Economic Systems - Reeths
advertisement

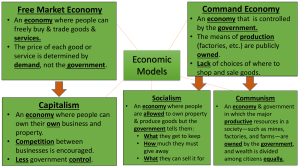
Economic Systems Capitalism Socialism Communism Definition A system for producing, selling, and distributing goods and services. Capitalism (Free Market) Economic system in which private individuals or groups use private capital (money) and labor to produce goods and services. Capitalism Features People control economic production and output. People decide what, where, and how to produce what consumers buy. Owners decide how much to pay workers and use profits. Prices are determined by supply and demand and competition. The role of government is to support businesses with minimal government involvement. Higher education and health care is paid for by the consumer. Effects of Capitalism People can own land and business. Unequal distribution of wealth Low unemployment rate: 3%-5%. Favors a democratic or free government. Creates the wealthiest nations. Creates economic classes: poor, working poor, middle class, and rich. Examples USA South Africa Japan Mexico Socialism An economic system in which the government owns most basic industries, such as transportation, communication, and banking: non basic industries are privately owned such as restaurants, hair salons, and factories. Socialism Characteristics/Basic Industries Basic industries are essential for a nation to function. Ex: transportation, communication Basic industries are ran for the good of society, not for profit. The government decides how much to pay for goods and how much to pay workers. Profits made from basic industry allow for nations to pay for health care and higher education. Socialism Characteristics/Non Basic Industries Non basic industries are nice, but not necessary. Ex: Internet Business Non basic industries and services follow a capitalist model. Non basic industries are privately owned and consumers decide what products to buy. Effects of Socialism Lessens gap between the poor and rich Gives citizens equal availability to healthcare and education. Welfare and insurance for unemployed are distributed. People live comfortable lives, but have less than those living in capitalistic countries. Examples of Socialist Countries Socialism is the ½ point between communism and capitalism. Spain, Portugal, Sweden, and Italy Communism Economic system in which the government owns all property such as farms and factories, for the benefit of the citizens. Communism Characteristics The government usually controls all aspects of citizens’ lives. The government controls the price of goods and services how much is produced, and how much workers are paid. People do not own businesses or factories, all means of production are owned by the government. Effects of Communism The governments of communist countries are usually violent in nature and do not support freedom. Communism is aimed to create a classless society. Unemployment and poverty are common. People are not able to make their own economic decisions or to earn their own fortune. The USA fought the Cold War to stop the spread of communism. Examples of Communism Cuba China North Korea