Tensions 1917-1944
advertisement

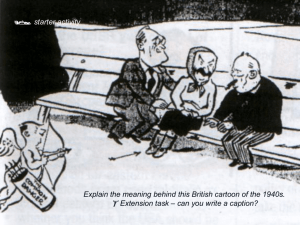
Starter activity: RECAP Complete answers to the questions on the sheet in front of you. This is to recap on important ideas we discussed in the previous lesson: 1) Explain Communism in your own words 2) Explain Capitalism in your own words 3) Explain what you think the message of the Bolshevik (Russian) cartoon is fro the 1920’s and what you think Western governments may have thought of this source Why did tension increase between the USSR and the West between 1917 and 1944? Lesson title: UNIT 1: THE SEEDS OF THE CONFLICT Objectives: 1. Recall your understanding of the systems of Capitalism and Communism 2. Explain the tensions which existed between the USA and USSR in the period 1917-44 3. Explain how these tensions were affected by the Second World War 4. Analyse the role of key individuals in relations between superpowers at the end of the Second World War Chamberlain meets Hitler, 1938 WWI soldiers The Russian Tsar (King) being murdered by Bolsheviks Cavalry officer, White Army in Russian Civil War Study the pictures. They all hint at reasons why tensions between the West and the USSR grew in this period. Key points before we start In 1917 there was a Revolution in Russia in which the Bolshevik Party led by Lenin seized power and replaced the Tsar (King) They were believers in Communism The USSR stands for United, Soviet, Soviet Republic (1923) What differences were there in ideology between Capitalism and Communism from 1917? Use pages 2-4 Communism Capitalism E.G Comintern and Third International Wilsonian Liberalism IDEOLOGY (2-3) ECONONOMIC (3-4) POLITICAL INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS Complete the grid to summarise the main differences between the two. Look carefully at international relations..... Wilson’s speech to Congress, 1917 Which of his principles are addressed in the speech? How did he think these would lead to greater world? What does this indicate about the seriousness of Wilson’s desires to uphold these values? How could Wilson’s principles be seen as a criticism of European countries at this time? Mini summary... Wilson’s ideas were not new – based on traditional US values But it was the fact that he was expressing them as a world vision – America had a moral duty to spread it’s values – marked clear shift away from traditional policy But short-term effect – rejected by Congress and US retreated to Isolationism His ideas would be picked up later Lenin’s concept of WORLD REVOLUTION and Wilson’s LIBERALISM represented two widely differing models for the conduct of International Relations. SEEDS of future CONFLICT lay in this hostility When circumstances were created which let these two competing views flourish, the Cold War was likely to follow What tensions existed between the USSR and Capitalist world in the 1920s? Your teacher will give you some cards relating to the potential causes of tension between the East and West. First code each cause of tension as either: ECONOMIC/ POLITICAL (National Interests) / IDEOLOGICAL/ PERSONAL Arrange them as a ‘diamond nine’ with the most significant reason at the top. Pause.... Did the fact that the USSR was Communist make a difference to relations between it and the West in this period? What other factors made relations between them hostile? What were the strains in the ‘Grand Alliance?’ (impact of WW2 on relations) Why did the Soviet Union become allies by 1941? What did they need from each other? Your task: The strains of the Grand Alliance Read p.8-10 and complete the table below. Then code your findings into: National Interest/ Personality/ Ideology/ Circumstances/ Factors which strengthened Factors which weakened the the Grand Alliance Grand Alliance Find out more on the Big Three You will be given 1, 2 or 3 You need to read and highlight according to the sheet then meet your other numbers to fill in your character profile sheet Plenary: Had relations between superpowers broken down by the end of 1944? YES NO Homework 1. Watch episode 1 ‘Comrades’ of Cold War series and make notes on increasing tensions – how and why? 2. Read extract from Isacc and make summary notes on development of tensions by 1944 using the question sheet to prompt your reading 3. Read chapter 2 from textbook and answer all questions from your course handbook.