April 3rd, 2014
advertisement

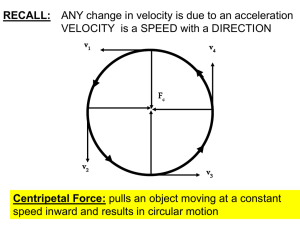
April 3rd, 2014 Homework: Study for test on Tuesday 4/8: Study Guide is online Force packet page: 9/10 due for check in tomorrow- Read pg. 60-61 Do Now Update T.O.C: pg. 16 Conservation of Momentum Open Notebooks to pg. 15 Open textbooks to pg. 56 What do you know about Action- Reaction forces… List examples- pg. 15: in NB What are some everyday activities that would not be possible with out action-reaction forceslook at fig. 15 on pg. 56 Example : 2 Skaters pushing against each other Newton’s Third Law? Why don’t the action and reaction forces cancel each other out? They do not cancel each other because they act on different objects She exerts an upward action force on the ball The ball exerts an equal but opposite downward force back on her wrists Apply Newton’s 3rd Law of motion to a pogo stickWhat are the action-reaction forces in a pogo stick jump? Action Forces- Reaction Forces- Momentum- How much it is moving Momentum •An objects momentum depends on velocity and mass Momentum… If these two objects are moving at the same velocity… which has a greater momentum? Momentum = Mass x Velocity What is the momentum of a 5kg object moving at a velocity of 6 m/s Conservation of Momentum The Law of conservation of momentum states: *When two objects collide momentum is not lost, it is transferred from one object to another object -- if there is no unbalanced forces acting– like friction. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W9Eq U1_DXUw http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qNou0xg3_cY Figure 18- pg. 60 In part A, why does the blue car move more slowly after the collision? ◦ Some of its momentum is transferred to the green car Using fig. 16 Answer the following questions in your notebook on pg 16: What happens to an objects momentum if they collide when: ◦ Both objects are moving ◦ One object is moving and the other is not