cell membrane review
advertisement
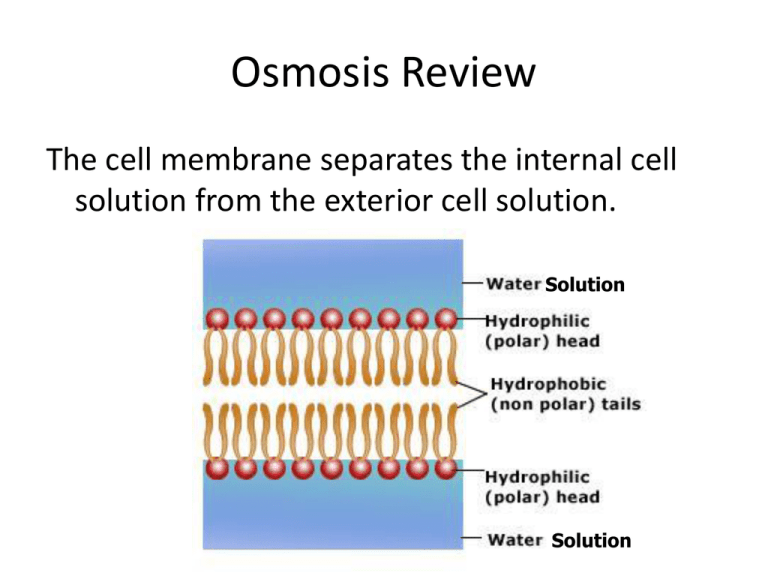
Osmosis Review The cell membrane separates the internal cell solution from the exterior cell solution. Solution Solution Cell Membrane consists of the lipid bilayer, carbohydrates, and proteins. Water can pass right through lipid bilayer What is a solution? A mixture of two or more substances. A solution consists of a solute and a solvent. A salt water solution… • Is salt the solute or the solvent? – Solute • Is water the solute or the solvent? – Solvent • What does the solute do? – Gets dissolved • What does the solvent do? – Does the dissolving A Salt Water Solution Solute (salt) Animation Solvent (water) Cell Membrane consists of the lipid bilayer, carbohydrates, and proteins. Water can pass right through lipid bilayer The solute can’t fit through the membrane but the water can. The water moves through to make both sides’ concentrations at a state of equilibrium. Unit 4: Let’s Review Osmosis or Diffusion 1. The student sitting next to you just came from gym class and forgot to shower and you can tell. Osmosis or Diffusion 2. After sitting in the bathtub for hours, your fingers start to look like prunes. Osmosis or Diffusion 3. The girl sitting two rows ahead of you in Math class put on way too much perfume this morning. Osmosis or Diffusion 4. One way to get rid of slugs in your garden is to sprinkle salt on them, so they shrivel up. Osmosis or Diffusion 5. Gargling with salt water when you have a sore throat causes your swollen throat cells to shrink and feel better. Osmosis or Diffusion 6. Oxygen molecules move from the air sacs in the lungs across the cell membranes into the blood Osmosis or Diffusion 7. The supermarket sprays water on the veggies in the produce section to keep the veggies crisp. 8. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, how will the WATER move? 9. When a cell is placed in a isotonic solution, how will the WATER move? 10. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, how will the WATER move? 11. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, how will the SOLUTES (ex. Salt) move? 12. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, how will the SOLUTES (ex. Salt) move? 13. When a cell is placed in a isotonic solution, how will the SOLUTES (ex. Salt) move? 14. What type of solutions are the cells in? 15. What type of solutions are the cells in? 16. Placing an animal cell in a hypotonic solution will cause water to ______________. A. move into the cell B. move out of the cell 17. During osmosis water molecules tend to move _______________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration 18. The substance that dissolves to make a solution is called the ___________________ A. diffuser B. solvent C. solute D. concentrate A or B 19 . The black dots in the diagram above represent solute molecules dissolved in water. In which beaker is the concentration of solute the greatest? A B A or B What TWO answers below that are true. 20. The way to make the concentration in the two containers above equal would be to _____ A. add more solute to container A B. add more solute to container B C. add more solvent to container A D. add more solvent to container B 21. When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system has reached __________________. A. maximum concentration B. dialysis C. osmotic pressure D. equilibrium 22.________________ transport requires energy from ATP to move substances across membranes. A. Passive B. Active 23. Draw and describe a plant cell in a hypotonic solution. How will a plant cell respond differently than an animal cell and why? 24. Draw and describe a plant cell experiencing plasmolysis. What type of a solution (hypo-, hyper-, or isotonic) would cause plasmolysis? 25. What would happen to the mass of a cell in a hypertonic solution? A hypotonic solution? An isotonic solution? Why? 26. Are the plant cells in hyper, hypo, or isotonic solution? http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player _embedded&v=GOxouJUtEhE 27. Animal Cells in which type of solution? 28. Animal Cells in which type of solution? 29. Animal Cells in which type of solution? 