View Conference Presentation
advertisement

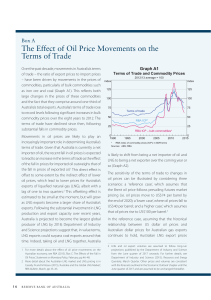
The Geopolitics of Australian Natural Gas Development Ronald D. Ripple, PhD Mervin Bovaird Professor of Energy Business and Finance Master of Energy Business Program School of Finance, Operations Management, and International Business University of Tulsa 32nd USAEE/IAEE North American Conference Anchorage, Alaska 28-31 July 2013 Outline Australia’s geopolitical role is that of an exporter of natural gas in the form of LNG. Australia’s role in the LNG trade; export trade partners. Australia’s natural gas resource base. Australia’s LNG projects. Australia’s trade advantages and disadvantages. Australia’s challenges: potential of US LNG exports. 75% increase in Australian exports: NWS expansion and Darwin LNG start-up China trade began in 2006 World trade increased 75% Asia trade increased 69% Japan trade increased 40% Source: BP’s Statistical Review of World Energy, 2012 & 2006 Australia’s Natural Gas Proved Reserves and Production, 1980-2011 [BP Statistical Review of World Energy, June 2012] Production supports exports and domestic use 2011: Australian production ~51 bcm, split roughly evenly between domestic and export use country-wide 2011: WA production was split roughly 2/3 – 1/3 export/domestic Australia’s Natural Gas Resource Base Source: Santos, Cooper Basin Unconventional Gas Opportunities & Commercialisation, Nov 2012. Source: EIA – World Shale Gas Resources: An Initial Assessment, April 2011. Source: EIA – World Shale Gas Resources: An Initial Assessment, April 2011. Australian LNG projects: Operating Under Construction and Planned (capacities – mtpa) Source: LNG Business Review, February 2012. Australian LNG Projects Three operating projects with total annual capacity at 24.2 mt. Seven projects under construction with total additional annual capacity of 61.5 mt. The 61.5 mtpa represents about $190 billion in investment from a range of international and domestic parties. The 61.5 mtpa represents 64.5% of all new capacity currently under construction world-wide. Sometime prior to 2020, Australia will surpass the 77 mtpa of Qatar. Australian LNG Advantage proximity to dynamic and growing Asian markets LNG Carrier shipping cost (only) comparison between Australia and Qatar 3 140,000 m tanker => ~ 2,995,000 MMBtu Destination - Tokyo [accounts for round trip travel time] Port Darwin Doha Days - hours Cost @$125,000/d Cost/MMBtu Dist (nautical miles) 14 knots 20 knots 14 knots 20 knots 14 knots 20 knots 3072 8d 19h 6d 10h $ 2,197,917 $ 1,604,167 $ 0.73 $ 0.54 6655 19d 10h 13d 21h $ 4,854,167 $ 3,468,750 $ 1.62 $ 1.16 Difference (Australia advantage) $ 0.89 $ 0.62 Australia LNG Disadvantage Source: recent CME research into the cost of doing business, CME WA. Australia’s US LNG Export Challenge? US natural gas resource base – shale gas revolution US natural gas export approvals Expected size of the Asia-Pacific LNG trade US LNG shipping distances Expected size of the Asia Market BP’s Outlook to 2030 projects Asia consumption from all sources to increase by 60%, relative to 2011, while Asia production is projected to increase by 52%. This will result in a gap, which is expected to continue to grow, of 159.2 mt equivalent in 2020. LNG capacity under construction in 2013 equals 95.3 mtpa, which includes the 61.5 mtpa in Australia and the 9.0 mtpa Cheniere Sabine Pass project in the US. US – Tokyo shipping distances Through the Panama Canal (once the expansion is complete) = 9,247 nautical miles. More than 3 times the Australian distances. Around South Africa = 15,957 nautical miles. More than 5 times the Australian distances. Conclusion Australia has played an important geopolitical role in the growth of the natural gas trade in LNG. Australia will continue to play an important role, especially as it expands to be the largest LNG exporter. Australia will face competition, even in traditional markets, but the market is also expected to grow substantially. Thank you for your attention. I am happy to answer questions? Prof Ronald D Ripple Email: ron-ripple@utulsa.edu Phone: 918-631-3659