National 5: Population Unit
Population
Structure
Success Criteria
• By the end of this lesson you should be able to:
• Explain what is meant by the term POPULATION
STRUCTURE.
• Interpret a POPULATION PYRAMID for both a
Developed and Developing Country.
• Explain the factors which affect population structure
for both Developed and Developing Countries.
• Describe what the Dependency Ratio is and how it is
calculated.
What is Population Structure ?
• The structure of the population
of a given country is defined in
terms of age and sex
distribution.
• Age is divided into different age
groups (e.g. 0-4, 5-9 and so on).
• Data on these characteristics are
plotted on a graph called a
population pyramid which is
based on grouping males and
females into different age groups
from 0 - 80+.
Factors affecting Population
Structure
• Factors which influence birth
and death rates (e.g.
availability of contraception
and health care).
• Migration into and out of a
country.
• Impact of wars.
• Impact of Disease and
Epidemics (e.g. AIDS)
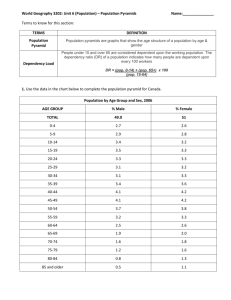
What Can Population Pyramids Tell Us ?
• Variations in levels of development.
• Imbalances in the population (either in terms of age or
sex).
• Changes in the population over time due to factors such
as wars and migration.
• Problems which specific countries may be facing in
relation to their populations.
• Analysis of population pyramids
reveals patterns of birth and death
rates and an estimation of the life
expectancy in general terms.
Population Pyramids For Developed (EMDC) and
Developing (ELDC) Countries
Population Pyramid For China
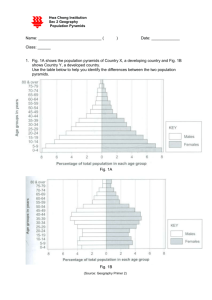
Population Structure of a Developed Country
A fairly high % of the
population within the upper
age groups from 60+. This
indicates that the country has
a high life expectancy and
also an ageing population.
A bulge in the middle
age groups (15-65)
indicating that most of
the population are within
this range.
A fairly low birth rate in both males and females.
Reasons For Structure
• Standards of health care, education, housing &
employment are all high.
• Average income per head of population is also high.
• The number of children per family is usually low due
to factors such as the widespread use of
contraception and couples having children much later
in marriage.
• Life expectancy is high and this accounts for the high
percentages in the age groups 60+
Population Structure of a Developing Country
A more definite pyramidal
shape where the number of
people in the age groups 15+
decreases fairly rapidly.
Very few people in the higher
age groups 60+ (i.e. a country
where the average life
expectancy is quite low).
A large proportion of the
population between the
ages of 0 – 15 years.
A high birth rate in both males and females.
Reasons For Structure
• Standards of health care, education, housing
and employment are all low.
• Average income per head of population is also
low.
• The number of children per family is also high
due to factors including lack of contraception,
early marriage, religion.
• Life expectancy is low and this accounts for
the fairly low percentages in the age groups
60+
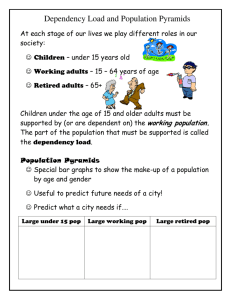
Dependency Ratio
• We have seen that the population pyramids for
Developing Countries can be identified by high
numbers of children and low numbers of older people.
• We have also seen that the population pyramids of
Developed Countries can be identified by low numbers
of children and high numbers of older people.
• The DEPENDENCY RATIO shows the relationship
between different age groups and shows how ’active’ a
country’s population is
Dependency Ratio
• The Dependency Ratio is calculated by
dividing the % of population who are
dependent by the % of population who are
active.
• The dependent population is composed of
children who are too young to work and the
elderly who are too old to work.
• The active population are those of working
age who generate the wealth of a country.
Dependency Ratio
• Every country would like a population in which there is a high % of
active people and a low % of dependents.
• Dependency ratios vary throughout the world.
• In India the dependency ratio is 1.02 which means that there is an
average of 1.02 dependents for every active member of the
population to support.
• This is a drain on a country’s resources and hinders development.
• In Canada, the dependency ratio is 0.46 which means there is only
an average of 0.46 dependents for every working adult to support.
• With falling birth rates and longer life expectancies in Developed
Countries dependency ratios are changing.
• Developed Countries now have more elderly dependents to support
with fewer young people coming through to fill the jobs left vacant as
older people retire.
Can I…?
• Explain what is meant by the term POPULATION
STRUCTURE.
• Interpret a POPULATION PYRAMID for both a
Developed and Developing Country.
• Explain the factors which affect population structure
for both Developed and Developing Countries.
• Describe what the Dependency Ratio is and how it is
calculated.