The Effect of Concentration and Surface Volume Ratio on the Rate
advertisement
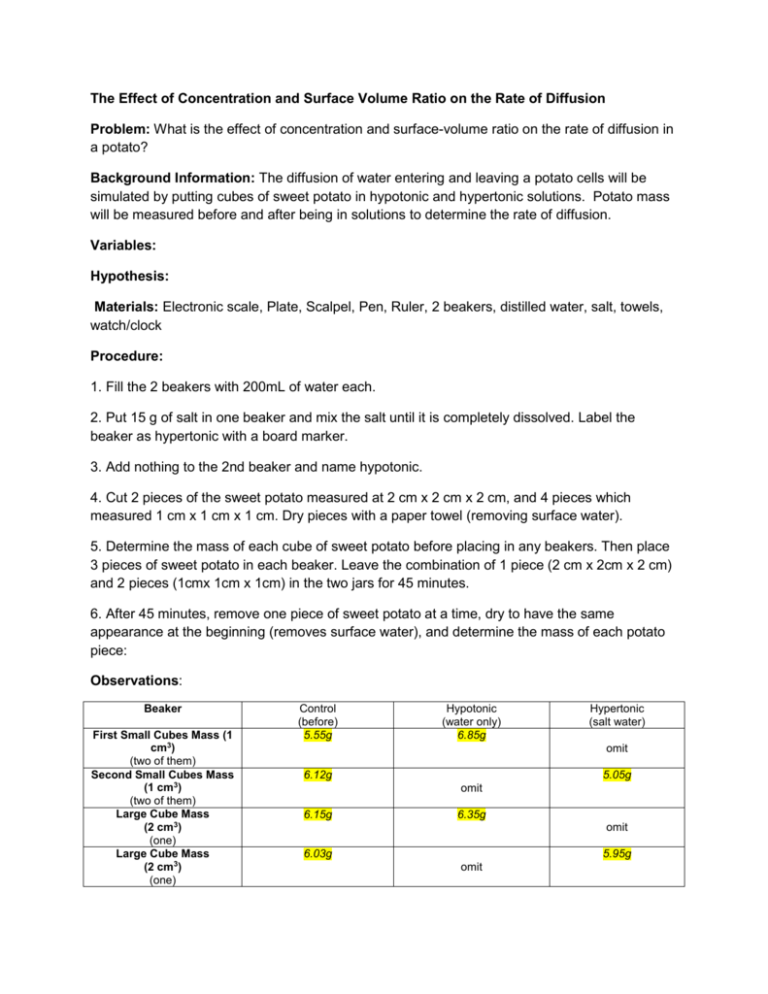
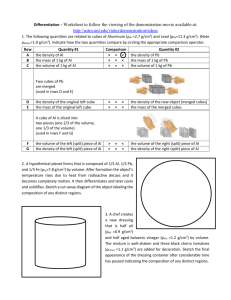
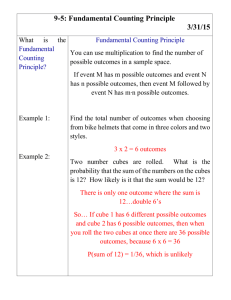
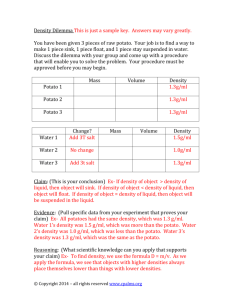
The Effect of Concentration and Surface Volume Ratio on the Rate of Diffusion Problem: What is the effect of concentration and surface-volume ratio on the rate of diffusion in a potato? Background Information: The diffusion of water entering and leaving a potato cells will be simulated by putting cubes of sweet potato in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. Potato mass will be measured before and after being in solutions to determine the rate of diffusion. Variables: Hypothesis: Materials: Electronic scale, Plate, Scalpel, Pen, Ruler, 2 beakers, distilled water, salt, towels, watch/clock Procedure: 1. Fill the 2 beakers with 200mL of water each. 2. Put 15 g of salt in one beaker and mix the salt until it is completely dissolved. Label the beaker as hypertonic with a board marker. 3. Add nothing to the 2nd beaker and name hypotonic. 4. Cut 2 pieces of the sweet potato measured at 2 cm x 2 cm x 2 cm, and 4 pieces which measured 1 cm x 1 cm x 1 cm. Dry pieces with a paper towel (removing surface water). 5. Determine the mass of each cube of sweet potato before placing in any beakers. Then place 3 pieces of sweet potato in each beaker. Leave the combination of 1 piece (2 cm x 2cm x 2 cm) and 2 pieces (1cmx 1cm x 1cm) in the two jars for 45 minutes. 6. After 45 minutes, remove one piece of sweet potato at a time, dry to have the same appearance at the beginning (removes surface water), and determine the mass of each potato piece: Observations: Beaker First Small Cubes Mass (1 cm3) (two of them) Second Small Cubes Mass (1 cm3) (two of them) Large Cube Mass (2 cm3) (one) Large Cube Mass (2 cm3) (one) Control (before) 5.55g Hypotonic (water only) 6.85g Hypertonic (salt water) omit 6.12g 5.05g omit 6.15g 6.35g omit 6.03g 5.95g omit Analysis: 1. Calculate the % increase or decrease of the mass of potatoes from the data observed in the table. Ensure that the calculations are provided for each cube type in both the hypotonic and hypertonic solution. % mass difference = cube after saturation ÷ cube before saturation (control) x 100 2. Calculate and compare the surface area to volume ratio for the 2cm3 and 1 cm3 cubes. Explain how higher surface area to volume ratio effected the rate of diffusion. 3. What do structures like roots in plants or the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, that have more surface area to volume ratios, tell you about their functions? Conclusion: