PPT slides - The Center for Effective Learning
advertisement

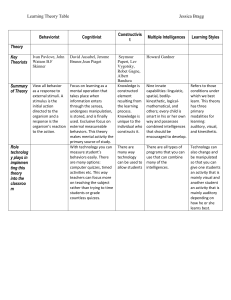
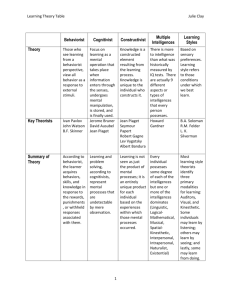
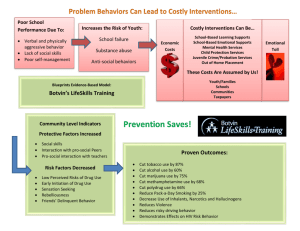
We’re All In This Together Setting the Emotional Conditions For Learning Collaboration & Cooperative Learning Session Goals • Understand the significance of the Stages of Group Development • Experience methods for developing groups and group norms • Identify strategies and content related to the Learning Principle It’s not easy To be wise Alone. Ishi, The Last Yahi Indian Stages in Group Development • Creating a Sense of Inclusion • Having a Say • Collaborative Action Developing a Sense of Belonging: Students and Adults… • • • • • • • Know each other’s names Participate as a member of a Learning Club Practice active listening Feel free to speak up in class Refrain from put downs Willing to work with new study partners Welcome and immediately include new students and visitors • Know and appreciate strengths of classmates • *Be certain to continually feed the emotional tone of the classroom by doing Sense of Belonging Activities routinely Creating Common Ground: Students and Adults… • Create and maintain conditions that make it safe to disagree • Understand that it’s okay to hold differing opinions • Realize it’s equally okay to change one’s mind without it being considered a sign of weakness or losing face • Learn to solve problems and make decisions together • Know that their ideas and opinions are valued Taking Action: Students and Adults… • Strengthen the sense of belonging by working together to accomplish an agreed-upon task • Give students practice in applying personal and social skills needed to create and maintain common ground • Provide practice in using concepts and skills of our curriculum in real-world situations • Give students practice in using the levers of our democratic society to affect change for the common good GROUP ROLES Reporter/Talker - Red Recorder/Writer or Drawer - Blue Liaison/Materials or Things - Yellow Facilitator/Helper - Green **Use pictures instead of words for Primary GROUP ROLES General group roles include the following: Recorder/Reporter/Facilitator/ Liaison-Materials Person I. In job alike groups, define your roles II. Report back to Learning Club and share out your responsibilities III. Be prepared to perform your duties Group Roles • Use a dictionary to define their job, each student recording the information on a 3x5 card • Brainstorm a list of responsibilities associated with the job/role • Identify and write a use statement for each of three LIFESKILLS or Lifelong Guidelines attached to the job In your learning clubs: 1. Each individual shares their quote and what it means to them 2. Describe something you are looking forward to today 3. Create an alliterative group name for your table using one of the LIFESKILLS (Be prepared to share out) Select an applause to go along with your name Organizing Groups • On a 3x5 card: – Write the names of three people with whom you would like to be in a group. – Guarantee: You’ll be with one person you select • Teacher works to make compatible groups using the cards. • If there is a student who no-one selects, you allow for more than one selected person to be in that group and make a special arrangement. Agreements • In newly formed groups have students create agreements by making “Look, Sound, Feel” charts for each of the Lifelong Guidelines: • Have students write up how they will ensure that each person has a say in group discussions and decisions. • All group members sign each of the documents. T-Chart for ____________ (Lifelong Guideline) Looks Like… Sounds Like… Feels Like… EE p. 8.21 T-Chart for ____________ (Lifelong Guideline) Doesn’t Looks Like… Doesn’t Sound Like… Doesn’t Feel Like… EE p. 8.21 Connection: Emotion & Movement • Students analyze historical or current events and literature for examples of collaboration and non-collaboration. • Provide opportunity for students to give appreciations to one another in groups and in the whole class community (appreciation box) • Focus on use of LLG and LS • Utilize Town Hall Meetings to solve problems, celebrate and acknowledge Humans are born into this world “hardwired” with specific fundamental behaviors: • • • • To connect/attach with their surroundings To receive and give care To engage in their environment To seek patterns/meaning within their environment • To respond in organized, effective/competent ways • To be “ultimately concerned” © Dr. Sigurd Zielke 2005 Susan Kovalik & Associates Connection: Multiple Intelligences • Ensure that project and group-work assignments include a number of intelligence needs • Ensure a balance of inquiries based on the multiple intelligences so students naturally seek out others for assistance. • Organize groups by a MI criteria, making certain that at least four intelligences represented. • Have students analyze the intelligences they will need to use in order to complete tasks. • Attach intelligence strengths to group roles. Connections: Patterns and Programs • Have students participate in shared reflections and analysis of what they’ve learned. • Help students recognize the mental programs and patterns inherent in effective group work. • Be purposeful in designing groupwork so it doesn’t become simply sharing the same assignment. • Students should be learning how to understand the world and one another. Connection to Learning Principles: Experience • Tasks should reflect real life expectations where one person alone could not complete the task successfully. • Social skills are always a part of the equation. • Vary leadership expectations • Form new groups for skill work, project work, and planning (students will soon become accustomed to working with all members of the class community. Never doubt that a small group of committed individuals can change the world. Indeed, it is the only thing that ever has. Margaret Mead • "Today we are faced with the preeminent fact that, if civilization is to survive, we must cultivate the science of human relationships... the ability of all peoples, of all kinds, to live together, in the same world, at peace.“ Franklin Delano Roosevelt Resources • Designing Groupwork by Elizabeth Cohen • Strategies for the Heterogeneous Classroom by Elizabeth Cohen • Cooperative Learning for All Grades by Spencer Kagan • TRIBES Learning Communities by Jeanne Gibbs