PowerPoint of Parent Mathmatics Night
advertisement

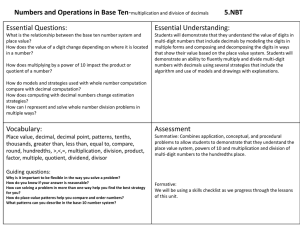
MIDWAY MATHEMATICS NIGHT Grades 5 & 6 Nov. 10, 2014 AG EN DA Dr. Brent Merritt Assistant Superintendent of Curriculum and Instruction • Welcome • Definition of Standards Debbie Perry (K-5) / Lisa Bray (6-12) District Mathematics Coordinators • Rationale for New Standards • Introduction to New Standards • Resources for New Standards • Questions and Answers Remarkable Teacher Teams • Learning Stations ST AN DA RD S Standards are statements that identify the knowledge and skills all students must achieve by the end of a grade level. Standards, or learning goals, become the guide that educators use to design curricula. Student mastery of standards is measured through state and local assessments, as well as in the classroom through informal and formal assessments, both formative and summative. ST AN Where does one find DA state RD curriculum S standards? TEA Website ST AN DA RD S The new mathematics standards are found on the Midway “Parents” page. Under: Academics and Testing Resources If you have questions during the presentation, please jot them down so that we can address them at QUESTION & ANSWER time! We will also be available for questions during learning stations. R A T I O N A L E State, National, International Test Results • Students can do calculations, but are not successful with application 2001…Adding It Up: Helping Children Learn Math Joint mathematics research on children grades K-8 • National Academy of Sciences • National Academy of Engineering • Institute of Medicine • National Research Council R A T I O N A L E 2001…Adding It Up: Helping Children Learn Math Research Implications: We need fewer, but deeper standards. • Readiness, supporting indicators • Process Standards • Curriculum focal points We should attend to all components of proficiency. • Conceptual Understanding • Procedural Fluency • Strategic Competence • Adaptive Reasoning • Productive Disposition R E S P O N S E 2010…Curriculum Focal Points (national) 2010…Texas Response to the Curriculum Focal Points 2012…New Texas Mathematics Standards 2013…Revised Texas Response to the Curriculum Focal Points 2014-2015 K-8 Implementation of new Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) FIFTH GRADE MATHEMATIC GRADE 5 CURRICULUM FOCAL POINTS Developing an understanding of and fluency with addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions and decimals. Understanding and generating expressions and equations to solve problems Representing and solving problems with perimeter, area, and volume Organizing, representing, and interpreting sets of data WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE? In some instances, there is little or no change to the actual student expectation. The difference, however, will be apparent in the knowledge and skills statement. PREVIOUS CURRENT 5(3)(B) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student adds, subtracts, multiplies, and divides to solve meaningful problems. 5(3)(B) Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods fro positive rational number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy. The student is expected to use multiplication to solve problems involving whole numbers (no more than three digits times two digits without technology). Similar The student is expected to multiply with fluency a threedigit number by a two-digit number using the standard algorithm. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE? In some cases, concepts were moved to fifth grade from other grade levels. Fifth received 3 standards from previous grade levels and 5 standards from subsequent grade levels. CURRENT STANDARDS FROM GRADE 3 The student is expected to use concrete models that approximate cubic units to determine the volume of a given container or other threedimensional geometric figures. FROM GRADE 7 The student is expected to represent multiplication and division situations involving fractions and decimals with models, including concrete objects, pictures, words, and numbers. Two extremes… WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE? In some standards, strategies or conceptual models are specified. These concepts and strategies build the conceptual foundation for procedural fluency with abstract representations such as the standard algorithm. EXAMPLES WITH CONCEPTUAL MODELS Multiplication 5(3)(D) Represent multiplication of decimals with products to hundredths using objects and pictorial models, including area models. Division 5(3)(F) Represent quotients of decimals to hundredths, up to 4-digit dividends and 2-digit whole number divisors, using objects and pictorial models, including area models. Both are “supporting.” ONE MORE EXAMPLE WITH CONCEPTUAL MODELS READINESS 5(3)(E) Solve for products of decimals to hundredths, including situations involving money, using strategies based on place value understandings, properties of operations, and the relationship to the multiplication of whole numbers. Fluency with decimal multiplication occurs in grade 6. Place Value Understandings 2.35 x 1.8 235 X 18 1880 2350 4230 2.35 is about 2 and 1.8 is about 2. 2 x 2 = 4…so the answer should be near 4. …so the decimal should go after the 4. This strategy also uses the relationship of multiplication of whole numbers… Properties of Operations 25.5 x 4 25 x 4 100 25.5 is the same thing as 25 + .5 .5 x 4 one half of 4 is 2 100 + 2 = 102 The distributive property works well when multiplying decimal numbers times whole numbers. Several Strategies Combined 6.34 x 1.5 6.34 one whole 6.34 + 3.17 one half of 6.34 9.51 I need one and a half of 6.34. One 6.34 is 6.34. A half of 6 is 3. A half of .34 is .17 Students may also use the standard algorithm. SIXTH GRADE MATHEMATIC GRADE 6 CURRICULUM FOCAL POINTS Using operations with integers and positive rational numbers to solve problems Understanding and applying ratios and rates and using equivalent rations to represent proportional relationships Using expressions and equations to represent relationships in a variety of contexts Understanding data representation A few other differences for both grades 5 & 6… Grades K-8 use the same process standards. In 2015-2016, grades 9-12 will implement these process standards. Personal financial literacy is included at K-8, and a new financial literacy course will be added to high school. RE Parent Page, Midway ISD website Drop-down menu under: parents > academic and SO testing resources > new mathematics standards UR resources CE TEA Website Far right column: “How do I…?” find the curriculum S standards (TEKS)? Pearson EnVision Online Platform https://www.pearsonrealize.com/ McGraw Hill Q U E S T I O N S ? Please know that your child is being led by excellent teachers who are doing an amazing job with a challenging transition! The gaps in skills and knowledge are huge this year throughout Texas. EXPLAIN YOUR THINKING… …a great question to ask your child! S T A T I O N S Spend a few minutes at the mathematics learning stations provided by Midway intermediate teachers. Plan to visit more than your child’s grade level to get a more complete picture of our new standards. Thank you so much for joining us tonight! We appreciate your interest in your child’s mathematical thinking. Email questions to: debbie.perry@midwayisd.org lisa.bray@midwayisd.org