Multiple Intelligences Howard Gardner
advertisement

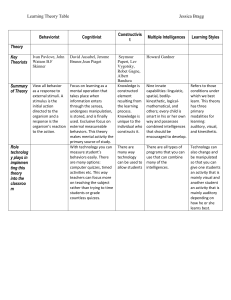
MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES Howard Gardner Harcubová Martina Hrušková Nikola Kundeliusová Petra 2012/2013 Psychology of behaviour at work CONTENT 1. Theory of multiple intelligences 2. MI 3. Practical application of the theory of multiple intelligences 4. Common Good Uses 5. 8 Different ways to learning 6. Sources THEORY OF MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES „An intelligence is the ability to solve problems, or to create products, that are valued within one or more cultural settings“ Gardner Theory by Howard Gardner developed in late 1970's and early 1980's probably the best known theory of pluralistic intelligences (Thorndike, Thurstone, Guilford, Stenberg…) criticism from both psychologists and educators too broad his eight different "intelligences" represent talents, personality traits and abilities a lack of empirical research MI we are all born with the potential for these intelligences development of this potential through whole life independent on the age but depends on stimuli received not just one type and level of intelligence no type of intelligence is intrinsically right or wrong identification of special knowledge PRACTICAL APPLICATION OF THE THEORY OF MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES A) IN THE WORKPLACE managers, training staff, and human resource specialist indicates behavioural and working styles, strength (the possibility to develop their weaknesses) in the job creation and staffing, career development and counseling processes (testing, assessment) more productive, more creative, and more human place greater profitability for the company and staff satisfaction PRACTICAL APPLICATION OF THE THEORY OF MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES B) IN THE EDUCATION Lesson Design Student Projects Misuses Educational implications of MI theory: Individuation - understanding of the intellectual profiles of individual learners Pluralization - important ideas, topics, theories and skills ought to be taught in more than one way -> activation of the multiple intelligences COMMON GOOD USES (FROM GARDNER HIMSELF) The cultivation of desired capabilities Approaching a concept, subject matter, discipline in a variety of ways The personalization of education. HELP TO • satisfy the educational needs of many more students • understanding the different possibilities of each students’ learning preference • stimulate a student’s learning in new ways 8 DIFFERENT PATHWAYS TO LEARNING words (linguistic intelligence) numbers or logic (logical-mathematical intelligence) pictures (spatial intelligence) music (musical intelligence) self-reflection (intrapersonal intelligence) a physical experience (bodily-kinesthetic intelligence) a social experience (interpersonal intelligence), and/or an experience in the natural world (naturalist intelligence) Try to Test your intelligence and find your strengths! http://www.literacyworks.org/mi/assessment/findyourstrengths.html THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION! SOURCES Kerka, Sandra. 1999. Multiple Intelligences and Career Development, Trends and Issues Alert 8 [online] November 11, 2012 [Cited: http://www.calpro-online.org/eric/textonly/docgen.asp?tbl=tia&ID=130] Gardner, Howard E. 1993. Multiple Intelligences: New Horizons in Theory and Practice. 1st edition. Basic books. ISBN: 978-0-465-04768-0 Joyce Martin. 2001. Profiting from Multiple Intelligences in the Workplace. Wales: Crown House Publishing Ltd. [online] November 11, 2012 [Cited:http://www.inlpa.org/index.cfm?CFID=37067&CFTOKEN=85524501&a=10095] Gardner, Howard. 2011. The theory of Multiple Intelligences: As Psychology, As Education, As Social Science. [online] November 11, 2012 [Cited: http://howardgardner01.files.wordpress.com/2012/06/473madrid-oct-22-2011.pdf] Gardner, Howard. Davis, Katie. Christodoulou, Joanna. Seider, Scott..The theory of Multiple Intelligence [online] November 11, 2012 [Cited: http://howardgardner01.files.wordpress.com/2012/06/443-davis-christodoulou-seider-mi-article.pdf]