Building Coaching Communication Skills
advertisement

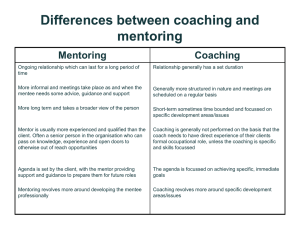
Building Coaching Communication Skills Steve Barkley Building Coaching Communication Skills Administrators and teacher leaders will focus on conferencing and facilitating skills that guide individual teachers and teaching teams in learning. These leaders will then be able to apply that knowledge learned toward being able to change teacher behaviors that will motivate student behaviors and increase student learning. School Change Source: Model developed by Stephen Barkley Student Achievement What is your definition of student achievement? Student Behaviors What student behaviors need to be initiated or increased to gain the desired student achievement? Student Behaviors • Reading as choice • Writing • Finding problem to solve • Researching • Asking Questions • Following a Passion • Persevering/Effort • Working independently and collaboratively • Taking risk in learning • Using technology to research and produce • Adapting to change Teacher Behaviors What teacher behaviors are most likely to generate these student behaviors? School Change Source: Model developed by Stephen Barkley Teacher Relationships What changes need to occur in how teachers work with each other to support the needed teacher behaviors? Leader Behaviors What leadership behaviors are needed to support the desired staff, teacher, parent, and student behaviors? Instructional Coaching EVALUATION Outside Criteria MENTORING SUPERVISION PEER COACHING Teacher’s Choice Coaching Options Technical Coaching Challenge Coaching Collegial Coaching Cognitive Coaching Pre-observation Conference Observation Post-observation Conference The Environmental Influences Closed Question Controls direction Open Answer Controls direction OPEN ENVIRONMENT • • • • • • • • Uncover Thinking Opinions Problem Solving Creativity Critical Thinking Discussion Emotions/Feeling Counseling CLOSED ENVIRONMENT • • • • • • • • Right/Wrong One Way Sequence Skills Test Control Authority Quick Fix The Environmental Influences Closed Question Controls direction Right/Wrong One Way Sequence Skills Test Control Authority Quick Fix Open Answer Controls direction Uncover Thinking Opinions Problem Solving Creativity Critical Thinking Discussion Emotions/Feeling Counseling Evaluative Creative Personalized Vision - Mission Strategy - Curriculum Agenda Tactics - Lesson Plan Operations - Teaching Skills Focus LISTENING TEST • You believe that . . . . . . . . . • My focus is . . . . . . . . . . . . . • I should notice . . . . . . . . . . Confirmatory Paraphrase Fact Attitude/Feeling Intention Commitment PRACTICE Teacher: My students won’t read an assignment so I don’t see how I can do anything other than present information in class hoping they will remember some of it. Teacher: My students won’t read an assignment so I don’t see how I can do anything other than present information in class hoping they will remember some of it. Fact You have not been able to get many of the students to work outside of class. Teacher: My students won’t read an assignment so I don’t see how I can do anything other than present information in class hoping they will remember some of it. Feeling You are worried that presenting information in class won’t get the student achievement that you want. Teacher: My students won’t read an assignment so I don’t see how I can do anything other than present information in class hoping they will remember some of it. Attitude If students read outside of class you would teach very differently. You want to find a way to get them to read outside of class. Gripes to Goals Gripes to Goals Too many students don’t care about their grades… there is no way to motivate them to work. Failing them isn’t a threat. • You have a strong desire for your students to do well. • Grades just don’t seem to be it. • You see a need to find a different way to motivate your students. Gripes to Goals I can’t deal with all the different levels of students in my class. • You believe that it is important to differentiate your instruction. • You’d like to know ways to increase your differentiation. Making Suggestions Phrase Positively Clear and Specific Congruent Pay-off Compliment Praise Approval APPROVAL • Indicate approval • Personalize • Cite the specifics Observation Form How are these used in your role? • Presenting • Training • Facilitating Presenting Training T Consider Experiment Practice Facilitating F P P P Leads to Action How are these used in your role? • Presenting • Training • Facilitating Learning (Often is) • • • • • Messy Spontaneous Irregular Non Linear Complex • • • • • Teaching Learning (Can be) (Often is) Neat Orderly Sequential Managed Documented • • • • • Messy Spontaneous Irregular Non Linear Complex Teaching (Can be) • • • • • Neat Orderly Sequential Managed Documented Teachers Must Study Learning and Student Work Observe Experiment Think Create Questions for Life Cue Words INDUCTION PERCEPTION Observe Notice Detect Picture See Hear Touch Feel Taste Smell Qualities Rule Pattern Generalization On the whole Common elements Common characteristics APPRAISAL INSIGHT Insights Inference Realization Overlapping Relationship Parallel Pattern Infer Connection Weigh Grade Rate Prioritize Appraise Rank (by value) best-to-worst most-to-least IDEA PREDICTION Ideas Goals Options Changes Ways Possibilities Opportunities Predict Forecast Hypothesize Consequences Affect Effect Happen ANALYSIS List Outline Classify Reasons Parts Sort Define SAME/DIFFERENT Sequence Categorize Analyze Factors Procedures Mind map Steps Compare Contrast Differentiate Same Different Alike Similar SUMMARY Main idea Main point Summary Focus Summarize Condense Reduce Sum up In a nutshell EVALUATION Belief Viewpoint Opinion Believe ACTION Apply Use Plan Combine Construct Interview Simulate Build Write Make Draft Draw Report Compute Do Graph Design Compose Role play Produce Create Judge Decide Evaluate Critique Questions for Life INDUCTION PERCEPTION Observe Notice Detect Picture See Hear Touch Feel Taste Smell Qualities Rule Pattern Generalization On the whole Common elements Common characteristics ANALYSIS List Outline Classify Reasons Parts Sort Define Sequence Categorize Analyze Factors Procedures Mind map Steps Row 1: Gathering Information SAME/DIFFERENT Compare Contrast Differentiate Same Different Alike Similar Questions for Life APPRAISAL INSIGHT Insights Inference Realization Overlapping Relationship Parallel Pattern Infer Connection Weigh Grade Rate Prioritize Appraise Rank (by value) best-to-worst most-to-least SUMMARY Main idea Main point Summary Focus Summarize Condense Reduce Sum up In a nutshell Row 2: Working with Information EVALUATION Belief Viewpoint Opinion Believe Judge Decide Evaluate Critique Questions for Life IDEA Ideas Goals Options Changes Ways Possibilities Opportunities PREDICTION Predict Forecast Hypothesize Consequences Affect Effect Happen ACTION Apply Use Plan Combine Construct Interview Simulate Row 3: Taking Action Build Write Make Draft Draw Report Compute Do Graph Design Compose Role play Produce Create Questions for Life Cue Words INDUCTION PERCEPTION Observe Notice Detect Picture See Hear Touch Feel Taste Smell Qualities Rule Pattern Generalization On the whole Common elements Common characteristics APPRAISAL INSIGHT Insights Inference Realization Overlapping Relationship Parallel Pattern Infer Connection Weigh Grade Rate Prioritize Appraise Rank (by value) best-to-worst most-to-least IDEA PREDICTION Ideas Goals Options Changes Ways Possibilities Opportunities Predict Forecast Hypothesize Consequences Affect Effect Happen ANALYSIS List Outline Classify Reasons Parts Sort Define SAME/DIFFERENT Sequence Categorize Analyze Factors Procedures Mind map Steps Compare Contrast Differentiate Same Different Alike Similar SUMMARY Main idea Main point Summary Focus Summarize Condense Reduce Sum up In a nutshell EVALUATION Belief Viewpoint Opinion Believe ACTION Apply Use Plan Combine Construct Interview Simulate Build Write Make Draft Draw Report Compute Do Graph Design Compose Role play Produce Create Judge Decide Evaluate Critique Teachers Must Study Learning and Student Work Observe Experiment Think Create Questions for Life Listen as Steve thinks through the questions he might use… A teacher tells you that she believes reading aloud is an important component of reading workshop time, but she doesn’t use it often because the students don’t listen during the reading. They fidget and are seldom able to respond to questions she asks.