Quality Teaching in a Culture of Coaching
advertisement

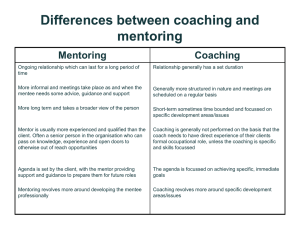
Instructional Coaching Professional Learning Communities School Improvement All With the End in Mind Stephen G. Barkley Executive Vice President Performance Learning Systems sbarkley@plsweb.com www.plsweb.com blogs.plsweb.com twitter.com/stevebarkley School Change Source: Model developed by Stephen Barkley Student Achievement What is the definition of student achievement that drives your work? 4 st Century Skills Core 21 Subjects Framework 21st Century Themes - Economics English Government Arts History Geography Reading or Language Arts Mathematics Science World Languages Civics - Global Awareness - Financial, Economic, Business & Entrepreneurship Literacy - Civic Literacy - Health Literacy st 21 Century Partnership Learning and Innovation Skills Learning and innovation skills increasingly are being recognized as those that separate students who are prepared for a more and more complex life and work environment in the 21st century, and those who are not. A focus on creativity, critical thinking, communication and collaboration is essential to prepare students for the future. But once the task called for “even rudimentary cognitive skill,” a larger reward “led to poorer performance.” Tough Choices or Tough Times • This is a world in which a very high level of preparation in reading, writing, speaking, mathematics, science, literature, history, and the arts will be an indispensable foundation ……. • …comfort with ideas and abstractions is the passport to the good life, in which high levels of education—a very different kind of education than most of us have had– are going to be the only security there is. 14 TOUGH CHOICES OR TOUGH TIMES .…comfort with ideas and abstractions is the passport to the good life, in which high levels of education—a very different kind of education than most of us have had– are going to be the only security there is. STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT GOALS • ACADEMICS - knowledge and skills to be successful in school and life. • LIFE SKILLS - aptitude, attitude and skills to lead responsible, fulfilling and respectful lives. • RESPONSIBILITY TO THE COMMUNITY - attributes that contribute to an effective and productive community and the common good of all. 16 Student Behaviors What student behaviors need to be initiated or increased to gain the desired student achievement? Student Behaviors • • • • • • Reading as choice Writing Finding problem to solve Researching Asking Questions Following a Passion • Persevering/Effort • Working independently and collaboratively • Taking risk in learning • Using technology to research and produce • Adapting to change Teacher Changes What changes in individual teacher practices are most likely to generate the changes we seek in students? 19 Teacher Behaviors • Teach the desired student behavior. • Model the desired student behavior. Staff Relationships Are there changes that need to occur in the way that staff members work with each other (staff relationships) in order for the desired individual staff member changes to occur? If so, describe. 21 Teacher Relationships • • • • Parallel Play Adversarial Relationships Congenial Relationships Collegial Relationships Roland S. Barth Relationships Within the Schoolhouse ASCD 2006 22 Changes Needed to Improve Student Achievement 1. What are the changes in student behavior, performance, choices, effort, etc., that you believe are precursors to the improvement in student learning that you seek? 2. YOU What changes must occur in individual staff/teacher practices to generate the changes you seek in students? What changes must occur in parent practices to generate the changes you seek in students? 3. Are there changes that need to occur in the way that staff members work with each other in order for the desired individual staff members changes to occur? 4. What are the behaviors/practices of school leadership that are necessary to initiate, motivate, and support these changes? 5. How do you see your role in the changing behaviors of students, teachers, teacher leaders, and administrator? 23 Instructional Coaching EVALUATION MENTORING Outside Criteria SUPERVISION PEER COACHING Teacher’s Choice Gordon’s Skill Development Ladder The Art of Teaching Unconsciously Talented Unconsciously Unskilled Consciously Unskilled Unconsciously Skilled Consciously Skilled Gordon’s (1974) Skill Development Ladder 25 Learning Dip 26 Trusting the Roles Teacher Coach Administrator 27 Analysis • Identify classrooms in your school that are closest to full implementation of your vision for learning. • Describe in detail the observable students behaviors. • Describe in detail the observable teacher behaviors. 28 Analysis • Identify classrooms in your school that must change the most to reach full implementation of your vision for learning. • Describe in detail the observable student behaviors. • Describe in detail the observable teacher behaviors. 29 Appraise Consider one area of teacher practice that is crucial to your desired student achievement. Rank your classrooms along this continuum. 1 2 Most Change Needed 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Full Implementation 30 Evaluation/Appraisal Select one skill set that you believe is most important. __________________ Rank teachers according to this system: • • • • • Unwilling Unaware Getting Ready Started Developing 31 What’s needed? Who provides it? MENTORING EVALUATION Outside Criteria SUPERVISION PEER COACHING Teacher’s Choice 32 Pre-Observation Conference Observation Post Observation Conference 33 E va lu a tive C re a tive Pe rso n a lize d V is io n - M is s io n S tr a te g y - C u rric u lu m Agenda T a c tic s - L e s s o n P la n O p e ra tio n s - T e a c h in g S k ills Fo cu s LISTENING TEST • You believe that . . . . . . . . . . . • My focus is . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . • I should notice . . . . . . . . . . . . How Administrators Support Peer Coaching Technical Coaching Collegial Coaching Challenge Coaching Staff Development Relationships Solutions & Opportunities Robert J. Garmston (1987) How are these used in your role? • Presenting • Training • Facilitating 37 Presenting 38 Training Consider Experiment Practice 39 Facilitating P P P 40 Consulting: Knowing when to use each role • Presenting • Training • Facilitating Vulnerability Individual Franchise My Work Design together My Time Implement individually Helping each other Trust Modify Individual Behavior, Consensus on implementation Team Shared responsibility for student achievement Vulnerability ACTION Trust Vulnerability Individual Franchise My Work Design together My Time Implement individually Helping each other Trust Modify Individual Behavior, Consensus on implementation ACTION Team Shared responsibility for student achievement Changes from PLC Implementation Teacher Conversations Teacher Behaviors/Actions Student Behaviors Student Achievement COACHING A NEW SKILL Select a skill or proficiency that you could train to others. Outline the activities you’d use to teach that skill. KEY ELEMENTS Knowledge Model Practice Observation with feedback • Ongoing coaching • • • • KNOWLEDGE Why Research Formal Informal How to Complex to simple MODEL PRACTICE Safe Environment Feedback Twenty to thirty repetitions over an eight to ten week period. Two Opportunities for Observation with Feedback Practice Environment: ex. Workshops Classroom Situations: ex. Coaching Joyce/Showers Research Training Components and Attainment of Outcomes in Terms of Percent of Participants — OUTCOMES — Components Knowledge Skill Transfer (thorough) (executive implementation) Study of Theory 10 (strong) Demonstrations 30 20 0 Practice 60 60 5 Peer Coaching 95 95 95 5 0 Beverly Joyce and Bruce Showers (2002) Student Achievement Through Staff Development 3rd Edition. Ch. 5: Designing Training and Peer Coaching: Our Needs for Learning. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development Understanding the Connection… In order to see the link between teacher behavior and student achievement, let’s use an example of: Higher Order Questioning Strategies Examine the relationship between students and teacher in questioning Higher Order Questioning: Skill Analysis Teacher Behavior 1 (T1): Student Response 1 (S1): Write questions into plans and start asking questions in class discussion Confusion, Reluctant to respond T1: Write questions, start asking; S1: Confusion, reluctant to respond; T2: Continue asking, increase wait time, model thinking; S2: Attempt to answer posed questions; T1: Write questions, start asking; S1: Confusion, reluctant to respond; T2: Continue asking, increase wait time, model thinking; S2: Attempt to answer posed questions; T3: Provides encouragement, probing, pausing; S3: Successfully responds; T1: Write questions, start asking; S1: Confusion, reluctant to respond; T2: Continue asking, increase wait time, model thinking; S2: Attempt to answer posed questions; T3: Provides encouragement, probing, pausing; S3: Successfully responds; T4: Withhold recognition for correct answers, cause students to assess each other and dialogue; S4: Students debate; T1: Write questions, start asking; S1: Confusion, reluctant to respond; T2: Continue asking, increase wait time, model thinking; S2: Attempt to answer posed questions; T3: Provides encouragement, probing, pausing; S3: Successfully responds; T4: Withhold recognition for correct answers, cause students to assess each other and dialogue; S4: Students debate; T5: Provide supportive and conflicting data; S5: Students pose higher level questions; Student Responses Teacher Behavior Changes Professional Development in Teacher Behavior… …leads to student achievement