E1 – Stimulus and response - IBDPBiology-Dnl
advertisement

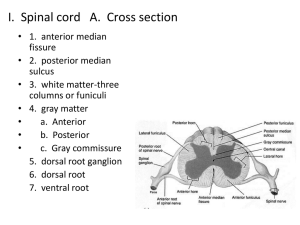
Core (for SL & HL) : E1 – Stimulus and response; E2 – Perception of stimuli; E3 – Innate and learned behaviour & E4 – Neurotransmitters and synapses Additional Higher Level (for HL only): E5 – The human brain & E6 – Further studies of behaviour E1 Stimulus and response E.1.1 Define the terms stimulus, response and reflex in the context of animal behaviour. E.1.2 Explain the role of receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, motor neuron and effector. E.1.4 Explain how animal responses can be affected by natural selection, using two examples. E1 Stimulus and response Definition of terms: Stimulus; a change in the environment (both internal and (or) external), that is detected by a receptor and elicits a response Response; body’s reaction to a stimulus. Reflex; a rapid and unconscious response to a stimulus. Draw a labelled diagram of a Reflex arc receptor cell sensory neuron white mater synapse relay neuron grey mater effector motor neuron Components of a reflex arc Components of a reflex arc & their role in the response of animals to stimuli Component receptors sensory neurons relay neurons Role in the response to stimuli detect stimuli & transform it’s energy into a nerve impulse transmit nerve impulse regarding stimuli to the CNS transmit nerve impulse within the CNS from sensory to motor neuron motor neurons transmit impulse from CNS to effector Synapses junction between two nerve cell or between a nerve cell & an effector receive messages from motor neurons & produce a response to the stimuli effectors Effect of natural selection on animal responses adaptation include behaviour such as; mating, hunting, migrating, communication etc. Example; in a nest of chicks, the chick which can call louder and gape more obviously is likely to be fed innate behavior patterns more by its parents and develop independently of the survive environment are inherited animals show variation in their the alleles responsible for successful behaviour are behavior eventually passed to the natural selection allows the best-adapted animals to offspring through survive and reproduce reproduction Example: how natural selection affect animal responses more food & mates in UK Blackcap (warbler) migrates to UK from Germany due to severe weather, food shortage & lack of mates during winter there is warmer winters in UK than in Germany resulting in ‘selection for’ those birds migrating to UK migratory blackcap increase in numbers due to greater chances of survival the alleles responsible for migration are eventually passed to the offspring through reproduction individuals that do not migrate are ‘selected against’ Revision Questions: define the following terms: stimulus; response & reflex explain the role of the following; receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli draw labelled diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex giving an example, explain the effect of natural selection on animal responses