Socialization and
Gender Roles
Chapter 5
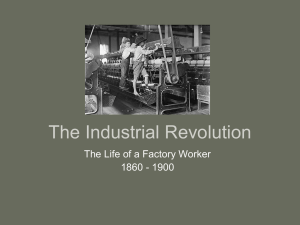
Sex and Gender
Sex refers to the biological characteristics with
which we are born.
Gender refers to the learned attitudes and
behaviors that characterize people of one sex or the
other.
Gender roles are the characteristics, attitudes,
feelings, and behaviors that society expects of
females and males.
Gender identity, usually learned in early childhood,
refers to one’s perception of him or herself as either
masculine or feminine.
Gender Quiz: Are Women and
Men Different?
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
T/F Women are the weaker sex.
T/F Boys are more group-centered, active, and aggressive
than girls.
T/F Women are more emotional than men.
T/F Women talk more than men.
T/F Women suffer more from depression.
T/F Women are more likely than men to divulge personal
information.
T/F Men smile more than women.
T/F Women and men don’t care whether a baby is a boy or a
girl.
T/F Most women are confident about managing their financial
affairs.
T/F A heart attack is more likely to be fatal for a man than for
a woman.
Gender Quiz: Are Women and
Men Different?
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
False Women are the weaker sex.
True Boys are more group-centered, active, and aggressive
than girls.
False Women are more emotional than men.
False Women talk more than men.
True Women suffer more from depression.
False Women are more likely than men to divulge personal
information.
False Men smile more than women.
False Women and men don’t care whether a baby is a boy or
a girl.
False Most women are confident about managing their
financial affairs.
False A heart attack is more likely to be fatal for a man than
for a woman.
Nature-Nurture Debate
Nature-Nurture Debate
Arguments favoring “Nature” (biological
differences between men and women) come
from the following sources:
Developmental and Health differences
Effects of sex hormones (chemical substances
secreted into the bloodstream)
Sex differences in the brain
Unsuccessful sex reassignment
Nature-Nurture Debate
Arguments favoring the “Nurture” side of the
debate, suggesting that culture shapes
human behavior, come from:
Cross cultural variations in gender roles
Cross cultural variations in male violence
Successful sex assignment particularly with
intersexuals (people born with both male and
female sex organs).
Nature-Nurture Debate
What can we conclude?
Women and men exhibit some sex-related genetic
differences.
Cross cultural research shows much variation in
characteristics typically ascribed to men and
women.
Nature and Nurture clearly interact to explain our
behavior.
How we learn gender roles
Social learning theory:
Cognitive development theory:
People learn attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors through
social interaction.
Learning occurs through reinforcement or imitation and
modeling.
Children acquire female or male values on their own by
thinking, reasoning, and interpreting information from their
environments.
Gender schema theory suggests people have mental
organization systems (schemas) to help them identify as
male or female.
Feminist approaches:
Gender is a role that is socially constructed.
Focus on power differences and inequality.
Who teaches gender roles?
Parents
Talking and communication patterns
Setting expectations
Providing opportunities
Toys, Sports, and Peers
Toys tend to be sex typed
Female athletes still face institutional barriers
Young children prefer same sex play partners
Who teaches gender roles?
Teachers and Schools
In elementary and middle school, boys usually
get more time to talk, are called on more often,
and receive more positive feedback.
In high school, counselors may steer students
into gender-typed futures.
In college, there are gender differences in
academic discipline.
Who teaches gender roles?
Books & Textbooks
Many books show gender typed behaviors
More nonstereotypical books are now available
Popular Culture and the Media—There are many
sex stereotyping examples in:
Advertising
Newspapers and Magazines
Television and other Screen Media
Music Videos
Traditional Views
and Gender Roles
Instrumental roles direct men to be procreators,
protectors, and providers.
Expressive roles direct women to provide
emotional support by being warm, sensitive, and
sympathetic. Women are the kinkeepers and family
mediators.
Traditional Views
and Gender Roles
Benefits
Promote stability, continuity, and predictability
Expectations are clear
Costs
For men, losing a job can become
catastrophic.
Women can feel trapped in exhausting, never
ending tasks of housekeeping.
Both men and women can be unhappy.
Gender Roles at Home
The “second shift”
refers to the
household work
and child care
many mothers face
after coming home
from work.
Men’s and
women’s
perceptions of their
domestic
contributions vary.
Gender Roles in the Workplace
Two key issues affect women, men, their partners
and families:
Sex discrimination continues to exist in many
professions.
Sexual harassment is any unwelcome sexual
advance or other conduct that makes a person
uncomfortable and interferes with her or his work.
Many men are confused about what sexual
harassment is and many women are reluctant to
report it.
Contemporary Gender Roles
Gender and the consumer marketplace
Numerous examples exist where women are
overcharged for car and home repairs or receive
inaccurate financial advice.
Gender and Communication
Deborah Tannen, a sociolinguist, suggests men
and women have different communication styles
that include:
Different purposes
Different rules
Different ways of interpreting communications
Religion and Gender Roles
Parenting
Domestic Roles
Religion shapes gender roles and family roles in many ways.
Example: the Ten Commandments.
Religion shapes the division of labor in the home. In evangelical
households, wives spend more time on traditional women’s work.
Role models
Religion influences role models. For example, many Christian
colleges remind female students to not work outside the home,
though this is in conflict with their female professors working.
Current Gender Roles:
Changes and Constraints
Role conflict refers to the frustration and
uncertainties a person experiences when confronted
with the requirements of incompatible roles.
Are we waging war against boys and men?
There are concerns about men’s and boys’ development,
especially with respect to education.
Some argue this concern is a backlash against girls’ and
women’s progress.
Is Androgyny the Answer?
In Androgyny, both culturally defined masculine and
feminine characteristics are blended in the same person.
A Global View:
Women around the World
The Gender Development Index (GDI) is
used to rank countries
Its indicators include life expectancy, educational
attainment, income, and “intentional commitment
to equality principles and policies”.
Top Ten countries are United States, Canada,
Australia, Japan, Iceland, the Scandinavian
countries, the Netherlands, and Belgium.
Bottom Ten countries are in Africa, including
Ethiopia, Niger, and Sierra Leone.
A Global View: Women around
the World