Introduction to the cold war - snshistory

Objectives:
1) Identify the structure and demands of the course
2)
3)
Explore the key characteristics of the Cold War
Explain these characteristics
INTRODUCTION TO THE COLD
WAR
Your Guide to A2 History:
This is your guide
It is £3 for the copying
Please put in your folder
Your target sheet goes in your exercise book where assessed work will be completed
It is a reference point for you and includes useful revision activities
Be disciplined
Keep well-organised notes
Be prepared to do much of the reading for lessons outside the class
As you move ever close to undergraduate work, be prepared to go that extra mile and use resources in the department, school or local public libraries
Look out for relevant news items or documentaries that discuss the Cold War and its aftermath Use the new departmental website www.snshistory.wordpress.com
to download class resources and sample students’ work
Visit museums (Imperial War Museum, which has an excellent Cold War section, the Science Museum – good on the Space Race)
Meet homework deadlines – students who regularly fail to do so will be put on subject report
Keep your folders organised!
It will help you to keep the following documents in the front of your folders: a glossary of keywords that you come across during the course.
and also….
a ‘ who’s who ’ of key figures a map of key events of the Cold War a timeline of key events
What will I be studying?
Origins of Cold War tensions
Emergence of Cold War, e.g.
The Berlin Blockade
The ‘Thaw’ & ‘Peaceful Co-existence’
The nuclear arms race & Cuba
The space race
Role of China
Détente
End of Cold War
Historiography of Cold War
How will I be examined?
A2 = 50% of total marks
Unit 3: ‘A World Divided: Superpower Relations,
1944-90’
Unit 4: Coursework
Written exam: 2 hours 2 nd June 2014
Answer ONE question from Section A (30 marks), and ONE from Section B (40 marks) - choice of 2 questions in both sections
Section A – discuss an historical issue
Section B – use source material & knowledge to discuss an historical event
Units Maxim um
A
3 100 80
B
70
C D
60 50
E
40
Grade boundaries
Your task
Warm up: Your teacher will give you some key facts associated with the Cold War. In partners match up the correct person with the interesting fact....
People/ answers
Franklin D Roosevelt
Winston Churchill
Berlin
U-2
The Iron Lady
The first living creature in space
Fidel Castro
Sputnik – the first artificial satellite
Duck and cover
Term used to describe improved relations between the USA and China in the 1970s through the medium of sport
One of the main cross-over points in the wall separating East and West Berlin
Korean War (1950-3)
Threatening to use all military means to resolve a diplomatic crisis
Joseph Stalin
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
Harry S Truman
Russia, Poland, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Bulgaria, Albania, Romania
Politburo
Ronald Reagan
How did the Cold War develop?
Watch this 4 minute clip to gain a very brief summary of the first 20 years of the Cold War https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PHwIkOv6
Rc4
Think about:
Why?
Features of the Cold War – e.g key turning points
Individuals
Your task What were the characteristics of the Cold War?
Read about the famous Kitchen debate of 1959 .
Highlight in red any evidence of tensions or differences.
What were the key characteristics of the Cold War?
Conflict of ideologies
Communism v. capitalism
Capitalism : production of goods and distribution is dependent on private capital with a view to making profit; capitalist economies run by individuals rather than by state
Communism : hostile to capitalism, which exploits workers; ideally all property, businesses
& industry should be state-owned, ‘each gives according to their ability to those according to their need’
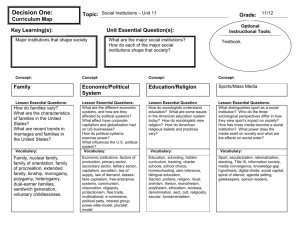
Your task: Finding out about the key characteristics of the Cold War
Create a spider diagram identifying the key characteristics of Cold War. Break into groups of 2 and share the research. Use Edwards, p.3-7 and any other sources of information you might have. Look for these areas:
Ideologies
Economics
Military tensions
Treaties
Propaganda
Espionage
Arms race
Space race
Sport & culture
Conflict of economic power
Marshall Plan (1947) – provision of fuel, raw materials, goods, loans, food, machinery advisers
US exploited it financial power to export Western values – dollar imperialism
1948-52, US Congress voted nearly
$13bn economic aid to Europe
Trade war with Communist countries, e.g. Cuba
Military power
Korean War (1950-3), Vietnam (early 1960s -
1973)
US military build-up, e.g. 1960 2.4 US military personnel around world; 1959, 1,500 military bases in 31 countries
Domino theory
Treaties
NATO (1949) – North Atlantic Treaty
Organisation
SEATO (1954)– South East Asia Treaty
Organisation
Warsaw Pact (1955)– military defensive pact amongst eastern European nations
COMECON (1949)– Council for Mutual
Economic Assistance
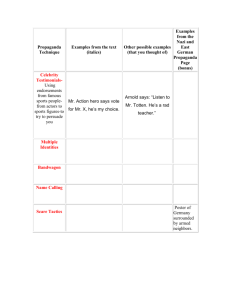
Propaganda
European Recovery Program – propaganda as much as economic exercise
Benefits of Marshall Plan advertised
Italy became a focus of economic rebuilding after WWII - ‘Operation Bambi’ used minstrels, puppet shows and film
Click here for an example of US
Cold War propaganda
Espionage
CIA (1947) – founded to co-ordinate information gathering on USSR and Allies.
Activities included:
Support for anti-Communist political leaders, e.g. Christian Democrats, 1948 elections
‘Regime change’, e.g. overthrow of left-wing govt in Iran & Guatemala, Operation
Executive Action (1961), collaborated with
Mafia to overthrow Fidel Castro
Arms Race
1945 US tested and detonated 1 st atomic bomb
1952 tested 1 st H-bomb (2,500x more powerful)
1953, USSR produced H-bomb
1961 enough nuclear weapons to destroy world
1967 China produced H-bomb
1981, USA 8000 ICBMs, USSR 7,000
MAD – Mutually Assured Destruction
Space race
1957, launch of Sputnik
1957, 1 st space animal in
1961, Yuri Gagarin 1 st man in space
21 July 1969 Apollo 11 mission successfully land 1 st man on moon
Laika, 1 st dog in space
Sport
1980, ‘Miracle on Ice’ – US hockey teams defeats USSR ‘giants’
1980 Moscow Olympics, 1984 LA Olympics – boycotted by US & USSR
Ballet – defections to West, e.g. Nureyev
World Chess Championships– Bobby Fisher v.
Boris Spassky (1972)
Plenary
Name one characteristic of Cold War from the following categories:
Ideologies
Economics
Military tensions
Treaties
Propaganda
Espionage
Arms race
Space race
Sport & culture
Homework: For tomorrow.
Complete your mind map.
Imagine you were asked to explain what Cold
War was to a GCSE student. Write a 100 word summary of the characteristics of Cold War at the bottom or on the reverse of your mind map.
Find a Cold War cartoon which relates to an aspect of one of the characteristics