Psych 6.1 PPT - heather
advertisement

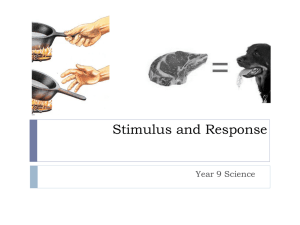
• Learning is achieved through experience. • Anything that we were born knowing how to do is not a result of learning, but everything else is. • We learn how to walk, we learn how to speak in the language of our parents, and we learn how to read. • Sometimes we learn to do things by trying them ourselves; at other times, we learn by watching others or by reading books. LEARNING CONDITIONING = LEARNING • Stimulus – something that produces a reaction (or response) from a person or animal. • Classical Conditioning is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus calls forth the response that is usually called forth by another stimulus. • The founder of classical conditioning was Russian psychologist Ivan Pavlov (18491936). IVAN PAVLOV RINGS A BELL • Pavlov discovered that dogs learn to associate one thing with another when food is involved. • He was studying salivation to find a relationship between the nervous system and digestion. • He discovered that dogs did not always wait until they had received meat to start salivating. • Sometimes they would salivate in response to the clinking of food trays when assistants entered the laboratory. • He looked into this by setting up an experiment where he would stimulate the dog by ringing a bell when meat was near. LETTERS OF LEARNING • There are four terms that are associated with Classical Conditioning. • Unconditioned Stimulus (US or UCS) is a stimulus that causes a response that is automatic, not learned. • Unconditioned Response (UR or UCR) is the automatic response to the US. • Conditioned Response (CR) is a learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral, or meaningless. • Conditioned Stimulus (CS) is the stimulus that becomes a learned stimulus through repeated association. • http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=hhqumfpxuzI QUESTION What are some examples that you can think of in which you have been classically conditioned to something? ACTIVITY Complete the worksheet of situations that apply to classical conditioning. In each situation identify the neutral stimulus, unconditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response. WARM-UP Define the parts in the classical conditioning equation: Neutral Stimulus Unconditioned Stimulus Unconditioned Response Conditioned Stimulus Conditioned Response ADAPTING TO THE ENVIRONMENT • Taste Aversion is a learned avoidance of a particular food. • Have you ever eaten a food that made you ill, perhaps because it was spoiled? • Did you then stay away from that food for a long time? • Example: Coyote EXTINCTION • Extinction occurs when conditioned stimulus is disconnected from the unconditioned stimulus. • Pavlov discovered that with repeated ringings of the bell (CS) not followed by meat (US), the dogs eventually stopped salivating (CR) when they heard the bell (CS). SPONTANEOUS RECOVERY • Spontaneous recovery is when the CR comes back when the CS is presented again even after an extended period of time. • Think about a song that you heard that brought back old feelings. • If it were to become popular again and you started hearing it everyday you probably would no longer experience the same rush of feelings after hearing it over and over. GENERALIZATION AND DISCRIMINATION • Generalization is when we associate similar objects to get a CR. • Pavlov’s Dogs and the Circles are an example of generalization. • Discrimination is knowing the difference between one CS and another. • A bear cub can distinguish between a wolf and a mouse is an example of Discrimination. FLOODING • Flooding is when a person is exposed to something they fear until fear responses to that stimulus are extinguished. • This uncomfortable for most people. • An example of this is that a person with a fear of heights may look out from a sixth story window until she or he is no longer upset by it. SYSTEMATIC DESENSITIZATION • Systematic desensitization is when people are taught relaxation techniques and are then exposed gradually to whatever stimulus the fear while they remain relaxed. • An example of this is a person who fears snakes being shown pictures while they are relaxed. COUNTERCONDITIONING • Counterconditioning is when a pleasant stimulus is paired repeatedly with a fearful one, counteracting the fear. • I hate bunnies but I love cookies. LITTLE ALBERT On page 134 in the textbook you will read the selection on baby Albert and then answer the 2 questions. While reading think about whether or not you feel this was ethical and why. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LVJMhk4oANM