File - Jill Mitchell
advertisement

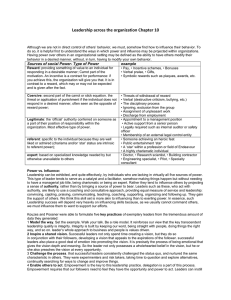
Logistics PPS8 Topic 5 Topic 5 The Behavioural Processes in Distribution Channels and Channel Conflict Distribution channels as part of a social system Channel power Channel conflict Channel communication Channel power sources Reward Power Coercive Power Legitimate Power Referent Power Expert Power Reward Power • Financial incentive to next channel member • Ability to be franchisee i.e. @ McD Coercive Power • “I kill you!” – Achmat the Dead Terrorist • Punishing the next channel member if fails to respond as it should • Coercive POWER sits with the big boys Pick n Pay Shoprite/ Checkers Woolies Spar Legitimate Power • Adhere to formal agreement • May be problems between independent organisations (i.e. M ask R not to discount …) • Higher legal recourse/ tighter in franchise channel Referent Power Channel member sees other as having same objectives and part of same reference group Expert Power = knowledge/ perceived knowledge one channel member has & influence power to change behaviour of other members Exercising power – the influencing strategies • Promise strategy – if you do what I say I will reward you • Threat strategy – if you don’t do what I say I will punish you • Legalistic strategy – do what we wish as we have contractually agreed to it … Exercising power – the influencing strategies • Request strategy – we ask: sweet, short and sharp with no indication of what may happen • Info exchange strategy – “This is how you could make your business more profitable …” now draw your own conclusions … • Recommendation strategy – “This is how you could make your business more profitable …” & conclusions Using power to exert influence in the distribution channel Promise Legitimacy Threat Coercion Legalistic Expertise, reward Request Referent, reward, coercion Info exchange Expertise, reward Recommendation Reward Using power to exert influence in the distribution channel Promise Reward Threat Coercion Legalistic Legitimacy Request Referent, reward, coercion Info exchange Expertise, reward Recommendation Expertise, reward CHANNEL CONFLICT CHANNEL CONFLICT “ … a situation in which one member of a distribution channel perceives another member as an adversary engaged in behaviour designed to injure, thwart/ block/ hinder from doing something, or gain scarce resources at the expense of the original member” Causes of channel conflict 2-3 causes each Conflict resolution Two main reasons for conflict: • Use of power • Attempt to gain more power Decision framework for evaluating channel conflict Importance of threatened channel in terms of current or potential volume of profitability Prospect Act to avert conflict Allow threatened channel to decline of destructive conflict Look for opportunities to reassure threatened channel and allow to leverage power Do nothing The four methods to solve channel conflict • • • • Problem-solving Persuasion Negotiation Politics Problem-solving Persuasion Negotiation Politics • Coalitions • Mediation and arbitration • Lobbying and judicial appeal COMMUNICATION IN THE DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL Communication • Perceptual differences (does “soon” mean within 24 hours?) • Secretive behaviour • Infrequent communication case study Page 136 … and answer questions on page 137