Federalism: Forging a
Nation
Chapter 3
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism: National and State
Sovereignty
The Argument for Federalism
Authority
divided into two levels: national
and regional
Protects
liberty
Moderates
government power by sharing
Strengthening
the union
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism: National and State
Sovereignty
The Powers of the Nation
Enumerated
17
powers
powerssecure defense & stable commerce
Implied
powers
“necessary
and proper” actionsgovernment
support
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism: National and State
Sovereignty
The Powers of the States
Oversight
safety
of public morals, education, and
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
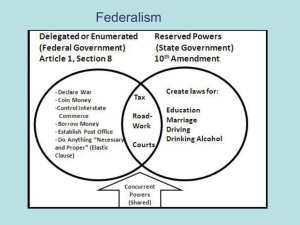
Federalism as a Governing
System, Figure 3-1
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism in Historical
Perspective
An Indestructible Union (1789-1865)
The
nationalist view: McCulloch v. Maryland
(1819)
The
states’-rights view: The Dred Scott
Decision (1857)
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism in Historical
Perspective
Dual Federalism and Laissez-Faire
Capitalism (1865-1937)
Dual
Federalism: separation of national
from state power
The
Fourteenth Amendment and State
Discretion
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism in Historical
Perspective
•
Dual Federalism and Laissez-Faire
Capitalism (1865-1937)
Judicial
Protection of Business
Supreme
National
court restricted national power
Authority Prevails
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism in Historical
Perspective
Toward National Citizenship
Equal
civil rights across all states
Fourteenth
Exceptions:
schools
Amendment
death penalty, quality of public
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism Today
Interdependency/Intergovernmental
Cooperative
federalism: shared policy
responsibilities
National,
state, and local levels work together
Medicaid: health insurance for the poor
Education
Law enforcement
Transportation
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism Today
Government Revenues and
Intergovernmental Relations
Fiscal
Federalism
Categorical
and Block Grants
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Federalism Today
A new Federalism: Devolution
Budgetary
The
Pressures and Public Opinion
Republican Revolution
Devolution,
Judicial Style
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The Public’s Influence
Setting the Boundaries of Federal-State
Power
Roosevelt’s
“New Deal”jobs during the
Great Depression
Lyndon
Johnson’s “Great
Society”increased social services
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
The Public’s Influence
Setting the Boundaries of Federal-State
Power
Republican
successes in Congressional
elections due to public’s dissatisfaction with
the federal government
© 2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.