The Industrial Revolution
advertisement
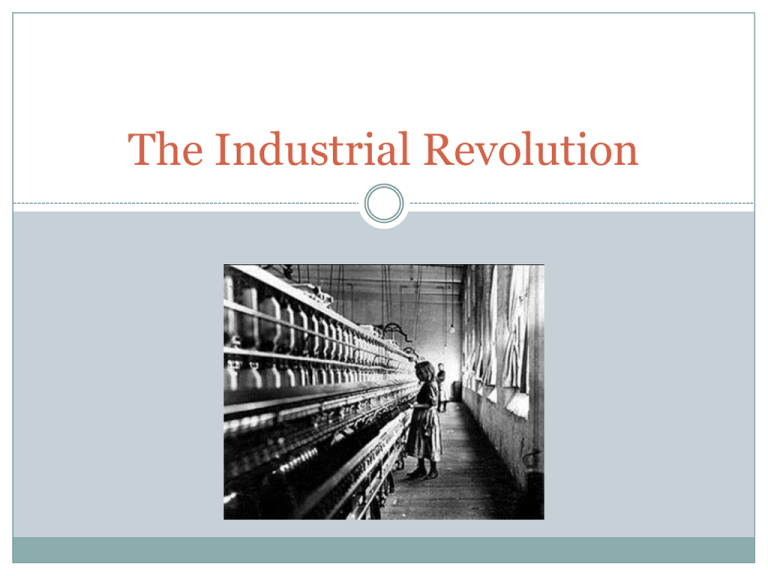
The Industrial Revolution Timeline of the Industrial Revolution 1848 – Marx’s James Watt’s Steam engine Communist Manifesto New tools begin Agricultural rev 1740 1760 1780 Car invented In Germany 1st railroad (in England) 1800 1820 1840 1860 1880 1845- Irish Potato Famine 1859 – Darwin’s Origin of Species 1900 1920 1st airplane The Agricultural Revolution Agricultural Revolution: a food was produced change in the way CHANGES Enclosed Fields – split up and organized farms Crop Rotation – more harvested per field CHANGES Better animal breeding – more food per animal New machinery – fewer workers needed RESULTS Much more food produced with fewer workers (Fewer farm jobs) Population grew Industrial Revolution: A change in the way things were made DOMESTIC SYSTEM Making products: At home By hand One person/family FACTORY SYSTEM Making products: In a factory By machine Many people What a Nation needs to have Industry Capital ($ for investment) Labor force (workers) Transportation system (materials and products) Raw materials (especially coal, iron, & cotton) Market (a place to sell products) Great Britain had ALL of these things! How Industrialization Effected Society URBANIZATION People moving into cities too quickly Overcrowding Unsafe living conditions How the Other Half Lives Working Conditions Child labor: Factory owners used kids as young as 5 because you could pay them less Long hours: 12-16 hour days Dangerous conditions: unsafe machinery & buildings passages http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7JPmVBxsTa8& feature=related Changing Social Roles Women: either run the household or work long hours for less pay than men Family: Working class families suffered; middle class families improved Children: Unhealthy, worked in unsafe conditions Transportation Greatly improved Canals and railroads built Steam engine increased speed Reactions to the Industrial Revolution Reactions to the Industrial Revolution Liberals Conservatives Want changes Want stability (no change) New republics Old monarchies Laissez-faire economy Nobles control economy Adam Smith Wrote The Wealth of Nations “Laissez-Faire” Government hands off of business Thomas Malthus Believed population was increasing faster than food supply Said solution was to let the poor starve Charles Darwin Wrote The Origin of Species Theory of Evolution Natural selection – survival of the fittest Social Darwinism Said the rich and powerful are the “fittest” Used to justify racism Used as an excuse to take advantage of working class, weak nations Socialism – economic system in which society owns business & everyone shares work and profits Utopian Socialism Marxist Socialism Everyone shares Started by Karl Marx everything Goal Peace and equality Workers of the world unite and violently overthrow the middle class (bourgeoisie) Goal end capitalism, create classless society The Arts Romanticism Late 1700s Emotion, not reason Ex. Beautiful landscapes Realism Early 1800s Show the world as it really was Ex. Dicken’s novels Impressionism Late 1800s Anti-realism Ex. Monet Attempts to Reform Society Attempts to Reform Society Sadler Report Education Report on Child labor Public schools created Led to child labor laws Get kids out of factories Suffrage Means the right to vote Extended to all men, then women Labor Legislation Safety conditions: less hours, safer machines Women and children: less hours, safer work Trade Unions: created to protect workers, used strikes and protests Global Migrations CAUSES Social Causes Population growth (cities too crowded) Poor living conditions Poor working situations Political Causes People were leaving monarchies and wanting democracy Improved Transportation Expanded the search for raw materials Search out new markets EXAMPLES of migration Europeans go to America for opportunity Irish come to America due to potato famine Essential Questions 1. How did the Agricultural Revolution support the Industrial Revolution? More food able to feed cities; less work on farms 2. How can the Industrial Revolution be considered the major turning point in history? Huge population increase; transportation inventions; new reforms 3. How did the abuses of the Industrial Revolution lead to the competing ideologies for social change? Ideologies compete to solve social problems Liberal vs. Conservative Capitalism vs. Socialism Essential Questions 4. Compare and Contrast the ideas of Adam Smith and Karl Marx? Capitalism – Adam Smith Definition Supporting Theory Role of the Government Who owns the means of production (factories & farms) Socialism – Karl Marx