Storing Graphics - Shawlands Academy
advertisement

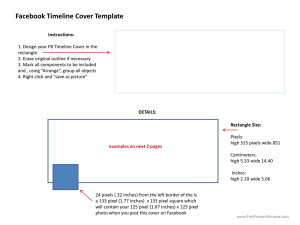
Computer Systems Nat 4/5 Data Representation Lesson 4: Storing Graphics 1. What does ASCII mean? 2. Describe how text is stored by a computer system 3. What is a control character? Int 2 Revision: 1. American Standard Code for Information Interchange 2. Each value has a unique ASCII value and this is stored in binary by the computer 3. A key that has an effect on screen Lesson Aims Pupils at National 5 level will be able to: Describe how a computer system stores a black and white bitmap image Calculate the storage requirements of a black and white bitmap image. Explain the difference between a vector and bitmap image Explain the terms pixel, dpi and resolution Nat 4/5 Lets look at a bitmap picture The whole image is made up of individual pixels. Pixel stands for picture element Nat 4/5 Bitmap Images A bitmap image stores each individual pixel. First you need to understand black and white images. These are constructed as follows: 0 is stored for a white pixel, 1 is stored for a black pixel Each black and white pixel takes up 1 bit of storage Nat 4/5 Resolution Resolution is the term given to the amount of pixels that the image is made of Also used for the amount of pixels displayed on the screen Higher resolution = clearer and more detailed picture Pixel Pattern using 8x8 grid Pixel Pattern using 16x16 grid Nat 4/5 Calculating Storage Requirements You are often required to calculate the storage requirements of a black and white bitmap image The steps are as follows: 1. Amount of pixels wide x Amount of pixels high 2. This answer is in bits You then convert the number into appropriate units (Kilobytes/Megabytes) Divide until its in an appropriate unit. Nat 4/5 Storage Space Example A black and white image is 800 pixels by 900 pixels. Calculate the storage requirements and express the answer in appropriate units. Step 1: Length x Breadth 800 * 900 = 720,000 bits Step 2: Convert into appropriate units 720,000/8 = 90,000 bytes 90,000 bytes /1024 = 87.89 Kb If you already know the amount of pixels in the image then use this method Nat 4/5 Alternate Storage Space Example Sometimes you will be given the size of the image and the resolution of the image. One way in which this can be measured is dpi Dots per inch is the amount of pixels in an inch. A black and white image is 4 inches by 6 inches with a resolution of 300dpi. Step (4*300) * (6*300) = 2,160,000 bits Step 1: (Length x dpi) x (Breadth x dpi) 2: Convert into appropriate units 2,160,000/8 = 270,000 bytes 270,000 bytes /1024 = 263.67 Kb If you are not given the amount of pixels in the image then use this method Nat 4/5 Vector Graphics The image below is an example of a vector image. For example attributes for the eyes(ellipses) may be Centre X/Y-co-ordinates Fill Colour Border Style Border Colour etc… Nat 4/5 Summary Bitmap images store every single pixel 1bit for each pixel 0 for white pixel, 1 for black pixel Resolution is the amount of pixels that make up an image Higher resolution means you have a more detailed image.