Backward Design April 2
advertisement

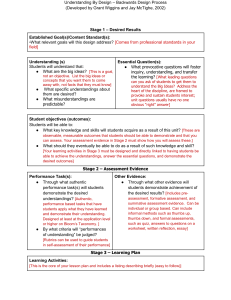
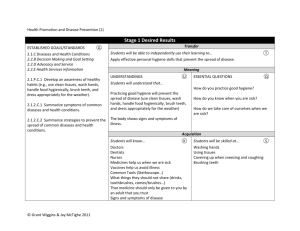
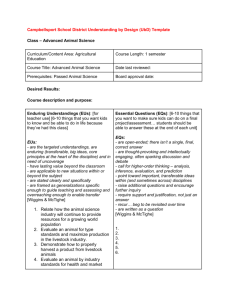
The mere imparting of information is not education. Above all things, the effort must result in helping a person think and do for himself/herself. Carter G. Woodson What is the primary goal in my course? • Cover the basic material • Impart new discipline knowledge • Facilitate student learning • Ensure student success • Other Traditional course design… • Content coverage • Activity centered • Not always clear connection to desired learning outcomes or larger understanding Traditional course design Choose text Identify chapters to be covered Develop lectures or labs Create exams Understanding by Design • Wiggins and McTighe • Represents BIG ideas with value beyond the classroom • Requires “uncoverage” • “Backward Design” - key • Engages students Understanding by Design – Why Bother? • Focus on what you want students to achieve • Move away from “coverage” • Improve student and faculty engagement • Connect course outcomes, assessments, and activities • Facilitates mapping of course outcomes and student assessment to program, department, and institution – level goals Understanding by Design by Grant Wiggins Two Big Ideas of Understanding by Design Jay McTighe Backward Design Identify Desired Results Determine Acceptable Evidence Plan Learning Experiences Stage 1: Identify the Desired Results • Outcomes Program, course, unit Learning Outcomes What will my students know? What will my students be able to do? What will my students be to understand/appreciate? Identifying Key Ideas Big-picture knowledge, allows One to find and retrieve information Prerequisites for success Students will know long after the class ends Something to think about…. Course Outcomes Concepts and issues - What must the student understand to demonstrate the intended outcome? Process skills -What skills must the student master to demonstrated the intended outcomes? Key Ideas…. Choose a course. Identify what is… worth being familiar with important to know and do enduring understandings Stage 1: Identify the desired results (based on Understanding by Design by Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe) Learning Outcomes • What relevant goals (eg. course outcomes) will this design address? Understandings: Q Essential Questions: Students will understand that …. • What are the big ideas? • What specific understandings about them are desired? • What misunderstandings are predictable? • Students will know… A • • What key knowledge and skills will the student acquire as a result of the this unit? What should they eventually be able to do as a result of such knowledge and skills? What provocative question will foster inquiry, understanding, and transfer of learning Students will be able to… Stage 2: Determine Acceptable Evidence How will you know if students have achieved the desired results and met the expectations? What will you accept as evidence of student understanding and proficiency? What is evidence of in-depth understanding as opposed to superficial or naïve understanding? What kinds of assessment evidence will anchor units and guide instruction? To what extent do the assessments provide fair, valid, reliable, and sufficient measured of the desired results? Fair allow for students of both genders and all backgrounds to do equally well. Valid an indication of how well an assessment actually measures what it is supposed to measure Reliable an indication of the consistency of scores across evaluators or over time projects formative essay or paper Plan a range of assessment give students opportunities to demonstrate that understanding balance use performance tasks portfolio observations summative criterion-based webpage quizzes and tests student self-assessment must support students in developing understanding authentic learning tasks Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Tasks: • Through what authentic performance tasks will students demonstrate the desired understandings? • By what criteria will performance of understanding be judged Other Evidence: • Through what other evidence (eg. quizzes, tests, observations, reading response) will students demonstrate achievement of the desired results? • How will students reflect upon and self-assess their learning? Criteria Rubrics 1 Rubric 2 Co-Constructing Criteria What makes a “good” oral presentation? List one attribute per sticky note. When complete put sticky notes on designated chart paper. • With your partners, group attributes together. • Title each category. • Share your categories and their content with the large group. Stage 3: Plan Learning Experiences “ Beyond learning about a subject, students will need lessons that enable them to experience directly the inquiries, arguments, applications, and points of view underneath the facts and opinions they learn if they are to understand them.” (Source: Understanding Design by Grant Wiggins & Jay McTighe, p. 99) The learning experience requires students to: “Theorize, interpret, use, or see in perspective what they are asked to learn…(or) they will not likely understand it or grasp that their job is more than recall.” Source: Understanding Design by Grant Wiggins & Jay McTighe, p. 99 ACTIVE LEARNING Video Rich Learning Experiences • Role-play • Project based • Problem-based • Practicums activities • Case studies • Simulations • Dramatizations • Service learning • Situational observations Authentic Learning Authenthtic Learning Assessment Backward Design Identify Desired Results Determine Acceptable Evidence Plan Learning Experiences What are the advantages of Understanding By Design approach to program, course, and unit development? What are the challenges of implementing an Understanding By Design approach? Additional thoughts, comments…. Alignment “Education is not filling a pail, but the lighting of a fire.” -William Butler Yeats