Welding
advertisement

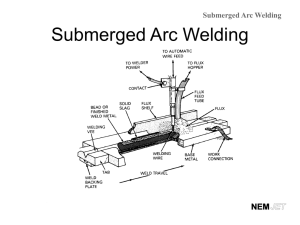
Welding After the lesson students will be able to identify different forms, understand techniques, and safety of welding What is it? A fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals, to become one. How is it done? Often done by melting the work pieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material (the weld pool) that cools to become a strong joint. Pressure sometimes used in conjunction with heat, or by itself, to produce the weld. What is similar to welding? Soldering and brazing, which involve melting a lowermelting-point material between the work pieces to form a bond between them, without melting the work pieces. What can be used for welding? Many different energy sources can be used for welding, including: Gas flame Electric arc: An electrical breakdown of a gas which produces ongoing plasma, resulting from a current flowing through normally a nonconductive media such as air. Laser Electron beam: A beam of high-velocity electrons applied to materials being joined. Friction: Generates heat through mechanical friction between a moving work piece and a stationary component, with the addition of a lateral force called "upset" to plastically displace and fuse the materials. Ultrasound: Where can welding be done? While often an industrial process, welding can be done in many different environments, including open air, underwater and in outer space. History of Welding Welding was used in the construction of the iron pillar in Delhi India, erected about 310 AD and weighing 5.4 metric tons. History of welding Until the end of the 19th century, the only welding process was forge welding, which blacksmiths had used for centuries to join iron and steel by heating and hammering them. Arc welding and oxyfuel welding were among the first processes to develop late in the century, and resistance welding followed soon after. History of welding Welding, was transformed during the 19th century. In 1802, Russian scientist Vasily Petrov discovered the electric arc and subsequently proposed its possible practical applications, including welding. From this many other forms, including current forms, have been born including: Carbon arc welding Alternating current welding Resistance welding Oxyfuel welding History of welding World War I and World War II caused a major surge in the use of welding processes, with the various military powers attempting to determine which of the several new welding processes would be best. Processes Forge welding Shielded metal arc welding Gas metal arc welding Flux-cored arc welding Gas tungsten arc welding Plasma arc welding Submerged arc welding Oxyfuel welding Resistance welding Spot welding and Seam welding Laser beam welding, Electron beam welding, and X-ray welding Explosion welding What you will do 1st hour: choose a process 2nd and 4th hour : find a partner and choose a process Research process on internet What is it History How it is used/done What is used All of important information What you will do Make a Power Point of at least 10 slides (have information, pictures, etc to present) Make all information relative/easy to follow Make a “notes” sheet on your process on a word document for students to follow along with, similar to the one I gave for my Power Point