Social Psychology: Influences on Behavior & Attitudes
advertisement

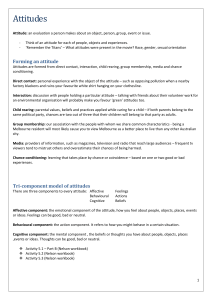
Social Psychology What influences us Social Psychology O Scientific study of how a person’s behavior, thoughts and feelings are influenced by the real, imagined, or implied presence of others Social Influence O The real or implied presence of others can directly or indirectly influence the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of an individual O Can occur even when a person may not want to go along with the group O Even in the presence of others Conformity O Changing one’s own behavior to match others O Asch’s study O Seven participants in a room O Told study on visual judgment O Only one real participant O Others were told to pick same wrong answer What happened? O The person gave the same wrong answer O An experiment in America now might not get the same results as in 1950’s O Other cultures might still conform O Hong Kong O Japan O Online experiment and the cultural different disappears Groupthink O When people of a group find group cohesiveness more important than considering the facts O War on Iraq O Titanic O Challenger O Why would group think occur? O Group can do no wrong O Stereotyped views of those that disagree O Exert pressure Compliance O Occurs when people change their behavior as a result of the influence of another person or group O Consumer Psychology O How to get people to buy what you are selling O Techniques O Foot in the Door O Door in the Face O Lowball O That’s not All Obedience O Changing your behavior at the command of an authority figure O Police officer O Teacher O Work supervisor O Military officer O How far would you go to obey? Milgram’s Experiment O Placed add in paper to recruit people O Told they were to test the effects of punishment on learned behavior O Participants believed that they had been randomly assigned to either the O Teacher, which is where they were all put O Learner, had a script to follow with each jolt Milgram’s what happened? O Many professionals believed the person would not go over 150 O 65% went all the way to the final 450 volt shock level O None quite before reaching 300 volts O Retesting in US and other countries concluded the same results Milgram, Why O Those that wen to 450 showed no personality traits to have high levels of obedience O Should this type of experiment even be done? O Cause self esteem issues with volunteers O Psychological stress Group Behavior O Group polarization O Members take a more extreme position than they would as individuals O Social Facilitation O Presence of others to have a positive impact on the performance of an easy task O Social Impairment O Negative impact O Social Loafing O Person puts in less effort when working with others Social Cognition O The way people think about other people and how those cognitions influence behavior toward those other people O First Impressions O How we perceive others O How we explain the behavior of others ABC’s of Attitudes O Attitude is a tendency to respond positively or negatively toward a certain person, object, idea or situation O You are not born with attitudes, they are learned in the environment that you grow up in O We may make up our minds before even trying something new Components of Attitude O Affective Component O Affect means emotions feelings O How you might feel about certain music, movies O Behavior Component O Action that you might take in regard to the person, object, or situation O Buy certain music, go to movies you like O Cognitive Component O way you think about yourself, an object or an event. Including beliefs and ideas O You might think the music you like is better than any other Attitude Formation O Learning, we learn our attitudes O Direct contact with the object, person, or situation O Direct instruction by a parent or another individual O Interaction with others, we may be influenced by who we spend time with O Vicarious Conditioning (observational learning) we may learn our attitudes by watching others in our lives, in the media, in books, at school Attitude Change O The art of persuasion O What does it take to change your attitude? Cognitive Dissonance O When we have a sense of discomfort when our behavior and beliefs do not match O When we do something against who we really are O How to fix it O Change our behavior O Change cognition to justify behavior O Form new cognitions to justify behavior Social Categorization O Assignment of a person to a category based on characteristics the person has in common with other people you have experienced in the past O Stereotypes are when the person is categorized superficially, when it is believed all people who look like that must be… Attribution O Explaining own behavior and the behavior of others O Situational cause, external factors, such as delays, the actions of others, or some other aspect of the situation O Dispositional cause, internal factors, such as personality or character Prejudice and Discrimination O Prejudice is holding an unsupportive and often negative attitude about member of a particular social group O Discrimination is treating people differently because of the prejudice toward the social group to which they belong Brown Eyes vs. Blue Eyes O Small town in Iowa in 1968 two days after the assassination of Dr Martin Luther King O See how the kids had discrimination/prejudice in them already O How quick the blue eyed kids fell into their “role” O http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XG1v6g 7TPX4 Ben Wilson O Played for Simeon Voc HS in Chicago O First Chicago basketball player to be named the top high school basketball player in the country O November 20, 1984, Wilson was shot O Family sued hospital for projected earning $10 Million dollars How do we learn it? O Social identity theory O We view ourselves as part of a certain group O We categorize others into certain groups O We compare ourselves to other groups, mostly in a better way O Stereotype vulnerability O Person’s awareness of the stereotypes associated with their social group How do we overcome it? O Education!!! O Learn about others different than yourself O Have contact with other cultures, colleges are a great way to have intergroup contact, no one is an outsider