nonspontaneous
advertisement

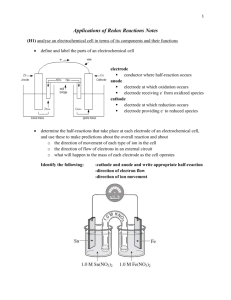
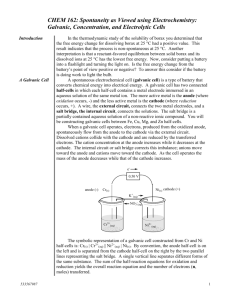
Topic: Electrolytic Cell Do now: p.19 in packet, cross out # 19 and do # 20 and #21. must label anode/cathode • Chemical rxns can produce electricity = galvanic (voltaic) cell OR • Electrical energy used to carry out chemical reactions = electrolytic cell Electrolytic Cell need electrical energy so NONSPONTANEOUS Chemical Potential Energy Galvanic Cell Electrolytic Cell Electrical Potential Energy Galvanic cell is a battery Electrolytic cell needs a battery Electrolytic Cells • • • Nonspontaneous Need battery or power supply Consumes energy = endothermic What’s the difference? Battery in one. Electrons in galvanic flowing from – to + Electrons in electrylic flowing from + to e- e- e- anode Electrolytic Cell a Fat Red Cat ate an Ox Use Table J, but opposite More active metal = cathode = negative Less active metal = anode = positive catode Galvanic Cell A Fat Red Cat ate an Ox Use Table J More active metal = anode = negative Less active metal = cathode = positive NONSPONTANEOUS SPONTANEOUS e- flow Anode to Cathode e- flow Anode to Cathode But from + to – from – to + (opposite then we’d think) (just like we’d think) That’s why we use the battery That’s why it’s spontaneous e- e- e- A POX on Electrolytic Cells • Anode – Positive – Oxidation A pox = a disease And electrolytic cell behave differently like they are diseased?! Various types of electrolytic cells 1. Fused Salt Cells – used to purify metals (Fused means melted = molten salt cell) • Add NaCl (s) and melt it • Now NaCl (l) • Why melt it?! Molten b/c need ions • Why add CaCl2(s)??! Lowers MP – don’t need as much heat • Na+1 is reduce to Na(l) • Na(l) is less dense then NaCl(l) so it floats on top • 20,000 tons of Na are produce this way in the US every year Fused Salt Cell (Molten salt cell) + - e- e- e- e- lose electron So oxidized So anode 2Cl- + Cl 2+ 12 e- Gain electron So reduced So cathode Na+ (l) Cl- Na+ + 1e- Na Na+ Cl- BUT WAIT SOMETHING IS WRONG WITH OUR ANODE Various types of electrolytic cells 2. Electroplating A layer of a second metal is deposited on the metal electrode that acts as the cathode • Used to enhance the appearance of metal objects and protect them from corrosion. Various types of electrolytic cells 2. Electroplating • cathode = object to be plated • anode - made of metal want to plate on object • solution: contains ions of plating metal + e- e- e- e- lose electron So oxidized So anode Ag Ag+ + 1e- Gain electron So reduced So cathode Ag+ + 1e- Ag NO3- NO3- 3. Electrolysis of H2O H2 is produced at one electrode, O2 at the other. 2H2O + energy 2H2 + O2 Can you tell from the picture which electrode is producing H2? What do every one of these have in common?