Regents Unit 13: Electrolytic Cells
advertisement

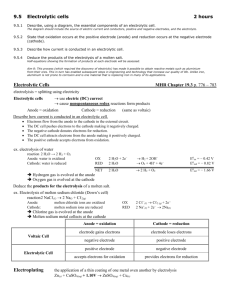
Electrolytic Cells Electrolytic Cells • Use electricity to force a nonspontaneous reaction to occur. Endothermic. • Electrolytic cells can be identified by the presence of a battery or a power supply. • There are many kinds of electrolytic cells. Galvanic Cell Chemical Potential Energy Electrolytic Cell Electrical Potential Energy Electrolytic Decomposition of H2O H2 is produced at one electrode, O2 at the other. 2H2O + energy 2H2 + O2 Can you tell from the picture which electrode is producing H2? Reversing a Galvanic Cell This time: Zn is reduced & Cu is oxidized. Two kinds of electrolytic cells • Fused Salt Cells – Preparation of pure metals (Fused means melted!) • Plating Cells – Designing surface to have specific properties Electroplating Move desired coating from anode onto object to be plated. Solution contains ions of element to be plated. Electroplating: Cu onto Al • Al is above Cu in Table J. • This reaction will not happen spontaneously. • Use an external energy source – a power supply or a battery – to force reaction to occur. An Ox ate a Fat Red Cat • Anode is still electrode at which oxidation occurs. • Cathode is still electrode at which reduction occurs. • Polarity of electrodes is different! – Anode is positive. – Cathode is negative. A POX on Electrolytic Cells. • Anode – Positive – Oxidation • In an electrolytic cell, the polarity is determined by the outside power supply. • The anode is hooked up to the positive terminal and the cathode is hooked up to the negative terminal. • Look at drawings in Regents questions. + Battery + - Loses mass Anode = Oxidation Cu Cu+2 + 2eCathode = Object to be Plated = Reduction Cu+2 + 2e- Cu Gains mass Element to be plated. Cu+2 and SO4-2 Notice: Net reaction is just moving Cu around. Cathode = object to be plated. Plating Anode is made of metal that you want to plate on object. Solution contains ions of plating metal. Fused Salt Cells • Used to purify metals from their ores. Schematic of fused salt cell + + Ox: 2Cl- Cl2 + 2e- - Red: Na+ + 1e- Na • Why does the NaCl have to be molten? • Which electrode will the Na+ ions be attracted to? • Which electrode will the Cl- ions be attracted to?