Improving cash flow
advertisement

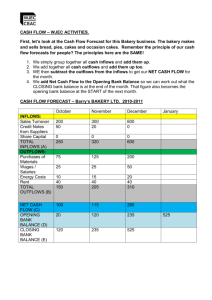
Pages 66-69 To appreciate the purpose of consumer protection laws & apply them to business To understand the main aspects of financial management as a means of managing cash flow more effectively. To analyse ways of increasing cash inflows and reducing cash outflows To appreciate the purpose of consumer protection laws & apply them to business Cash is vital to a business’s success and includes notes, coins and money in the bank. Cash flow is: The flow of money coming into and going out of a business Cash Inflows: the cash coming into a business Cash from the individual Loan from the bank Cash payments from sales Cash outflows Cash going out of a business Equipment & Wages & training Advertising Stock Telephone, gas, electric & other bills Interest on loans Maintenanc e & repairs Net cash flow is the money left over when a business takes its outflows from its inflows. In other words, NET CASH FLOW IS: the receipts of a business minus its payments Example: If Nestle have £30,000 per month coming in and pay out £10,000 in costs, their NET CASH FLOW is £20,000. Costa Coffee In pairs, list the cash inflows and cash outflows that Costa Coffee may have Cash inflows Payments from customer Interest on bank accounts, savings & investments Franchise fees, royalty payments etc Merchandise Receipt of bank loans/overdrafts Cash outflows Purchase of stock, raw materials or tools. Wages, rents and daily operating expenses. Purchase of fixed assets PCs, machinery, office furniture, etc. Loan repayments. Dividend payments. Income tax, corporation tax, VAT and other taxes. Reduced overdraft facilities. ‘Deliberately changing monetary values like cash flows to achieve financial objectives’ Increasing sales revenue Long term solutions Cash flow e.g. loans Improving C.F from customers Destocking Sales revenue = Selling price x quantity sold Main ways to boost sales revenue: 1. Improved marketing: Using alternative or additional forms of advertising or product trials 2. Better products: Introducing new or differentiated products to the marketplace Reducing stocks of finished products (possibly having a sale to shift stock surpluses). 1. 2. 3. Reduce trade credit Chase up late payments Employ a factor (A Factor is a financial company, often a bank that will advance the money owed to a business by its customers) What longer term solutions are there to improving cash flow? Solutions: Bank loan, issue shares (PLC’s) or sale of assets. Reduce your orders for materials & stock Lease rather than buy Delay paying invoices Improve & reduce outflows A inflow and smaller cash outflows over a period of time B inflow and smaller cash inflows over a period of time C outflow and smaller cash inflows over a period of time D outflow and smaller cash outflows over a period of time. A improved cash flow because more raw materials will be ordered B improved cash flow because fewer raw materials will be ordered C improved cash flow because fewer finished products will be sold D a deterioration in cash flow because more finished products will be sold. Answer B A Increasing the amount of materials bought from suppliers B Increasing the level of stocks of raw materials held by the business C Reducing the length of time customers are given to pay their invoices D Reducing the amount of time taken by the business to pay its suppliers Answer C 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is meant by the term ‘financial management’? What is the difference between a cash inflow and a cash outflow? Give three examples of cash inflows to a business. Explain the purpose of de-stocking. Identify and explain one long term solution that might improve a firm’s cash flow. 6. Outline three possible ways that cash flows out of a business. 7. What is meant by the term ‘factor’? 8. If a firm has a positive cash flow does this mean it is making a profit? 9. How might changing the order levels of materials affect a business? 10. ‘Delaying the payment of invoices is good for the cash outflow.’ Explain what is meant by this and how it may affect a business. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is meant by the term ‘financial management’? What is the difference between a cash inflow and a cash outflow? Give three examples of cash inflows to a business. Explain the purpose of de-stocking. Identify and explain one long term solution that might improve a firm’s cash flow. 6. Outline three possible ways that cash flows out of a business. 7. What is meant by the term ‘factor’? 8. If a firm has a positive cash flow does this mean it is making a profit? 9. How might changing the order levels of materials affect a business? 10. ‘Delaying the payment of invoices is good for the cash outflow.’ Explain what is meant by this and how it may affect a business. Revision Q: Answers 1. Financial management is the deliberate action of changing monetary variables to achieve financial objectives, such as improved cash flows. 2. A cash inflow is cash coming into a business. A cash outflow is cash moving out of a business. 3. Any three from the following (receiving): sales revenue; interest received from savings; returns on other investments; sale of assets; money paid by debtors; rental of land or buildings; any other relevant answer. 4. One way a business can increase its cash inflow is to make a conscious decision to reduce its stocks of finished products by selling them off, known as de-stocking. Often it takes the form of a sale where the finished goods are offered at reduced prices to customers for a limited period. This usually results in customers buying more and an increase in revenue. 5. One of the following: bank loans – taking out a loan from a bank o other similar institution to inject capital into a business; issuing shares – selling shares in the business to investors in return for capital; selling assets – selling machinery, buildings or land that is not needed; sale and leaseback – selling machinery, buildings or land then leasing them back to raise a lump sum. 6. Any three from the following (paying for): raw materials; wages and salaries; rent; interest on loans; electricity or gas; VAT; corporation tax; any other relevant answer. 7. A factor is a financial company, such as a bank, that advances the money that a business is owed by its customers immediately and charges a fee for its services. A firm can typically get up to 90% of the value of invoices by using a factor. 8. Cash flow is not the same as profit. Cash flow is the amount of money flowing into and out of a business over a given period of time whereas profit is the amount of money that is left over after the total costs have been subtracted from total revenues over a given period of time (usually a year). It is possible that businesses can have cash flow problems but still be a profitable venture. A positive cash flow simply means more money has flowed into the business over a period of time than has flowed out. It says nothing about overall costs and revenues, however. 9. The order levels that a business places add to the cash outflow. By changing the amounts that are ordered the level of cash outflow can be directly affected. Reducing the levels ordered will clearly reduce any cash outflow. Cutting order levels will, however, have an effect on the production quantities that a firm enjoys. The fewer raw materials ordered will result in lower production quantities. Clearly this is a strategy that can only be used if the sales levels are falling as well. There could be an argument that if a firm is overproducing then this strategy could also be employed to bring production levels in line with sales volumes, leading to efficient working practices such as Just-In-Time. 10. One way in which a business can improve its cash outflow is by delaying any payment on invoices due. This is where a firm does not pay its invoices on time, for example after 30 days. The longer it can be delayed the better the cash flow position as there will be less cash flowing out of the business. It can, however, have a negative effect on the reputation of a firm as one that does not