Calculating the Dependency Ratio
advertisement
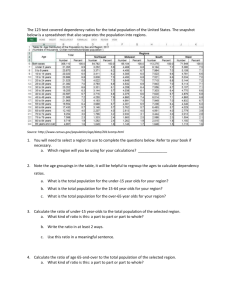
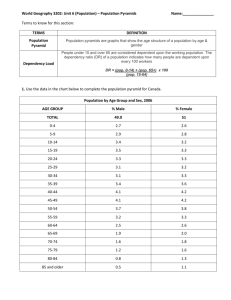
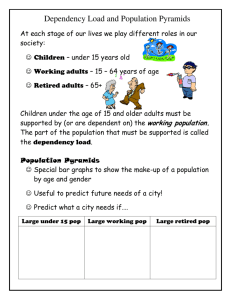
Calculating the Dependency Ratio AP Human Geography Retired Dependents Workforce Child Dependents Source US Census Bureau International Data Base Retired Dependents Workforce Child Dependents Dependency Ratio • The ratio between the number of dependants (anyone above or below the working age) and the number of people in the potential labor force. • young dependents (YD): Anyone younger than 15 • old dependants (OD): Anyone 65 and older • Dependency ratio = YD + OD x 100 People of working age Calculating Dependency Example • Dependency ratio = YD + OD x 100 People of working age YD= 500 OD= 250 People of working age = 600 • Dependency ratio = 500 + 250 x 100 600 Dependency Ratio = 125 (which means that for every 100 workers, there are 125 not working) Importance of Dependency Ratio • It’s important because it shows the ratio of economically inactive compared to active. • Economically active will pay much more income tax • Economically inactive (dependents) are bigger recipients of government spending (education, pensions and health care) Forecast for Dependency Ratios Solutions for Higher Dependency Ratios • Raising retirement age in line with longer life expectancies • Encouraging immigration of people in early 20s and 30s • Reduced government funded pensions and encouraging private pensions (401K/403B) Costs and Benefits of Ageing and Youthful Populations Ageing Populations Causes Costs Benefits Life expectancy has increased, causing increased proportions of elderly 1. Heavy Burden on state finances through pensions and welfare payments. 2. Large demands on health systems 3. Reduced workforce 4. Population decline- if there’s also declined birth rates 1. Workforce can work longer 2. Elderly can help look after grand-children which allows parents to work full-time. Youthful Populations Causes Costs Benefits Many LEDCs are have high birth rates. 1. High demand for education. 2. Need for many women to stay at home to care for children 3. High rates of unemployment 4. Increased poverty- more people are born into families, which are already poor. 1. Large potential workforce often leading to cheap labor, which can attract new investment. 2. Less money is spent on healthcare. Guided Practice • Use the Age/Sex Structures for Area A and B to complete the questions on the back to ultimately calculate the dependency ratios for both areas. • Raise your hand if you need help.