Triangle Trade,
Mercantilism, and the
Impact of SLAVERY
(Unit 1, Segment 2 of 5)
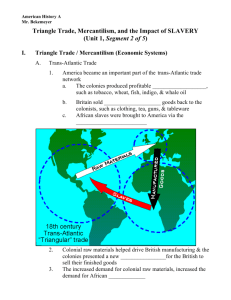
Trans-Atlantic Trade
■ America became an important part of the
trans-Atlantic trade network
– The colonies produced profitable raw
materials, such as tobacco, wheat, fish,
indigo, & whale oil
– Britain sold manufactured goods back to
the colonists, such as clothing, tea, guns,
& tableware
– African slaves were brought to America
via the Middle Passage
Trans-Atlantic Trade Patterns (Before 1660)
Colonial raw materials helped
drive British manufacturing
& the colonies presented a
new market for the British to
sell their finished goods
South
Middle
New
England
South
South
New
What were the topEngland
3
colonial exports?
Trans-Atlantic Trade
Patterns (Before
The increased
demand1660)
for
colonial raw materials,
increased the demand for
African slaves
This pattern of trade between Europe,
the colonies, and Africa became known as the
Triangular Trade
Trans-Atlantic
Trade
Patterns
When the British
colonies
were(Before
first 1660)
founded, there were few restrictions
on who the colonists could trade with
Mercantilism
■ By the 1650s, the British gov’t began to
embrace the economic policy of
mercantilism:
– The colonies exist to generate wealth
for the mother country
– Promoted a balance of trade (more
exports than imports)
– Meant that colonial trade must be
regulated & controlled
Mercantilism
Slavery in the “Southern”
Colonies
■ Slavery in the Southern colonies was far
more common than in the Northern
colonies:
–Cash-crop agriculture, like tobacco &
rice, required workers
–By 1660, fewer indentured servants
were coming to America
–80-90% of Southern slaves were field
workers, most on plantations
Slavery in the “Southern”
Colonies
■ Slave culture in the South:
–Slaves came from a variety of places
in West Africa & had a variety of
languages & cultures
–Music & dance were used to
maintain their African culture
–Families were common, but
marriage was not recognized
–Slave religion often blended African
rituals with Christianity
The Slave Population
■Slavery led to resistance:
–Runaway slaves were common
–Sabotaging of field tools &
intentionally slowing down the
work were common techniques
of slave resistance
Impact of the Slave Trade
Approx. 1500-1800 (?)
Slave Trade outlawed in Denmark (1803), G.B. (1807),
U.S. (1808), France (1814), Netherlands (1817), Spain
(1845)
Slavery itself?
The Numbers:
15th-16th Centuries – 2,000 Africans exported per
year
17th Century – 20,000 “…”
18th Century – 55,000 “…”
1780s – slave exports averaged 85,000 per year, some
times exceeding 100,00 per year
TOTAL NUMBER EXPORTED: 10 - 12 million
(2 + million died during transport--the middle
passage)
Impact of the Slave Trade
What impact did slave trade have upon African
society?
Not all of Africa was affected equally by the trade
The role of Geography: Kingdoms of Rwanda and Burundi
were safe because they were interior kingdoms
Some African societies benefited economically and
flourished (Ex.) Oyo, Asante, and the Dahomey built
powerful states with newly obtained firearms
Losses from the Slave trade:
Individual societies drastically impacted (Angola and
Senegal—near slave ports)
Distortion of gender ratios (2/3rds of slaves exported
were male)
Caused political turmoil among African societies
Q. How could this happen? How is
one able to justify enslaving
another, especially in such a
brutal fashion?
A. Dehumanization (see reading)
The Legacy of Slavery
Read ”Why is it important to study
the history of slavery? What is
its legacy?”
1. When finished write one
complete sentence that
summarizes James Horton’s
argument.
2. Do you agree or disagree with
James Horton? Explain why.
Slavery in the 21st Century
Read Newsweek article, “Slavery:
Human Bondage is Immoral and
Illegal…”
1. Compare slavery in the 21st Century
with what you know about the
Triangular trade.
Complete the Venn Diagram
Journal ?s
1. What if you were alive during the triangular trade?
2.
3.
4.
What if you knew then what you knew now?
Is ignorance bliss? You can no longer claim
ignorance about he modern slave trade. Will this
make any practical difference?
21st Century Slavery claims more lives than the
triangular trade. They say knowledge is power. Is
it? What power do you have now that you know
about this slave trade?
If racism is the legacy of the triangular trade, what
is will be the legacy of the 21st Century sex trade?