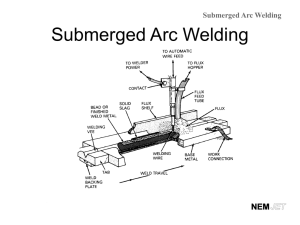
Leaving Cert Engineering
advertisement

Leaving Cert Engineering Damian Keenan 2013 Instructions • Answer Section A and Section B of Question 1 and FOUR other questions. • All answers must be written in ink on the answer book supplied. • Diagrams should be drawn in pencil. • Squared paper is supplied for graphs, as required. • Please label and number carefully each question attempted. Q1 – You must answer Section a & section B • Section A • Given 13 short questions – answer 10 • Read them all and pick the ten you know, • Section B • Basic principles of operation and applications of the Stirling engine from its invention in 1816 to its modern uses.” Q2 Material Testing • 2012 – • compare impact tests, • Tensile tests on different materials- explain brittleness-elastic and plastic states • NDT, aircraft internal & external flaws – 2 types for each, • Name one for internal faults in welded joints, Q2 Material Testing 2011 • Metal fatigue & metal creep • Compare Hardness testers – method of measurement & test material • Stress/ strain graph – find young's & proof 0.1% stress • NDT – Explain why NDT, Describe a test using ultrasonic Q2 Material Testing • 2010 • Why test metals till they break – id & describe impact tester – how it works and why • Load/extension graph – find UTS 0.1% proof stress • NDT – Describe Eddy Current testing – x ray testing, Q2 Material Testing • 2009 • Hardness tester with diamond – identify & describe features • Stress/strain graph – id points on graph (elastic, plastic)- describe shape of specimen at middle and end • NDT – why use in cast bike engines, describe a test used on surface flaws in aluminium, Q2 Material Testing • 2008 • Micoscopic vrs macroscopic examination of metals – explain Creep, 2 factors that influence creep – compare indentors in brinnel & vickers • Stress strain graph, find youngs & 0.1% proof stress • Id NDT to determine surface & internal flaws on casting – describe test to locate internal defect Q2 Material Testing • 2006 • Compare Brinell & Vickers, explain elastic limit, id 2 factors to prevent early fatigue, • Load/extension graph – find tensile strength & youngs • NDT – why used in industry, describe test to detect internal flaws. Q3 heat treatment & iron carbon • • • • 2012 Describe – Annealing, normalising, carburising Describe the flame hardening shown & use, Name different regions of graph – describe eutectic and eutectoid Q3 Heat treatment & Iron Carbon • 2011 • Describe Induction hardening - distinguish grey & white cast iron – explain stress relieving in metals • Name different regions of graph – outline cooling 0.4% steel from 900 degrees c • Identify pyrometer and state function – describe how it works using the pictures, Q3 heat treatment & iron carbon • 2010 • Compare Soaking & water cooling – distinguish optical & thermo electric pyrometer – describe normalising • Name different regions of graph – describe martinsite • Describe heat treatment for slideways – describe this process Q3 heat treatment & iron carbon • 2009 • Id 3 quenching media used in heat treatments- discuss safety in case hardening, discuss induction hardening, what is pearlite, • Id heat treatment processes as temp zones A,B,C,- explain Allotropy, • Id pyrometer (thermo electric) – how does it work, Q3 heat treatment & iron carbon • 2008 • Eutectic vrs eutectoid point, one method measuring furnace temp, compare microstructures martensite & ferrite, explain recrystallisation in heat treatment • Name different regions of graph – outline cooling 0.4% steel from 900 degrees c • Describe pack carburising, outline flame hardening, Q3 heat treatment & iron carbon • 2007 • 2 methods measuring furnace temperature, describe allotropy, explain soaking in annealing, difference between grey and white cast iron, • Name different regions of graph – describe eutectic and eutectoid (2012) • Name 3 quenching media in terms of speed of cooling, outline induction hardening, Q3 Heat treatment & Iron Carbon • 2006 • Select two temp zones on the dwg & explain the treatment processes they represent, • Compare – ferrite & martensite, upper and lower critical temp, stainless steel & high speed steel, eutectic & eutectoid point • Optical pyrometer – id & state its function and how it works, Q5 Welding • 2012 • Describe S.A.W. & where used • Describe Colour coding oxyacetylene equip – 3 safety precautions preparation equip & materials • Describe multi run welds • Describe auto welding of car panels, • Describe main features of TIG & MMA Q5 Welding • 2011 • Describe MMA – identify & state function of the MMA circuit, • How minimise electrical hazards in MMA – 3 ways to prevent atmospheric contamination – why TIG for Aluminium – Function of Dissolved acetylene, • Describe Seam welding & SAW Q5 Welding • 2010 • Name TIG & MIG – name application for each and how they work, • State (oxyacetylene equip) – 3 safety precautions integrated into the equip – 2 functions of slag in MMA – Use for SAW, Describe resistance welding • Describe Electro-slag