Rigor & Relevance Framework - Saluda County School District 1
advertisement

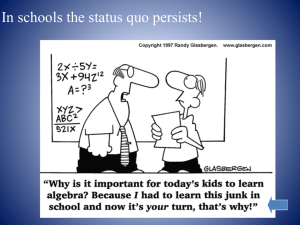
SYNTHESIS EVALUATION RIGOR IS… Work that requires students to work at high levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy combined with application to the real world. www.leadered.com Three Misconceptions of Rigor • MORE – does not mean more rigorous. • DIFFICULT – increased difficulty does not mean increased rigor. • RIGID – “all assignments are due by… no exception.” Dick Jones, Sr. Consultant ICLE INCREASING RIGOR 6. Evaluation Assimilation of knowledge 5. Synthesis 4. Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension 1. Knowledge/Awareness Acquisition of knowledge 1. Knowledge list name identify show define recognize state 2.Comprehension 4. Analysis Analyze Organize Deduce Choose Contrast Compare distinguish 5. Synthesis design hypothesize support write report discuss plan create summarize explain paraphrase interpret describe compare paraphrase differentiate demonstrate 3. Application solve illustrate calculate use interpret relate manipulate apply classify 6. Evaluation evaluate choose estimate judge defend criticize justify Why Do I Need To Know This?? Relevance is… • From real life • Heavily dependent upon prior life experiences (just Google it) • Age appropriate • Rich enough to allow for pattern-seeking as a means of identifying/creating meaning • Used within the life of the learner • Not involved in an external rewards system because the brain is a self-congratulator if meaning is present Rigor/Relevance Framework • The Rigor/Relevance framework is a fresh approach to looking at curriculum standards and assessment. It is based on traditional elements of education yet encourages movement to application of knowledge instead of maintaining an exclusive focus on acquisition of knowledge. • It is a “Tool” for educators to: • Assess • Create • Implement Misconceptions of Relevance • COOL – relevance doesn’t exclusively mean what the students do for “fun” • EXCLUSIVE – relevance without rigor does not ensure success. Rigor/Relevance Framework Quadrant C: Quadrant D: Activities are often complex and require students to come up with solutions that deepen understanding. Learning experiences are high in rigor and relevance and require unique solutions to unpredictable problems. Quadrant A: Quadrant B: Experiences focus on recall or discovery of basic knowledge. Activities provide definite opportunities for students to apply knowledge, typically to a real world problem. 6 5 4 3 2 1 Copyright Lucey, 2008 1 2 3 4 5 Rigor/Relevance Framework 6 5 4 Student Thinks Student Thinks and Works Teacher Works Student Works 3 2 1 Copyright Lucey, 2008 1 2 3 4 5 Rigor/Relevance Framework Mathematics - Middle Level C R I G O R High D Express probabilities as fractions, percents, or decimals.. A Low Devise a scale to test consumer products and graph data. B Plot the coordinates for quadrilaterals on a grid. Make a scale drawing of the classroom. Low RELEVANCE High Rigor/Relevance Framework Science - Elementary D C R I G O R High Make diagrams of animal life cycles. B A Low Design a zoo. Make daily observations of the life cycle of a selected species. Create a field book about organisms in local rivers. Low High RELEVANCE Rigor/Relevance Framework Social Studies - Elementary D C R I G O R High Contrast citizens’ Read story about survival responsibilities under and brainstorm strategies different forms of for surviving a disaster government. (e.g., snowstorm, tornado). B A Low Memorize names, locations and capital cities of U.S. states. Describe geographic and climatic characteristics of the local community. Low High RELEVANCE Rigor/Relevance Framework English - Elementary C R I G O R High D Brainstorm as many words as possible to describe an object. B A Low Create new words to describe phenomena or objects. Memorize spelling words. Write a story about the school using specific words. High Low RELEVANCE Rigor/Relevance Framework Science - Middle Level D C R I G O R High Identify chemicals dissolved in an unknown solution. B A Low Collect data and make recommendations to address a community environmental problem. Construct models of molecules. Low Collect data on dissolved oxygen, hardness, alkalinity, and temperature in a stream. RELEVANCE High Rigor/Relevance Framework English - Middle Level D C R I G O R High Analyze commercials for fact and opinion. B A Low Write directions for assembling a product or carrying out a procedure. Locate information in a technical manual. Assemble a product following written directions. Low High RELEVANCE Rigor/Relevance Framework Art - Elementary R I G O R High Low C D Contrast painting styles. Express emotions and feelings with color and images. A B Explain the color wheel. Create holiday crafts/ornaments. Low High RELEVANCE Rigor/Relevance Framework Music C R I G O R High D Compare and contrast different musical styles. B A Low Compose a song. Memorize notes. Perform musical piece from memory. Low High RELEVANCE Rigor/Relevance Framework Physical Education D C R I G O R High Compare benefits of different forms of cardiovascular exercise. B A Low Design an exercise program for senior citizens. Acquire fundamentals of basketball Play a baseball game High Low RELEVANCE Rigor/Relevance Framework 6 5 4 3 2 1 • • • • Make diagrams of animal life cycles. Classify a group of similar objects to create a dichotomous key. Research characteristics and habits of insects. Write a story describing the movement of water through municipal systems. C • Memorize names of planets in the solar system. • Demonstrate phases of the moon. • Match pictures of insects with their names. • Make a model of the layers of the Earth’s atmosphere. A 1 2 • • • • Design a plan for a zoo that meets the needs of a variety of animal species. Set up an experiment to test life length of batteries. Research and write a field guide for identifying local trees. Build a simple device to accomplish a task using string, tape and rubber bands. D • Develop a food list for a space trip. • Create a class book about the animal and plant life in local rivers. • Take photographs of insects to describe characteristics and behaviors. • Study examples of paper airplanes and then create one. B 3 4 5 TJ Mears - ICLE - leadered.com Quadrant A • Memorize the names of planets in the solar system. • Demonstrate phases of the moon. • Match pictures of insects with their names. • Make a model of the layers of the Earth’s atmosphere. Quadrant B • Develop a food list for a space trip. • Create a class book about the animal and plant life in local rivers. • Take photographs of insects to describe characteristics and behaviors. • Study examples of paper airplanes and then create one. Quadrant C • Make diagrams of animal life cycles. • Classify a group of similar objects to create a dichotomous key. • Research characteristics and habits of insects. • Write a story describing the movement of water through municipal systems. Quadrant D • Design a plan for a zoo that meets the needs of a variety of animal species. • Set up an experiment to test life length of batteries. • Research and write a field guide for identifying local trees. • Build a simple device to accomplish a task using string, tape and rubber bands.