Biliary
advertisement

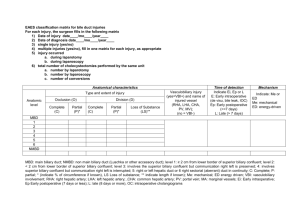
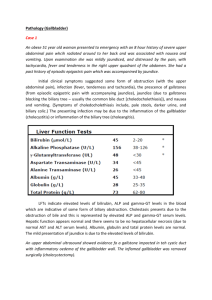
Biliary Disease Gallbladder and Biliary Tree • Imaging Studies Available – X-ray – Computed tomography – Radioisotope scan (hepatobiliary scan) – Ultrasound: the most sensitive study for gallstone Gallstones • 81% consist of cholesterol and are radiolucent (cannot be seen on plain films) • 19% contain calcium and are radioopaque (can be seen on plain films) Gallstones • Size: can be very small (1-2 mm) to very large (several cm) • Shape: single stone – round, large • Multiple stones – small, faceted Gallstones • Complications include – Obstruction of bile duct: commonly cystic duct and common bile duct – Cholecystitis (infection/ inflammation of the gallbladder) – Abscess (complication of cholecystistis) – Perforation: • peritonitis, inflammation infection of peritoneum • gallstone ileus, stone erodes into GI tract and causes obstruction Gallbladder • Ultrasound – Stones all appear ECHOGENIC (white) • May be either radiolucent or radio-opaque – Beyond stone is an acoustic shadow – Bile is HYPOECHOIC (black) – Polyps, neoplasm typically are isoechoic (equal echo density) to adjacent soft tissues Gallstones • AP abdomen • Several facetted calcified densities • Dense rim less dense center • Separate from renal calculi and costocartilage by different positions • Use oblique films, gallbladder anterior so move away from spine Gallstones • Ultrasound upper abdomen • Longitudinal scan • Round echogenic structures in gallbladder • Acoustic shadowing Dilation of Bile Ducts • Causes include – Stone (most common) – Carcinoma Dilated Common Bile Duct • Longitudinal US through liver hilum • Typical double channel sign • Dilated common bile duct (blue arrow) anterior to portal vein (red arrow) • Duct usually smaller than vein • Stone(not seen) distal in duct Bile Duct Dilatation • Axial CT midabdomen • Dilated common bile duct (arrowhead) • Dilated intrahepatic ducts • Round fluid structure anterior to kidney is distended gallbladder Common Bile Duct Stone • Axial imaging lower than prior example • High density structure obstructing calculi (arrow) • Large round area gallbladder HIDA Imaging • Radionuclide targeted to hepatocytes • Non filling of the common bile duct or gall bladder indicates obstructive process Acute Cholecystitis • No filling of the gallbladder 60 minutes after injection of isotope • Rapid accumulation within the liver and bile ducts with spill into the doudenum Bile Leak Ida Scan Accumulation of isotope outside of the biliary tree MR Cholangiography Stone • Emerging technology • Visualize stone as a filling defect in the common duct (blue arrow)