Attitude
advertisement

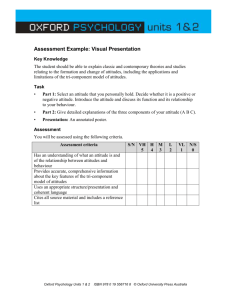
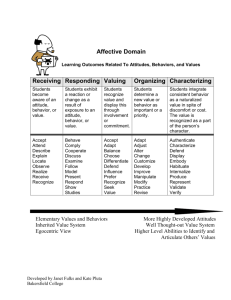
SERVICE ATTITUDE By Jasmine I. Aquino SERVICE EXCELLENCE Using our expertise to respond to the needs and wants of others in a timely and positive manner by meeting and exceeding their expectations through individualized and holistic assistance Empowerment enables employees to make decisions and provide service excellence by acting in the best interest of all stakeholders. However, a sense of empowerment comes from within the individual. What can YOU do to provide service excellence to others? EMPOWER THE BEAST WITHIN •Behavior •Empathy •Attitude •Service •Trust ATTITUDE Our personal perspective following the evaluation on a given matter based on past experiences and current values HOW IS A PERSON’S ATTITUDE SHAPED? •Classical Conditioning •Operant Conditioning •Observational Learning •Persuasion •Cognitive Dissonance CLASSICAL CONDITIONING OPERANT CONDITIONING OBSERVATIONAL LEARNING PERSUASION COGNITIVE DISSONANCE HOW DO WE COMMUNICATE ATTITUDE? •Verbal – Denotation, Connotation •Vocal – Pitch, Volume, Cadence •Visual – Appearance, Body Language TEN POSITIVE ATTITUDE PRINCIPLES • Positive Thinking Principle • Proactive Principle • Appreciation Principle • Small Stuff Principle • People Principle • The Self-Esteem Principle • Overwhelm Principle • The Flexibility Principle • Response/Ability Principle • The Self-Awareness Principle POSITIVE THINKING PRINCIPLE Proactive Principle Appreciation Principle Small Stuff Principle PEOPLE PRINCIPLE Self-Esteem Principle Overwhelm Principle Flexibility Principle Response/Ability Principle The Self-Awareness Principle BIBLIOGRAPHY Alexander Hamilton Institute. “Bad Attitudes & Complaints: Handling Workplace Negativity.” Centerpiece Human Resources. 14 Jun. 2012. Business Management Daily. http://www.businessmanagementdaily.com/19426/bad-attitudes-complaints-handling-workplace-negativity. May 2014. Biswas-Diener, Robert and Kashdan, Todd B. “What Happy People Do Differently.” Psychology Today. 2 Jul. 2013. http://www.psychologytoday.com/articles/201306/whathappy-people-do-differently. May 2014. Bridges, William. Making Transitions: Making the Most of Change. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, 1991. Buckingham, Marcus and Curt Coffman. First, Break All the Rules: What the World’s Greatest Managers Do Differently. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1999. Constance, Joe. “Building Positive Attitudes in the Workplace.” Constant Training. 24 Feb. 2011. http://www.constanttraining.com/downloadfiles/AttitudesWorkbook.pdf. May 2014. Covey, Stephen R. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1989. Pearce, Terry. Leading Out Loud: Inspiring Change Through Authentic Communication. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 2003. Ray, Linda. “The Effect of Employee Attitude on Productivity in the Workplace.” Global Post. http://everydaylife.globalpost.com/effect-employee-attitude-productivityworkplace-3168.html. May 2014. Root, George N. III. “How Do Negative & Positive Attitudes Affect the Workplace?” Chron. http://smallbusiness.chron.com/negative-positive-attitudes-affect-workplace21287.html. May 2014. Rosner, Bob and Campbell, Sherrie. “Maintaining a Positive Attitude in the Workplace.” Recession-Proof Your Career. Pay Scale. http://www.payscale.com/positiveattitude-in-the-workplace. May 2014. Wallace, Ed. Business Relationships That Last: 5 Steps to Transform Contacts into High Performing Relationships. Austin: Greenleaf Book Group Press, 2010. Wengrzyn, Rob. “Types of Attitudes in the Workplace: Cognitive, Affective & Behavioral Components.” Education Portal. http://educationportal.com/academy/lesson/types-of-attitudes-in-the-workplace-cognitive-affective-behavioral-components.html#lesson. May 2014.