court – Knights assassinated Becket, who was honored as a martyr – Henry II eased attempts to regulate the clergy Evolving Traditions of English Government • King John I – Oppressive and cruel ruler – Lost English lands to French King Phillip II – Excommunicated by Pope Innocent III • Magna Carta (1215) – English nobles force John to sign this to affirm their rights – Main Idea: No one, even the king, is above the law Evolving Traditions of English Government • Development of Parliament – England’s legislature – Contains a House of Lords and a House of Commons – Most important power = power to approve taxes Successful Monarchs in France • The Capetians – Hugh Capet was chosen as King of France in 987 – He increased the power of the monarchy • Hereditary rule • Pitted nobles against each other • Gained support of Church and middle class • Established strong bureaucracy Successful Monarchs in France • Philip Augustus – Gave royal jobs to middle class members who were paid – Expanded landholdings of the monarchy • Louis IX – Model ruler – Made a saint Successful Monarchs in France • Philip IV – Clashed with Pope Boniface over taxing clergy – Arrested the pope – he later died – New pope was a Frenchman who moved the papacy to Avignon • The Estates General – Representative body from nobles, clergy, and townspeople – Had less power than English Parliament