Plant Reproduction
Click to Enter
ClickBiology
Instructions
ClickBiology
•
Ensure that you complete all activities and worksheets when instructed to do so.
The pad icon will indicate when you should fill in your worksheet.
•
Work your way through the presentation by clicking on the background to move
to the next page or to activate an animation. The mouse icon will indicate that a
click will activate an animation or require buttons to be pressed in the quizzes.
•
You can navigate around the presentation by using the arrow links that appear
when you place your cursor on the lower left hand part of the screen.
•
Some slides have embedded movies which will start when you click on the
image. The video camera symbol tells you when a movie is available. There is
sound so you may want to wear headphones if people are working near you.
•
You can return to the home page by clicking on the clickbiology icon.
•
At the end of the module there is a test that will provide a results page which you
will print off and hand in to your teacher.
•
The speaker symbol means that there are some audio explanation available for
the slide
ClickBiology
Plant Reproduction Home Page
4
1
Seed dispersal
Flower structure
5
2
Germination
Pollination
3
6
Fruit development
Test
ClickBiology
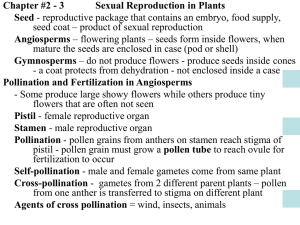
Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Click image to view a video on plant reproduction
If the hyperlink does not work then copy and paste this url into a new browser
window and you can watch the video then, url:
http://vimeo.com/1594037?pg=embed&sec=1594037
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
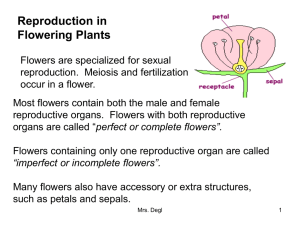
Flower structure
stigma
anther
style
stamen
filament
carpel
ovary
ovule
petal
sepal
peduncle
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
receptacle
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Structure and function of the flower
stigma
anther
style
stamen
filament
carpel
ovary
ovule
petal
sepal
receptacle
peduncle
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Flower Structure Quiz
• What is the name of the structure labelled X in the
diagram?
carpel
sepal
X
stamen
peduncle
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Flower Structure Quiz
• Where is pollen made?
stigma
sepal
anther
ovary
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Flower Structure Quiz
• Where is the ovule found in a flower?
petals
style
nectary
ovary
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Flower Structure Quiz
• Which parts of the flower are labelled below:
X
X = style, Y = stigma
X = filament, Y = anther
Y
X = stigma, Y = style
X = anther, Y = filament
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Pollination
The pollen grain contains the male sex cell (gamete)
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther
to the stigma
• This is an example of cross-pollination as the
pollen travels from one flower to a different flower.
This is desirable in plants as it promotes variation.
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Pollen can be carried between flowers by insects
or by wind
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Insect-pollinated flowers are adapted to attract
insects to them to enable transfer of pollen
Pollen has
barbs for
hooking onto
insect fur
nectar and a
scent present
Anthers positioned
to rub pollen onto
insects
Sticky stigma
to collect pollen
Flower Structure
Pollination
Brightly
coloured petals
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Wind-pollinated flowers are different in structure
because they do not have to attract insects to
them but do need to be exposed to the wind.
Pollen grains are very
small and light. They
occur in very large
numbers
Anthers are exposed to the
wind so that pollen can
easily be blown away
Stigma are
feathery to catch
pollen carried on
wind
Petals are small
and green as there
is no need to attract
insects
Flower Structure
No scent or nectary
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Self-pollination occurs when pollen falls from the
anther onto the stigma of the same flower
• Self-pollination is
not desirable as it
reduces variation
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Flowers will prevent self-pollination by either
having stigma above stamen or…
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
…by having stamen and stigma mature at different
times.
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Click on the icons below to view the
summary videos on pollination
If the hyperlink does not work then copy and paste
this url into a new browser window and you can
watch the video then, url:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bZ3J4UWwd2Q
Pollination (9 minutes)
If the hyperlink does not work then copy and paste
this url into a new browser window and you can
watch the video then, url:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ge3EM8AERV0
Insect pollination (1 minute)
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Pollination Quiz
• Pollination is the transfer from….?
the stigma to anther
style to stamen
ovule to filament
anther to stigma
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Pollination Quiz
• The two mechanisms for pollination are?
