Federalism
advertisement

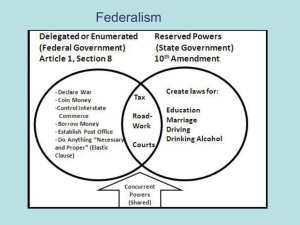
Federalism 3 Video: The Big Picture 3 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED IA_1/polisci/presidency/Edwards_Ch03_Federalism_Seg1_ v1.html Learning Objectives 3.1 3.1 3.2 3.2 3 Define federalism and contrast it with alternative ways of organizing a nation. Outline the constitutional basis for the division of power between national and state governments, the establishment of national supremacy, and states’ obligations to each other. Learning Objectives 3.3 3.4 3 Characterize the shift from dual to cooperative federalism, the role of fiscal federalism in intergovernmental relations today, and diversity in policies among the states. Explain the consequences of federalism for diversity in public polices among the states. Learning Objectives 3.5 Assess the impact of federalism on democratic government and the scope of government. 3 Video: The Basics 3 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED IA_1/polisci/presidency/Seg2_Federalism_v2.html Defining Federalism What is federalism? Unitary system Power given to central government Confederation Weak national government and power given to states Intergovernmental relations 3.1 Authority relations in three systems of government 3.1 3.1 Which organizing system does the government in the United States use? a. Confederate b. Unitary c. Federal d. Intergovernmental 3.1 3.1 Which organizing system does the government in the United States use? a. Confederate b. Unitary c. Federal d. Intergovernmental 3.1 Constitutional Basis of Federalism Division of Power National Supremacy States’ Obligations to Each Other 3.2 Division of Power States retained many powers Organize local governments and elections Ratify Constitutional amendments Equal representation in Senate 3.2 Some Powers Denied States by the Constitution 3.2 Division of Power Federal obligations to states Cannot divide states Cannot tax interstate exports Protect states against invasion Overlapping responsibilities 3.2 National Supremacy Which level should do what? Debates over areas of policy responsibility Supremacy clause Civil War The Struggle for Racial Equality Tenth Amendment Eleventh Amendment 3.2 Wallace and segregation 3.2 National Supremacy Implied Powers McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) Enumerated powers Elastic clause 3.2 Supremacy Clause and Immigration 3.2 National Supremacy Commerce power Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) Promote economic development Regulate economic activity Expansion then retraction 3.2 States’ Obligations to Each Other Full faith and credit Defense of Marriage Act (1996) 3.2 States’ Obligations to Each Other Extradition Privileges and immunities 3.2 3.2 Which clause of the Constitution requires states to honor contracts signed in other states? a. Privileges and immunities b. Full faith and credit c. Necessary and proper d. Commerce 3.2 3.2 Which clause of the Constitution requires states to honor contracts signed in other states? a. Privileges and immunities b. Full faith and credit c. Necessary and proper d. Commerce 3.2 Explore the Simulation: You Are a Federal Judge 3.2 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/long/long_longman_media _1/2013_mpsl_sim/simulation.html?simulaURL=3 Video: In Context 3.2 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED IA_1/polisci/presidency/Seg3_Federalism_v2.html Intergovernmental Relations From Dual to Cooperative Federalism Devolution? Fiscal Federalism 3.3 From Dual to Cooperative Federalism Dual federalism Separate spheres of authority Layer cake Interpret federal power narrowly Cooperative federalism Shared costs Federal guidelines Shared administration 3.3 Interstate highways 3.3 From Dual to Cooperative Federalism Cooperative federalism in action Schools Highways and State Alcohol laws 3.3 Devolution? Party divide on federalism Democrats favor national government Republicans favor states Devolution since Reagan Loosening federal regulations 1994 Congress Harnessing federal government power 3.3 Fiscal Federalism The Grant System Categorical grants Specific purpose Crossover sanctions Crosscutting requirements Project grants Formula grants Block grants 1994 Congress Scramble for federal dollars Mandate blues 3.3 Fiscal Federalism The Grant System Categorical grants Specific purpose Crossover sanctions Crosscutting requirements Project grants Formula grants Block grants 1994 Congress Scramble for federal dollars Mandate blues 3.3 FIGURE 3.1: Fiscal federalism: Federal grants to state and local governments 3.3 No Child Left Behind Act 3.3 3.3 Which of the following gives states more discretion in using federal funds? a. Categorical grant b. Formula grant c. Block grant d. Mandate 3.3 3.3 Which of the following gives states more discretion in using federal funds? a. Categorical grant b. Formula grant c. Block grant d. Mandate 3.3 Explore Federalism: Which States Win or Lose in the Federal Aid Game? 3.3 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/long/long_edwards_mpslgi a_16/pex/pex3.html Diversity in Policy Diversity in public opinion reflected Policy innovation facilitated Diversity has its downside 3.4 3.4 Which of the following is a result of federalism? a. Diversity of policies in states b. States can be policy innovators c. States can spend less on education d. All of the above 3.4 3.4 Which of the following is a result of federalism? a. Diversity of policies in states b. States can be policy innovators c. States can spend less on education d. All of the above 3.4 Video: Thinking Like a Political Scientist 3.4 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED IA_1/polisci/presidency/Seg4_Federalism_v2.html Understanding Federalism 3.5 Federalism and Democracy Federalism and the Scope of the National Government FIGURE 3.2: State and local spending on public education 3.5 Federalism and Democracy Contributions to democracy Decentralizes politics Disputes resolved at lower levels of govt. Majorities can be heard at state level More opportunities for participation Losing elections less painful Detriments to democracy Electoral College Thwarting national majorities 3.5 Number of governments in America 3.5 Federalism and the Scope of the National Government Why national government grew Economic intervention Industrialization Quotas Subsidies Preventing monopolies Occupational health and safety Urbanization Housing Social welfare 3.5 FIGURE 3.3: Fiscal Federalism: The size of the public sector 3.5 3.5 Federalism has contributed to democracy in all of the following ways except: a. The Electoral College b. More opportunities for participation c. Disputes resolved at lower levels d. More points of access 3.5 3.5 Federalism has contributed to democracy in all of the following ways except: a. The Electoral College b. More opportunities for participation c. Disputes resolved at lower levels d. More points of access 3.5 Video: In the Real World 3.5 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED IA_1/polisci/presidency/Seg5_Federalism_v2.html Discussion Question 3 In what ways has federalism contributed to democracy? In what ways has federalism been detrimental to democracy? Has this pattern followed the Framers’ intentions? Could they have foreseen the issues the federal government and the states would have to deal with after industrialization? Video: So What? 3 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED IA_1/polisci/presidency/Edwards_Ch03_Federalism_Seg6_ v2.html Further Review: On MyPoliSciLab Listen to the Chapter Study and Review the Flashcards Study and Review the Practice Tests 3