Cyber Ecosystem & Data Security
advertisement

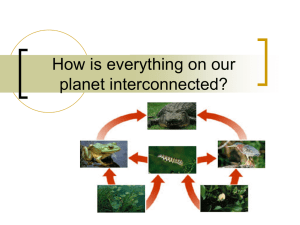
Cyber Ecosystem & Data Security Subhro Kar CSCE 824, Spring 2013 University of South Carolina, Columbia S What is an Ecosystem? S Definition S Functional Units S Relationships S Balance S Comparison with Cyber Space Biological Ecosystems S The system is closely related S The balance is always maintained S Relationships are well defined S Monitored by nature Source: http://www.tutorvista.com/content/biology/biology-iv/ecosystem/food-web.php Evolution of the Cyber Ecosystem S A typical Network Diagram Source: http://www.broadband.gov/plan/16-public-safety/ What is a Cyber Ecosystem? S Entities in network are not merely considered in isolation S Each member has a specific goal S Each member is related to every other member in one way or the other S Processes are important S Anticipate and prevent attacks S Limit the speed of attacks across devices S Recover to a trusted state What is a Cyber Ecosystem? S Devices has a level of built in Security S Automated responses S Immunity Malware Ecosystem S Each member in the ecosystem has a specific purpose S Each of the members respond to the behaviour of other members S Automated upto an extent S Monitoring the whole process Building Blocks S Automated Course of Actions S Pro-active responses S Speed of response matches the speed of attacks S Being able to decide on solutions based on historical data S Sharing of Information at different levels from local to global S Rapid learning procedures S Communications guided by policy rather than constraints S High levels of collaboration and interoperability S Authentication Types of Attacks S Brute force attacks S Malware S Hacking attempts S Social Engineering S Insiders S Physical loss and theft Monitoring S Monitoring forms one of the foundations of the Cyber Ecosystem S Informs about anomalies so that proper countermeasures can be taken S Does not always happen at the system level contrary to standard device monitoring Business Process Monitoring S Holy grail of monitoring systems S Highest level of abstraction S Generally related to long running transactions S Can serve as a ready metric for overall success of the system S Can only detect problems post their occurrences S Uses complex business logic S Goal: To maintain business continuity Functional Monitoring S Lower level than Business Process Monitoring S Granularity limited to a single application or node in a distributed architecture S Goal: To assess the availability as well as performance of a system S Generally done by bots running scripts on individual systems S Incapable of deciding on countermeasures Technical Monitoring S Monitoring as a typical system administrator understands S Lowest level of monitoring and responsible for individual pieces of software S Subsystems are considered in isolation and has nothing to do with their contribution to the system S Ideal place for designing incident response since the monitoring system is aware of how to modify behaviour of individual subsystems. Intelligence and Experience Gathering S Currently lacking in existing systems S Could be based on statistical models and data modeling S Should become more accurate based on experience S Should be able to heuristically identify attacks S Could put up some defence against 0 day attacks Okay!! I got attacked… Now what??!! S Incident Response S Targets for restoring the balance of the ecosystem just like its biological brother S Either filter it out or sacrifice parts of the system to facilitate containment S Not an isolated process. There are lots of loopbacks to the monitoring S Dynamically adjusts itself to adjust response based on current monitoring data How does everything fit together? S It is a continuous process S Dynamic S Historical data is important S Business continuity important S The goal of the attacker might not be the epicenter of the attack Source: http://blogs.csoonline.com/business_continuity_event_planning_the_incident_response_team Incident Response Implementation S Firewalls S Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems S Log servers S Configuration Management Servers S Offline resources like Debuggers Desired Cyber Ecosystem Capabilities S Automated Defense Identification, Selection, and Assessment Authentication S Interoperability S Machine Learning and Evolution S Security Built in S Business Rules-Based Behavior Monitoring S General Awareness and Education Desired Cyber Ecosystem Capabilities S Moving Target S Privacy S Risk Based Data Management S Situation Awareness S Tailored Trustworthy spaces Where we stand… S The ecosystem is far from automated. We have a long way to go S Triangulating automated decisions are complicated. Most of the processes are manual and will probably remain so in the near future S The weakest link is generally the End Users S Insiders can cause havocs S It is always about the financial incentive of being able to build a proper ecosystem. References S Developing a healthy cyber ecosystem, http://www.mitre.org/news/digest/homeland_security/10_11/cyber_ecosystem.html S Enabling Distributed Security in Cyberspace, http://www.dhs.gov/xlibrary/assets/nppd-cyber-ecosystem-white-paper-03-23-2011.pdf S Cybersecurity Ecosystem – The Future? http://www.nextgov.com/cybersecurity/cybersecurity-report/2011/03/cybersecurityecosystem-the-future/54390/ S Enabling Distributed Security in Cyberspace, http://blogs.msstate.edu/ored/Cyber%20Ecosystem%20I3P%20Presentation%2016%2 0April%202012%20MSU%20ras.ppt Questions?? Source: http://what-if.xkcd.com