practicequestionsbarrons
advertisement
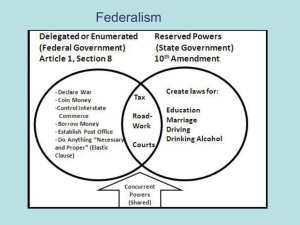
Federalism Practice Questions Barron’s Which of the following represents the theoretical definition of federalism? A. Division of power between the federal government and state governments B. A strict separation of power between the federal government and the state governments C. A division of power between the federal government and state governments where the power emanates from the states D. A singular relationship that is characterized by control emanating one way from a central government Answer • A. Division of power between the federal government and state governments • Advocates of a strong federal system believe in all of the following EXCEPT: A. State and local governments do not have all the resources necessary to deal with the problems facing the country B. Local politicians are provincial in their point of view C. State and local governments cannot support the vast programs necessary to support citizens D. Local leaders are more suited to solve problems than national leaders E. An elitist group would be more likely to gain control in a country dominated by local interests Answer D. Local leaders are more suited to solve problems than national leaders According to the writings of the Federalist Papers, which of the following reflects a major reason for the support of a federal system? A. Local governments are best suited to meet the needs of the majority interests of the country B. Local governments will maintain their authority and will be able to care for their citizens C. The central government is best suited to recognize the needs and interests of local governments D. There will be a constant clashing of opinions between the interests of the local and federal governments E. Factions would be strengthened by the formation of a federal system of a government Answer B. Local governments will maintain their authority and will be able to care for their citizens All the following Supreme Court cases dealt with the issue of federalism EXCEPT A. Gibbons v Ogden B. Marbury v Madison C. McCulloch v Maryland D. Barron v Baltimore E. Fletcher v Peck Answer B. Marbury v Madison The constitutional provision used in the Supreme case McCulloch v. Maryland was: I. the necessary and proper clause II. The supremacy clause III. the interstate commerce clause A. I only B. II only C. I and II only D. II and III only E. I, II, and III Answer C. I and II only The constitutional basis of dual federalism can be found in: A. The B. The C. The D. The E. The “necessary and proper” clause Tenth Amendment elastic clause implied power provision enumerated powers Answer B. The Tenth Amendment Which general area of policy is generally left up to the states? A. Foreign policy B. Military policy C. Relations among the several states D. Health and welfare E. immigration Answer D. Health and welfare Which general are of policy is generally left up to the central government? A. Health B. Interstate commerce C. Education D. Police E. Voting requirements Answer B. Interstate commerce Which kind of federalism best describes an autonomous relationship between the states and national government? A. Cooperative federalism B. Creative federalism C. Layer cake federalism D. Fiscal federalism E. Marble cake federalism Answer C. Layer cake federalism All of the following are characteristics of marble cake federalism EXCEPT: A. There are mingled responsibilities and blurred distinctions between the levels of government B. The federal government becomes more intrusive in state affairs C. There is a greater sharing of responsibilities between the federal and state levels D. The national government exercises its power independently from state governments E. There is a greater cooperation between the federal and state governments Answer D. The national government exercises its power independently from state governments Creative Federalism of the Great Society was characterized by: I. shared costs between the national and state governments II. Guidelines and rules set down by the federal government III. Singular administration programs A. B. C. D. E. I only II only I and III only I and II only I, II, and III Answer D. I and II only Which historical period represents the introduction of competitive federalism? A. The Civil War B. The New Deal C. World War II D. The Great Society E. The 1970s and 1980s Answer E. The 1970s and 1980s Which type of federalism is characterized by a pattern of competitive grants? A. Dual federalism B. Cooperative federalism C. Fiscal federalism D. Creative Federalism E. Marble cake federalism Answer C. Fiscal federalism Which of the following best represents the components of fiscal federalism? I. the passage of funded mandates II. The passage of revenue sharing measures III. The passage of categorical grants A. I only B. II only C. III only D. I and III only E. I, II, and III Answer E. I, II, and III An alternative developed by the federal government that places the primary fiscal responsibility on the states was: A. Revenue sharing B. Project grants C. Formula grants D. Unfunded mandates E. Reimbursement grants Answer D. Unfunded mandates Which of the following laws was challenged by states because they felt that the federal government imposed an unfair unfunded mandate: A. Family and Medical Leave Act B. Motor Voter Registration Act C. Clean Air Act D. Clean Water Act E. Crime Bill Answer B. Motor Voter Registration Act Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan’s vision of a new federalism favored: A. An increase in the power and authority of the federal government B. A cooperative spirit between the federal and state governments C. An increase in federal mandates D. The downsizing of the federal government E. A decrease in the defense budget Answer D. The downsizing of the federal government Which of the following provisions of the Republican Contract with America addresses the issue of federalism? I. term limits constitutional amendment II. Balanced budget constitutional amendment III. Welfare reform act A. I only B. II only C. III only D. I and II only E. II and III only Answer E. II and III only