Demography and Aging
What is “demography”?
Demography is the study of populations
Counting and describing people
Age, sex, income, marital status…
Demographers calculate
life expectancy
birth and fertility rates
average age at marriage…
Three basic processes affect
population
Fertility
Mortality
Migration
Many factors affect these processes
Economic development, technology,
religious and cultural values…
“Population aging”
1. How do we measure this?
Indicators of population aging
Greater numbers of older people
Higher median age
A higher percentage of our population is
“old”
In 1900, 4% of US population was 65+
In 1996, just under 13%
2. What was the U.S. “baby boom” and
when did it take place?
(and why do we care?!)
3. Which age group in the U.S.
population is growing fastest?
What is causing this shift in
age?
Increasing life expectancy
Declining birth rates
=changes in mortality
=changes in fertility
4. Which of these is most important?
Fertility rates, 1950 and 2005
Africa: 6.7 -> 5.1
Asia: 5.9 -> 2.5
Latin American / Caribbean: 5.9 -> 2.6
North America: 3.5 -> 2.0
Europe: 2.7 -> 1.4
5. What explains gains in life
expectancy?
6. Gender distribution
Are the majority of U.S. older adults
men or women? Why?
Population pyramids
Also known as “age-sex pyramid” or
age structure diagram
Shows how the “shape” of population
changes
Often from pyramid (more younger people
at the bottom, few old people) to rectangle
(more equal distribution between ages)
United States, 1950
United States, 2000
United States, 2050
India, 2000
India, 2025
India, 2050
Russia, 2000
Russia, 2050
Want to see more?
http://www.census.gov/ipc/www/idb/inf
ormationGateway.php
Global Aging: Which countries are
the “oldest”?
Percent Aged 65 and Over: 2000
Percent Aged 65 and Over: 2030
Uneven geographic distribution
Differences in fertility, mortality, and
migration create different population
characteristics in different areas
Differences between countries
Differences within countries
Which places in the U.S. are “old”?
Which places are “young”?
What difference does that make??
Percentage of Population
Age 65+ by State
Interactive census tools…
http://www.census.gov/
Other demographic trends…
Increasing diversity
Increasing levels of education
Changes in families
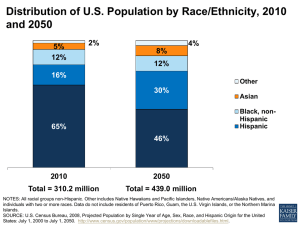
Distribution by Race and
Ethnicity
Education, Percentage and Level
65+
Education, Percentage by Race
and Hispanic Origin
Changes in families…
…affect who is available to take care of
an older person.
Smaller families
Marriages and births at later ages
Increased likelihood of divorce
More blended families
…and the living arrangements of older
people.
Percentage by Age Living Alone
7. Who helps us when we are
old?
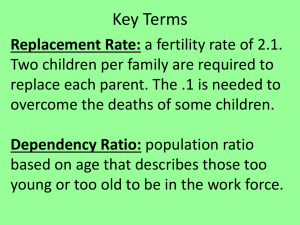
Dependency ratios
Old age dependency ratio - % of
population 65+ compared to % of
population 18 to 64 (the “workers”).
Fewer workers supporting more older
people
So old age dependency ratio is
INCREASING
Other ratios…
Childhood dependency ratio - %
population age 0-17 compared to %
population 18 to 64.
This is DECLINING
Overall dependency ratio - STABLE