Teaching by Fostering Learning Strategies
advertisement

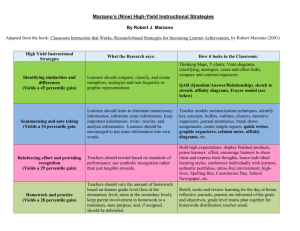
Teaching by Fostering Learning Strategies •EDU 221 Learning Strategies • Change of Schedule (no quiz #3; final will be over chapters 11-14-videotapes; Dec. 7th Classroom Management Strategies & working with parents) • HYLA #2 findings • Chapter 11 Group Presentation • Chapter 11 PP For Tuesday: Read Chapter 12 Learning Strategies • Goal: – Learning Strategies are designed to help learners become cognitively active learners. • 3 Main Criteria – involves intentional cognitive processing by the learner – occurs at the time of learning – intended to improve learning Passive to Active • teach students how to learn not just what to learn • learning strategies help students: – recall specific facts – organize material into coherent structure – integrate material with prior knowledge ***All are traits of active learning.*** Benefits • Learning strategies help students become skilled learners. • Highly skilled students can look at new material and perform the following actions. – Be able to select relevant material – Know how to organize the material into a coherent structure – Integrate the new material with previous knowledge Mnemonic Strategies What Are Mnemonic Strategies? • Techniques that help students remember material through memorization • Promote transfer 2 ways • By memorizing the basic facts and then using the information without much effort • When a student has learned information a mnemonic can help make the information seem more meaningful. Willingham, D. (2008). What will Improve a Students Memory? Letter Examples – Acronym Example: • ROY G BIV – Colors of the rainbow – Acrostic Example: • My Very Eager Mother Just Served Us Nine Pickles – To remember the order of the planets in the solar system Why Mnemonics Work • Dual Coding- strategies involve imagery as well as verbal representation, meaning more ways to find it in memory. • Organization- provide organization into which new information fits, tends to hold it together rather then separate in memory • Association- involves forming associations between information which allows for better recall of the information. Structure Strategies Goal: Prompt active learning by encouraging learners to mentally select relevant pieces of information and relate them to one another within a structure. “Dual-coding” Theory -Paivio, 1991 • Stored in Memory in Two Forms: – Linguistic: words or statements – Non-linguistic: mental pictures of physical sensations • Most information is delivered linguistically • Structure Strategies designed to help students see relationships between information with the help of visual representations Graphic Organizers Help organize the information being presented by visually representing meaningful relationships among concepts. • Concept Maps: Depicts information hierarchically • Venn Diagrams: Allow comparisons (similarities and differences) Graphic Organizers cont. • Fishbone diagrams: examine cause and effect relationships • Webs or Mind Maps: free associations and links among ideas More Graphic Organizers • Life cycle diagrams: how a series of events or stages are related to one another in a repeating process • Chain of Events/Time Lines: time-sequence patterns Generative Strategies What are generative strategies? • Learning strategies that are used to help integrate the information that was presented to the learner. • Promote Mathemagenic Activity Generative Strategies • • • • Note taking Summarizing Repeating information out loud Answering questions All require students to integrate the given information to information the previously learned. Slotte and Lonka (1999) • It is more beneficial to take summary notes rather than verbatim notes. – Summary notes require more in depth thinking • Organizing material • Integrating material – Verbatim notes do not require the student to put information into their own words, which leads to a lower grasp of concepts. Generative Strategies • • • • Note taking Summarizing Repeating information out loud Answering questions All require students to integrate the given information to information the previously learned. Questioning Method • Aimed at getting the student to create questions relating to the information in order to build onto their knowledge base. • If a student is taught how to construct questions about certain aspects of a topic they are more likely to integrate previous knowledge to the new information. • Questioning can lead to deeper understanding and lead to transfer of the information.