Wind and water
Insect and wind
Insect and water
Wind and birds
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Pollination Quiz
• Cross-pollination…
Increases variation
Decreases variation
Is only performed by insects
Is only performed by wind
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Pollination Quiz
• Flowers are adapted for wind-pollination by…
Having bright petals and a scent
Having a nectary
Having feathery stigmas
Having sticky stigmas
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Fertilisation and Fruit Development
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Once pollination occurs a tube grows from the
pollen grain down through the style to the ovule
stigma
style
carpel
ovary
ovule
Note: Petals not shown in
order to simplify diagram
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Fertilisation occurs when the male gamete
fuses with the ovule (the female gamete)
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Watch this short introductory video to review
fertilisation (1 minute)
If the hyperlink does not work then copy and paste this url into a new browser
window and you can watch the video then, url:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pVhH2GPlckE
ClickBiology
Seed Dispersal
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Watch the video on seed dispersal
(lasts just under 10 minutes)
If the hyperlink does not work then copy and paste this url into a new
browser window and you can watch the video then, url:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zbQ1jWl3AOM
ClickBiology
After fertilisation the petals, stamen and sepals fall off.
The ovule turns into a seed, the fertilised egg inside
develops into an embryo plant.
Cotyledon:
Food store
Testa:
tough seed coat
Plumule:
Embryo shoot
Micropyle:
Hole made by
pollen tube
Embryo
plant
Radicle:
Embryo root
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Water leaves the seed, it dehydrates and becomes
dormant because metabolic reactions stop.
The ovary develops to become a fruit.
Fleshy wall
of the ovary
(yes, you are
eating an
adapted ovary
when you
crunch into an
apple!
seed
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Seeds need to be dispersed away from the parent
plant in order to reduce competition for space,
light, nutrients and water.
• Seeds can be dispersed by:
•
•
•
•
Wind
Water
Mechanical
Animals
ClickBiology
Seed dispersal quiz
• Which mechanism for dispersal is used by the seed
shown in the picture
water
mechanical
wind
animal
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Seed dispersal quiz
• Which mechanism for dispersal is used by the seed
shown in the picture
mechanical
animal
water
wind
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Seed dispersal quiz
• Which mechanism for dispersal is used by the seed
shown in the picture
water
wind
animal
mechanical
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Seed dispersal quiz
• Which mechanism for dispersal is used by the seed
shown in the picture
animal
mechanical
water
wind
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fertilisation
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Germination
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
The seed contains the embryo plant and
cotyledons (starch stores)
Testa
Water enters the seed
through the micropyle
and activates enzymes.
Plumule
(embryo shoot)
The water also softens
the testa to allow it to
split.
Radicle
(embryo root)
Cotyledon
Micropyle
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Enzymes are used in seed germination
Plumule
starch
amylase
secreted
embryo plant
The enzymes break
starch down into
maltose and then
glucose. The glucose
is used in respiration
to provide energy for
growth
maltose
Radicle
This is the first part
to grow out of the
seed as it needs to
absorb more water
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Whilst germinating the plant uses food stores in
the cotyledon to provide energy for growth
light
The seedling can now
photosynthesise and
make its own food
germination
Plant growth and development
soil
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Changes in dry mass of the germinating seed:
Seed loses weight as it uses
up starch stores in the
cotyledons as the seedling
cannot photosynthesise yet
Dry mass/g
Weight increases as
the seedling can
photosynthesise and
plant grows
Dry mass is the
mass of solid
matter with all
water removed
Days
Flower Structure
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
Conditions required for germination
Pyrogallol (absorbs oxygen)
No light
Oxygen
present
Oxygen
present
Oxygen
present
Oxygen
present
No
oxygen
moist
4oC
A
Flower Structure
dry
moist
moist
moist
Warm
B
Warm
C
Warm
D
Warm
E
Pollination
Fruit Development
Seed Dispersal
Germination
Test
ClickBiology
END
www.clickbiology.com
ClickBiology