30. Intravenous solutions (IV’s) must be prepared so that they are isotonic to red blood cells. A solution of 99.1% water and 0.9% salt is isotonic to red blood cells. Red blood cells will burst if placed in A. a solution of 99.3% water and 0.7% salt. B. a solution of 90% water and 10% salt. ANSWERS Osmosis or Diffusion 1. The student sitting next to you just came from gym class and forgot to shower and you can tell. DIFFUSION Osmosis or Diffusion 2. After sitting in the bathtub for hours, your fingers start to look like prunes. OSMOSIS Osmosis or Diffusion 3. The girl sitting two rows ahead of you in Math class put on way too much perfume this morning. DIFFUSION Osmosis or Diffusion 4. One way to get rid of slugs in your garden is to sprinkle salt on them, so they shrivel up. OSMOSIS Osmosis or Diffusion 5. Gargling with salt water when you have a sore throat causes your swollen throat cells to shrink and feel better. OSMOSIS Osmosis or Diffusion 6. Oxygen molecules move from the air sacs in the lungs across the cell membranes into the blood. DIFFUSION Osmosis or Diffusion 7. The supermarket sprays water on the veggies in the produce section to keep the veggies crisp. OSMOSIS 8. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, how will the WATER move? IN THE CELL 9. When a cell is placed in a isotonic solution, how will the WATER move? IN AND OUT OF CELL AT AN EQUAL RATE 10. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, how will the WATER move? OUT OF THE CELL 11. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, how will the SOLUTES (ex. Salt) move? DOES NOT MOVE (TOO LARGE TO DIFFUSE ACROSS CELL MEMBRANES) 12. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, how will the SOLUTES (ex. Salt) move? DOES NOT MOVE (TOO LARGE TO DIFFUSE ACROSS CELL MEMBRANES) 13. When a cell is placed in a isotonic solution, how will the SOLUTES (ex. Salt) move? DOES NOT MOVE (TOO LARGE TO DIFFUSE ACROSS CELL MEMBRANES) 14. What type of solutions are the cells in? HYPOTONIC HYPERTONIC ISOTONIC 15. What type of solutions are the cells in? 16. Placing an animal cell in a hypotonic solution will cause water to ______________. A. move into the cell B. move out of the cell 17. During osmosis water molecules tend to move _______________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration D. in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration 18. The substance that dissolves to make a solution is called the ___________________ A. diffuser B. solvent C. solute D. concentrate A or B 19 . The black dots in the diagram at the left represent solute molecules dissolved in water. In which beaker is the concentration of solute the greatest? A B A or B What TWO answers below that are true. 20. The way to make the concentration in the two containers above equal would be to _____ A. add more solute to container A B. add more solute to container B C. add more solvent to container A D. add more solvent to container B 21. When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system has reached __________________. A. maximum concentration B. dialysis C. osmotic pressure D. equilibrium 22.________________ transport requires energy from ATP to move substances across membranes. A. Passive B. Active 23.Draw and describe a plant cell in a hypotonic solution. How will a plant cell respond differently than an animal cell and why? Cell Wall prevents cell from bursting!!! 24. Draw and describe a plant cell experiencing plasmolysis. What type of a solution (hypo-, hyper-, or isotonic) would cause plasmolysis? 25. What would happen to the mass of a cell in a hypertonic solution? A hypotonic solution? An isotonic solution? Why? Hypertonic solution- Mass decreases Hypotonic solution- Mass increases Isotonic solution- Mass stays the same 26. Are the plant cells in hyper, hypo, or isotonic solution? http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player _embedded&v=GOxouJUtEhE HYPERTONIC SOLUTION 27. Animal Cells in which type of solution? HYPOTONIC 28. Animal Cells in which type of solution? HYPERTONIC 29. Animal Cells in which type of solution? ISOTONIC 30. Intravenous solutions (IV’s) must be prepared so that they are isotonic to red blood cells. A solution of 99.1% water and 0.9% salt is isotonic to red blood cells. Red blood cells will burst if placed in A. a solution of 99.3% water and 0.7% salt. B. a solution of 90% water and 10% salt. You can access the book at: my.hrw.com Login: astudents90 Password: a7k7