Musculoskeletal System

Chapter 19
Image Slides
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
1
LEARNING OUTCOMES
19.1 Overview of Bone and Cartilage
Explain the macroscopic and microscopic structure of bone.
Distinguish the structure and function of the three types of cartilage.
Describe how bones change during a person's lifetime.
19.2 Bones of the Skeleton
Summarize the five major functions of the skeleton.
List the major bones that comprise the axial and appendicular skeletons.
Compare the structure and function of fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, and synovial joints.
19.3 Skeletal Muscles
Explain how antagonistic muscle groups can move bones in different directions.
Identify the major muscles in the human body.
Describe six characteristics that are used to name skeletal muscles.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
19.4 Mechanism of Muscle Fiber Contraction
Describe the microscopic structure of a muscle fiber.
Review the sliding filament model of muscle contraction.
Summarize how activities within the neuromuscular junction control muscle fiber contraction.
Indicate three ways that muscle cells can generate ATP.
19.5 Whole Muscle Contraction
Explain what is happening to an isolated muscle fiber during summation, tetanus, and fatigue.
Describe how muscles generate different levels of contractive force.
Explain the types of exercise that require more fast-twitch versus slow-twitch muscle fibers.
19.6 Disorders of the Musculoskeletal System
List three common disorders that affect the bones and joints and three that affect the muscles.
Identify some of the most common steps that can be taken to help prevent osteoporosis.
Co 19
4
Fig. 19.1
5
Fig. 19.2
6
LEARNING OUTCOMES
19.1 Overview of Bone and Cartilage
Explain the macroscopic and microscopic structures of bone .
Distinguish the structure and function of the three types of cartilage .
Describe how bones change during a person's lifetime ( growth ).
Fig. 19.3
8
Fig. 19.10
9
LEARNING OUTCOMES
19.2 Bones of the Skeleton
Summarize the five major functions of the skeleton.
List the major bones that comprise the axial and appendicular skeletons .
Compare the structure and function various types of joints (fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, and synovial joints).
10
Table 19.1
11
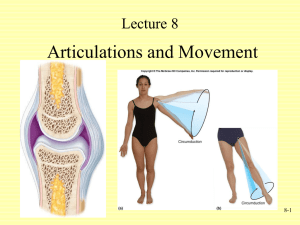
Fig. 19.11
12
LEARNING OUTCOMES
19.3 Skeletal Muscles
Explain how antagonistic muscle groups can move bones in different directions.
Fig. 19.13
14
Fig. 19.14
15
Fig. 19.15
16
Page 380
17
LEARNING OUTCOMES
19.4 Mechanism of Muscle Fiber Contraction
Describe the microscopic structure of a muscle fiber .
Review the sliding filament model of muscle contraction.
Summarize how activities within the neuromuscular junction control muscle fiber contraction.
Indicate a way that muscle cells can generate ATP .
Fig. 19.17
19
LEARNING OUTCOMES
19.5 Whole Muscle Contraction
Describe how muscles generate different levels of contractive force .
Explain the types of exercise that require more fast-twitch versus slowtwitch muscle fibers .
Fig. 19.18
21
Fig. 19.19
22
Fig. 19.20
23
LEARNING OUTCOMES
19.6 Disorders of the Musculoskeletal System know common disorders that affect the bones and joints and that affects the muscles.
Identify some of the most common steps that can be taken to help prevent osteoporosis .