welding & oxyacetylene • Or outline why robots for spray painting – testing pipes or placing electronic parts, Q5 Welding • 2009 • Id Seam & spot welding, describe how they work • Distinguish MIG & TIG - state 2 functions of electrode coating in MMA – 2 factors when installing a welding station in school – describe multi run welds, • Describe transformer circuit in MMA, S.A.W. • Or advantage using air to power robots for assembly – benefits using robotic control for hazardous environments Q5 Welding • 2008 • Describe TIG using name, how it works, uses • Oxyacetylene – 2 safety features in the equip, explain two parts of the gauges, whats dissolved acetylene, difference oxydising & carburising flames • Describe main features of spot welding & MIG • Or 2 industrial uses where robots are used, advantages of stepper motors in robots Q5 Welding • 2007 • SAW – Describe how it works and where used • Redraw incomplete transformer circuit, describe function of a & b, advantages multi run welds, 3 safety precautions preparing materials for welding • Describe seam welding & electro slag welding • Or 2 safety factors setting up robotic welding facility, Q5 Welding • 2006 • MIG welding, name it , how it works, where its used, • MMA – 2 functions of electrode, 2 important functions of the slag, explain bridge rectifier, know 3 safety hazards and remedy for each, • Describe spot welding & TIG • Or benefits robots in car assembly, what is ‘working envelope’ Q6 Polymers • 2012 • Describe compression moulding, polymer used, and a component • Distinguish thermo & thermosetting using polymerisation process, bonding, structure, properties • Explain – elastomer, catalyst, blow moulding, G.R.P. Laminate Q6 Polymers • 2011 • Describe Addition polymerisation, name a material, • Describe extrusion, state polymer, name component • Explain – Plasticiser, Filler, Lubricant, stabiliser, pigment Q6 Polymers • 2010 • Identify calarindering and describe how it works – name one part produced • Distinguish thermo & thermosetting using bonding, structure, properties (same as 2012) • Explain – stabiliser, glass transition temp, condensation polymerisation, elastomer, elastic memory in perspex Q6 Polymers • 2009 • Id Calandering & extrusion, id one component, describe how they work, • Describe polymerisation for polyethylene • Explain, Blow moulding, Elastomer, Catalyst, Co –polymer, Thermosetting plastic, Q6 Polymers • 2008 • Extrusion–id function of 3 part, id a component • Distinguish thermo & thermosetting using polymerisation process, bonding, properties (2012) • Explain Transfer moulding, GRP, Cross linking, Laminate, Polymer filled materials Q6 Polymers • 2007 • Id & describe how transfer moulding works , name 1 component, • State function of pigments, plasticisers, lubricants • Explain condensation polymerisation, extrusion, elastomers, van der walls forces, monomer, Q6 Polymers • 2006 • Distinguish thermo & thermosetting using polymerisation process, bonding, internal structure, properties, (2008) • State function of fillers, stabilisers, catalyst, foaming agent • Describe injection moulding process, how it works, one part produced, name some parts. Q8 mechanisms • 2012 • Describe ball bearings, vee belt pulleys • Explain – idler gear, car batteries, ratchet & pawl mechanism, heat sink in electronics, advantages of solar panels, • Describe method of independent drive to each wheel of moon buggy • Or electronics question Q8 mechanisms • 2011 • Describe bevel gears & roller bearings • Explain vee pulleys, chain & sprocket, toggle, LDR, function electronic transistor, • Describe mechanism to control steering of gokart, • Or electronics question Q8 mechanisms • 2010 • Identify Universal joint & cam shaft and cams • Explain bevel gears, double acting cylinder, clutch, idler gear, capacitor, • Describe mechanism to control up & down dentists chair, • Or electronics – id circuit diagram Q8 mechanisms • 2009 • Id socket set ratchet & timing belt, suggest use • Explain helical gears, preventing slip in pulley belt system, crank & slider, integrated circuit, solenoid, • Describe mechanism to rotate jewellery box • Or id & describe function of the electronic components Q8 mechanisms • 2008 • Id and use for bevel gears & ball bearing • Explain electrical relay, clutch, shuttle valve, rack & pinion, capacitor, • Describe a mechanism to lift heavy loads • or id & describe function of the electronic components Q8 mechanisms • 2007 • Id rack & pinion & worm gears, state where used • Explain Idler gears, Universal joint, solenoid, pneumatic flow regulator, solar panel, • Describe mechanism to automatically open a door • Or id & describe function of the electronic components Q8 mechanisms • 2006 • Id Timing toothed belt & cam and follower and give an application, • Explain compound gear train, advantage gears over pulleys, outline function of idler gear, outline between bevel and worm gears, describe 2 uses of rack and pinion mechanism • Describe the operation of a power hacksaw • Or id & describe function of the electronic components,